Project-Based Learning immerses students in hands-on experiences that promote critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem solving. This engaging approach fosters deeper understanding by allowing learners to apply knowledge in practical contexts. Discover how Project-Based Learning can transform Your educational journey by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
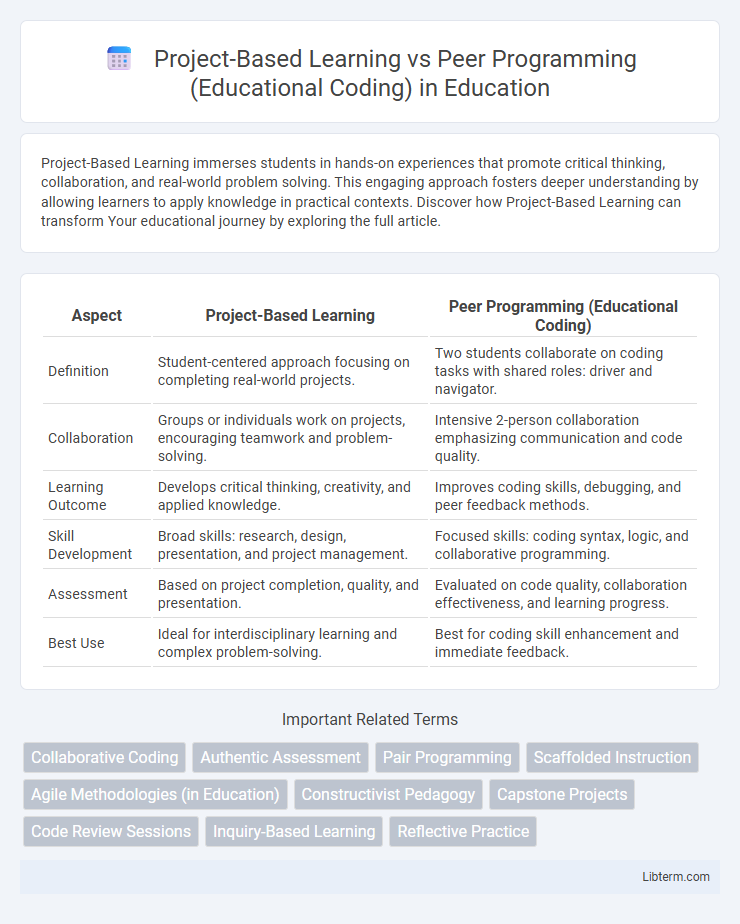
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning | Peer Programming (Educational Coding) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach focusing on completing real-world projects. | Two students collaborate on coding tasks with shared roles: driver and navigator. |
| Collaboration | Groups or individuals work on projects, encouraging teamwork and problem-solving. | Intensive 2-person collaboration emphasizing communication and code quality. |
| Learning Outcome | Develops critical thinking, creativity, and applied knowledge. | Improves coding skills, debugging, and peer feedback methods. |
| Skill Development | Broad skills: research, design, presentation, and project management. | Focused skills: coding syntax, logic, and collaborative programming. |
| Assessment | Based on project completion, quality, and presentation. | Evaluated on code quality, collaboration effectiveness, and learning progress. |
| Best Use | Ideal for interdisciplinary learning and complex problem-solving. | Best for coding skill enhancement and immediate feedback. |
Introduction to Project-Based Learning in Coding
Project-Based Learning (PBL) in coding emphasizes hands-on experiences where students create real-world software projects, enhancing problem-solving and collaboration skills. This method integrates coding concepts with practical application, allowing learners to develop both technical and soft skills through iterative design and debugging processes. By engaging in comprehensive projects, students gain deeper understanding of programming languages, frameworks, and development workflows compared to isolated coding exercises.
What is Peer Programming in Educational Settings?
Peer programming in educational settings involves two students collaboratively working on the same coding task, where one writes the code (the driver) and the other reviews each line (the navigator), enhancing problem-solving and communication skills. This method promotes active learning through immediate feedback and shared knowledge, improving coding proficiency and fostering teamwork. Peer programming contrasts with project-based learning by emphasizing real-time collaboration rather than independent task management.
Core Principles: Project-Based Learning vs. Peer Programming
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers on learners engaging in real-world projects to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration skills through hands-on experiences. Peer Programming emphasizes paired collaboration, where two programmers work together on the same code, fostering immediate feedback, knowledge sharing, and improved code quality. Both approaches prioritize active learning and teamwork, but PBL focuses on end-to-end project completion while Peer Programming concentrates on continuous, iterative coding practices.
Skill Development: Collaborative vs. Independent Problem-Solving
Project-Based Learning enhances collaborative problem-solving by immersing students in real-world coding challenges that require teamwork, communication, and collective decision-making. Peer Programming fosters independent problem-solving skills through pairing, where learners continuously review and refine each other's code, promoting active learning and critical thinking. Both methods develop essential coding capabilities, but Project-Based Learning emphasizes collaborative skills while Peer Programming sharpens individual analytical abilities.
Real-World Application and Engagement
Project-Based Learning in educational coding fosters real-world application by involving students in comprehensive coding projects that mirror industry challenges, enhancing problem-solving skills and technical proficiency. Peer Programming emphasizes collaboration and immediate code review through paired coding sessions, promoting active engagement and knowledge sharing in a controlled, interactive environment. Both approaches boost student engagement, with Project-Based Learning offering deeper context through extended tasks, while Peer Programming provides continuous feedback and social learning opportunities.
Assessment and Feedback Mechanisms
Project-Based Learning in educational coding emphasizes formative assessment through iterative project milestones, enabling detailed feedback on problem-solving and coding skills development. Peer Programming incorporates continuous real-time feedback, where paired learners engage in code reviews and collaborative debugging, fostering immediate correction and shared knowledge construction. Both approaches integrate assessment strategies that promote reflective learning, but Project-Based Learning offers more structured evaluation rubrics, while Peer Programming prioritizes dynamic interpersonal feedback.
Benefits of Project-Based Approaches in Coding Education
Project-based learning in coding education fosters deep understanding by engaging students in real-world applications, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for software development. This approach enhances collaboration and communication as learners work on complex projects, simulating professional coding environments. The hands-on experience gained through project-based methods leads to improved retention of programming concepts and greater motivation compared to traditional peer programming models.
Advantages of Peer Programming for Learners
Peer programming enhances coding skills through real-time collaboration, enabling learners to immediately identify and correct errors. It fosters effective communication and teamwork, essential for professional software development environments. This method accelerates problem-solving abilities and deepens understanding by combining diverse perspectives and knowledge.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Project-Based Learning (PBL) often faces challenges such as uneven workload distribution among students and difficulty in assessing individual contributions, which can hinder skill development and fair evaluation. Peer Programming encounters limitations including potential personality clashes, dependency on a more knowledgeable partner, and reduced opportunities for independent problem-solving. Both methods require careful implementation to address collaboration dynamics and ensure balanced learning outcomes in educational coding environments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learner Needs
Project-Based Learning (PBL) fosters real-world problem-solving skills by engaging students in complex coding projects, making it ideal for learners who thrive on hands-on, integrative experiences. Peer Programming emphasizes collaboration and immediate feedback, supporting learners who benefit from social interaction and iterative coding practice. Selecting the right approach depends on individual learning styles and goals, with PBL suited for autonomous, project-driven students and Peer Programming enhancing teamwork and communication skills among diverse coding learners.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com