Experiential learning immerses you directly in real-world experiences, enhancing knowledge retention and practical skills through active participation. This hands-on approach bridges the gap between theory and practice, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Discover how you can transform your learning journey by exploring the full potential of experiential methods in the article below.
Table of Comparison
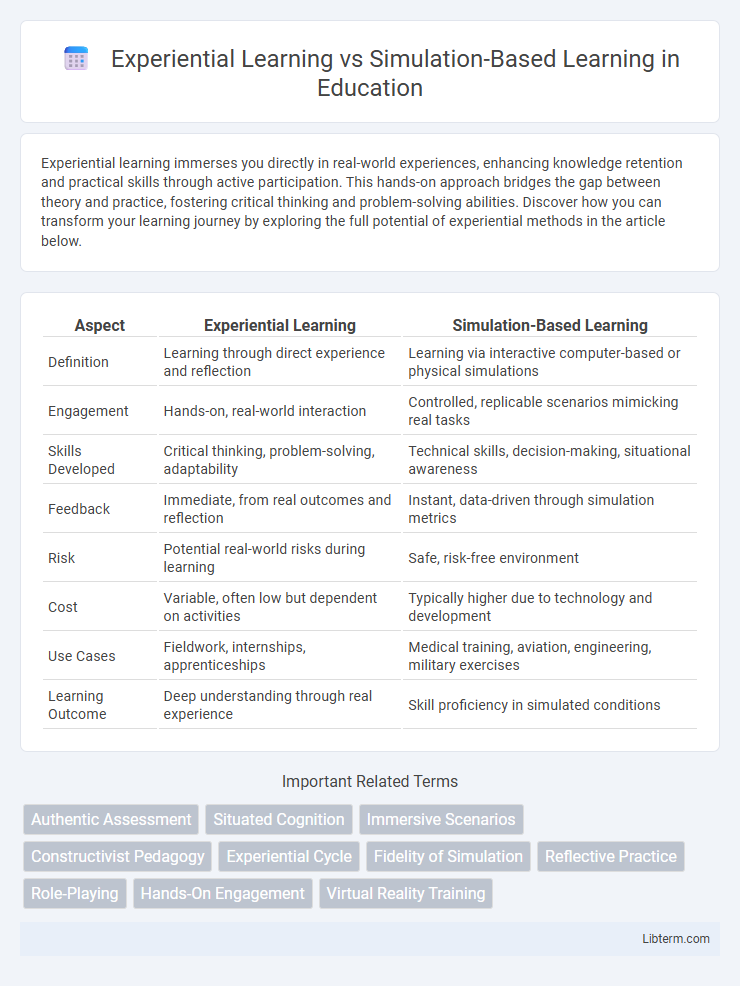
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Simulation-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection | Learning via interactive computer-based or physical simulations |
| Engagement | Hands-on, real-world interaction | Controlled, replicable scenarios mimicking real tasks |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, problem-solving, adaptability | Technical skills, decision-making, situational awareness |
| Feedback | Immediate, from real outcomes and reflection | Instant, data-driven through simulation metrics |
| Risk | Potential real-world risks during learning | Safe, risk-free environment |
| Cost | Variable, often low but dependent on activities | Typically higher due to technology and development |
| Use Cases | Fieldwork, internships, apprenticeships | Medical training, aviation, engineering, military exercises |
| Learning Outcome | Deep understanding through real experience | Skill proficiency in simulated conditions |
Understanding Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes direct engagement with real-world tasks to foster deep understanding and skill development through concrete experiences. It involves active participation, reflection, and application, allowing learners to construct knowledge by doing and assessing outcomes in authentic contexts. This approach contrasts with simulation-based learning, which uses controlled, virtual environments to replicate scenarios for practice and decision-making without real-world risks.
What is Simulation-Based Learning?
Simulation-based learning is an educational approach that uses virtual or physical models to replicate real-world scenarios for training purposes. It allows learners to practice skills, make decisions, and experience consequences in a risk-free environment, enhancing retention and engagement. This method is widely applied in fields such as healthcare, aviation, and military training to improve practical competence and critical thinking.
Key Differences Between Experiential and Simulation-Based Learning
Experiential learning involves real-world engagement where learners directly participate in authentic tasks, promoting hands-on skills and personal reflection. Simulation-based learning uses virtual or controlled environments that mimic real-life scenarios, enabling risk-free practice and immediate feedback. The key difference lies in experiential learning's emphasis on actual experience, while simulation prioritizes safe, repeatable scenarios for skill development.
Core Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential Learning centers on direct engagement through real-world experiences, emphasizing active participation, reflection, and application of knowledge to deepen understanding and skill development. This approach follows Kolb's Learning Cycle, which includes concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. Simulation-Based Learning, while often interactive and immersive, primarily replicates scenarios to practice skills safely, but it relies on the foundational Experiential Learning principles for effective knowledge transfer and retention.
Advantages of Simulation-Based Learning
Simulation-Based Learning offers immersive, risk-free environments that enable learners to practice complex skills and decision-making without real-world consequences. It provides immediate feedback through realistic scenarios, enhancing retention and critical thinking compared to traditional experiential learning. This method also allows repeatable and scalable training, ensuring consistent skill development across diverse learner populations.
Real-World Application: Experiential Learning In Action
Experiential learning immerses students in real-world environments, allowing direct interaction with authentic situations to develop practical skills. This approach fosters critical thinking and problem-solving through hands-on activities such as internships, fieldwork, and live projects. Unlike simulation-based learning, experiential learning emphasizes tangible outcomes by engaging learners in actual contexts that mirror professional challenges.
Technology’s Role in Simulation-Based Learning
Simulation-based learning leverages advanced technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and artificial intelligence (AI) to create immersive, interactive environments that closely replicate real-world scenarios. These technologies enable learners to practice complex skills safely, receive immediate feedback, and adapt experiences based on performance data. As a result, simulation-based learning enhances knowledge retention and skill acquisition more effectively than traditional experiential learning methods.
Assessment and Evaluation Methods
Experiential learning assessments emphasize reflective journals, real-world project outcomes, and peer feedback to measure skill application and personal growth. Simulation-based learning uses objective metrics like scenario completion rates, decision accuracy, and time efficiency to evaluate learner performance under controlled conditions. Both methods incorporate formative and summative evaluations but differ in their focus on qualitative insights versus quantitative data for competency measurement.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Experiential learning often faces challenges such as inconsistent real-world conditions and limited scalability, making it difficult to standardize outcomes across diverse learner groups. Simulation-based learning encounters limitations in replicating complex human emotions and unpredictable scenarios, which can reduce the depth of skill acquisition and adaptability. Both approaches also demand significant resource investment, including time, technology, and expert facilitation, constraining widespread implementation in educational settings.
Choosing the Right Learning Strategy for Your Goals
Experiential learning emphasizes real-world, hands-on experiences that foster deep understanding through direct engagement, ideal for developing practical skills and critical thinking. Simulation-based learning offers controlled, risk-free environments where learners can practice scenarios repeatedly, making it effective for mastering complex procedures and decision-making under pressure. Selecting between these strategies depends on your objectives: use experiential learning to enhance adaptability and real-world application, and simulation-based learning to refine precision and confidence in specific tasks.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com