Everyday language shapes how you communicate effectively in daily interactions, making conversations clear and relatable. Mastering simple, concise expressions enhances understanding across diverse audiences. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for using everyday language confidently.
Table of Comparison
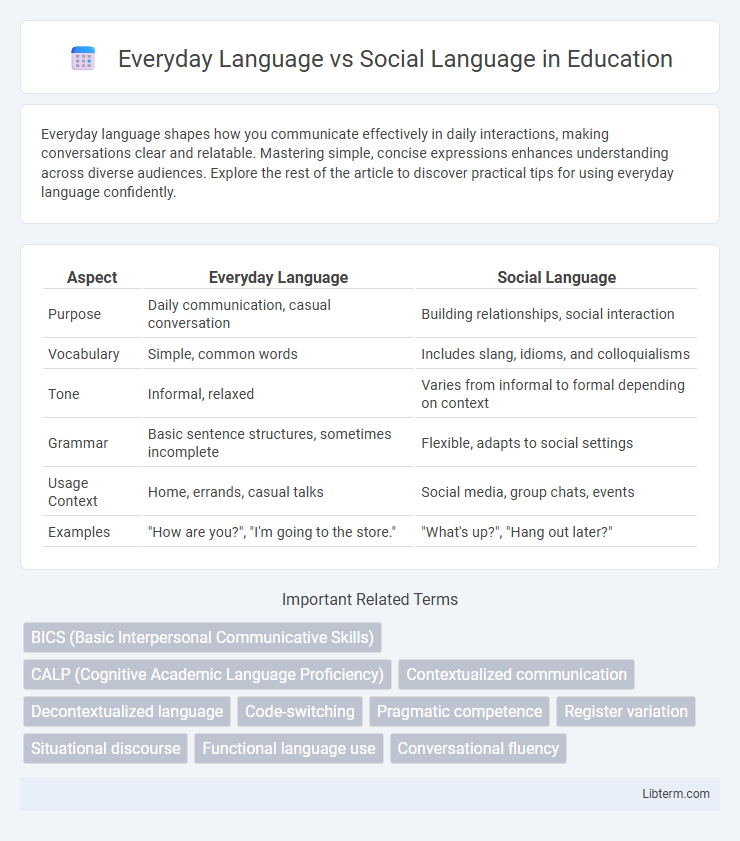
| Aspect | Everyday Language | Social Language |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Daily communication, casual conversation | Building relationships, social interaction |
| Vocabulary | Simple, common words | Includes slang, idioms, and colloquialisms |
| Tone | Informal, relaxed | Varies from informal to formal depending on context |
| Grammar | Basic sentence structures, sometimes incomplete | Flexible, adapts to social settings |
| Usage Context | Home, errands, casual talks | Social media, group chats, events |
| Examples | "How are you?", "I'm going to the store." | "What's up?", "Hang out later?" |
Understanding Everyday Language
Everyday language involves the informal, natural communication used in daily interactions, characterized by simple vocabulary and straightforward expressions. Understanding everyday language requires familiarity with common phrases, idiomatic expressions, and context-driven meanings that vary across cultures and social settings. Mastery of everyday language facilitates effective communication in personal and workplace environments by enabling clear, relatable exchanges.
Defining Social Language
Social language refers to the specific use of communication skills in varying social contexts, encompassing appropriate tone, grammar, and vocabulary to effectively engage with others. It involves understanding unspoken rules, such as turn-taking, politeness strategies, and interpreting nonverbal cues. Mastery of social language is crucial for building relationships, navigating conversations, and functioning within different cultural or group norms.
Key Differences Between Everyday and Social Language
Everyday language consists of informal, casual expressions used in routine interactions, characterized by simple vocabulary and relaxed grammar, while social language involves more structured communication tailored to social settings, emphasizing politeness, tone, and context appropriateness. Vocabulary in everyday language includes slang and colloquialisms suited for friends and family, whereas social language adapts to formal or group dynamics, employing respectful terms and nuanced expressions. The primary distinction lies in the adaptability to audience and setting, where social language requires awareness of social norms and roles, contrasting with the spontaneous nature of everyday conversation.
Role of Context in Language Use
Everyday language relies heavily on context to convey meaning effectively, as speakers use shared background knowledge, situational cues, and nonverbal signals to interpret messages. Social language, particularly in formal or group settings, depends on specific social roles, conventions, and cultural norms that shape communication patterns and expectations. Context influences word choice, tone, and structure, ensuring appropriate interpretation across diverse social interactions.
Vocabulary Choices in Daily Interactions
Vocabulary choices in everyday language prioritize simplicity, clarity, and commonly understood words to facilitate straightforward communication during daily interactions. Social language, however, incorporates colloquialisms, slang, and culturally specific terms that reflect group identity and social context, enriching interpersonal connections. Understanding these distinctions enhances effective communication by aligning word choice with the audience's familiarity and social setting.
Pragmatics: How We Adapt Language Socially
Pragmatics plays a crucial role in distinguishing everyday language from social language by guiding how individuals adapt their speech based on context, audience, and social norms. Everyday language often relies on informal expressions and shared understanding, while social language requires sensitivity to politeness, tone, and nonverbal cues to maintain appropriate interpersonal dynamics. This adaptive use of language ensures effective communication and social cohesion across diverse cultural and situational settings.
Nonverbal Communication in Everyday and Social Settings
Nonverbal communication such as body language, facial expressions, and gestures plays a crucial role in everyday language, enhancing clarity and emotional connection in routine interactions. In social language settings, nonverbal cues often carry cultural or contextual meanings that influence group dynamics and social cohesion. Mastery of nonverbal signals improves interpersonal understanding and effective communication across diverse social environments.
Code-Switching in Conversations
Code-switching in conversations often occurs when speakers alternate between everyday language and social language to navigate different social contexts effectively. Everyday language comprises informal, familiar expressions used in casual settings, while social language involves more structured, context-specific vocabulary suited for formal or group interactions. This dynamic linguistic adjustment enhances communication clarity and social adaptability.
Challenges in Navigating Everyday and Social Language
Navigating everyday language involves understanding informal phrases, slang, and context-dependent meanings that vary by region and culture, posing challenges for clear communication. Social language requires mastering politeness strategies, tone, and nonverbal cues to maintain relationships and social harmony, which can be difficult for individuals unfamiliar with social norms or cultural nuances. The interplay between these two language types often leads to misunderstandings, as pragmatic use and implicit meanings differ significantly in diverse social settings.
Tips for Enhancing Language Skills in Social Contexts
Enhancing language skills in social contexts requires practicing active listening and engaging in diverse conversations to build vocabulary and cultural understanding. Incorporating idiomatic expressions, slang, and colloquial phrases common in everyday social interactions boosts fluency and relatability. Regular participation in group discussions, role-playing scenarios, and social media interactions also sharpens pragmatic language use and non-verbal communication cues.
Everyday Language Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com