Inquiry-Based Learning empowers students to actively explore questions, problems, and scenarios, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. This hands-on approach encourages curiosity and self-directed learning, preparing students to navigate complex information effectively. Discover how this transformative methodology can enhance Your educational experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
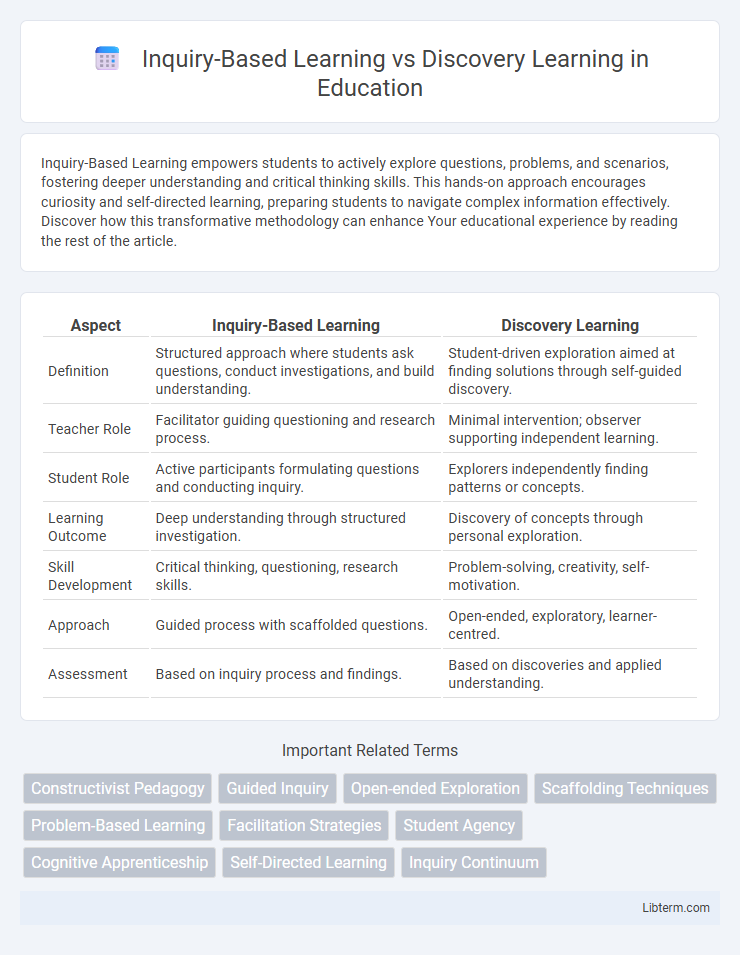
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Discovery Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured approach where students ask questions, conduct investigations, and build understanding. | Student-driven exploration aimed at finding solutions through self-guided discovery. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator guiding questioning and research process. | Minimal intervention; observer supporting independent learning. |
| Student Role | Active participants formulating questions and conducting inquiry. | Explorers independently finding patterns or concepts. |
| Learning Outcome | Deep understanding through structured investigation. | Discovery of concepts through personal exploration. |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, questioning, research skills. | Problem-solving, creativity, self-motivation. |
| Approach | Guided process with scaffolded questions. | Open-ended, exploratory, learner-centred. |
| Assessment | Based on inquiry process and findings. | Based on discoveries and applied understanding. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based and Discovery Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven questioning and investigation to develop deep understanding, often guided by a teacher's facilitation. Discovery Learning encourages learners to explore and find solutions independently through hands-on experiences and experimentation. Both approaches prioritize active engagement but differ in the level of guidance and structure provided during the learning process.
Defining Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning is an educational approach centered on student-driven questioning, exploration, and problem-solving to construct knowledge actively. It emphasizes guided investigation where learners formulate hypotheses, gather and analyze data, and draw conclusions. This method contrasts with Discovery Learning by providing structured support and scaffolding to ensure deeper understanding and curriculum alignment.
Understanding Discovery Learning
Discovery Learning emphasizes active student exploration where learners construct knowledge through direct interaction with concepts and materials, fostering deeper comprehension and long-term retention. This approach contrasts with Inquiry-Based Learning by prioritizing learner-driven investigation over guided questioning, encouraging autonomy and intrinsic motivation. Effective implementation of Discovery Learning requires providing an environment rich in resources and opportunities for experimentation to maximize conceptual understanding.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on students actively posing questions, investigating problems, and constructing knowledge through guided exploration and critical thinking. It emphasizes a scaffolded approach where teachers support learners by providing resources, facilitating discussion, and encouraging reflection to deepen understanding. This method contrasts with Discovery Learning by offering more structured guidance to ensure learning objectives are met while fostering curiosity and engagement.
Fundamental Features of Discovery Learning
Discovery Learning emphasizes student-centered exploration, where learners actively investigate questions or problems without direct instruction, fostering deep understanding through experience. It relies heavily on intrinsic motivation, trial-and-error, and hypothesis testing to develop problem-solving skills and critical thinking. Fundamental features include learner autonomy, minimal guidance, and contextual learning environments that encourage curiosity and self-directed discovery.
Comparing Key Differences
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes guided questioning and structured exploration where educators facilitate the learning process by posing specific questions and providing frameworks, enhancing critical thinking and knowledge construction. Discovery Learning allows learners to independently explore concepts through trial and error without explicit guidance, fostering creativity and problem-solving but risking misconceptions without proper support. The key difference lies in the level of teacher involvement and the balance between open-ended exploration and scaffolded inquiry within the learning environment.
Similarities Between Inquiry-Based and Discovery Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning and Discovery Learning both emphasize active student engagement and foster critical thinking by encouraging learners to explore questions and problems independently. Both approaches prioritize hands-on experiences and investigation, allowing students to construct knowledge through personal observation and experimentation. Collaborative discussions and reflection commonly support the learning process, enabling deeper understanding and retention of concepts.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Approach
Inquiry-Based Learning promotes critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging students to ask questions and explore concepts thoroughly, but it requires skilled facilitators to guide effectively and can be time-consuming. Discovery Learning fosters autonomy and creativity through hands-on experiences and self-directed exploration, yet it may lead to misconceptions without adequate support and is less structured. Both methods enhance engagement and motivation but demand careful balance between guidance and freedom to optimize educational outcomes.
Best Practices for Classroom Implementation
Effective implementation of Inquiry-Based Learning (IBL) in classrooms emphasizes structured questioning techniques, scaffolding student exploration, and promoting reflective discussions to deepen conceptual understanding. Discovery Learning requires carefully designed tasks that balance guidance with open-ended exploration, ensuring learners remain focused while constructing knowledge through experience. Incorporating formative assessments and collaborative group work can enhance both methods, fostering critical thinking and active engagement among students.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Students
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes structured questioning and guided exploration, ideal for students who benefit from scaffolded support and clear objectives. Discovery Learning encourages open-ended investigation, fostering creativity and independent problem-solving for learners with strong self-motivation and critical thinking skills. Selecting the right approach depends on student readiness, learning goals, and the level of teacher guidance required to maximize engagement and comprehension.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com