The scientific method is a systematic process used to explore observations, formulate hypotheses, conduct experiments, and analyze data to draw valid conclusions. This approach ensures that scientific inquiries remain objective and reproducible, allowing researchers to build reliable knowledge over time. Discover how mastering the scientific method can enhance your critical thinking and deepen your understanding in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
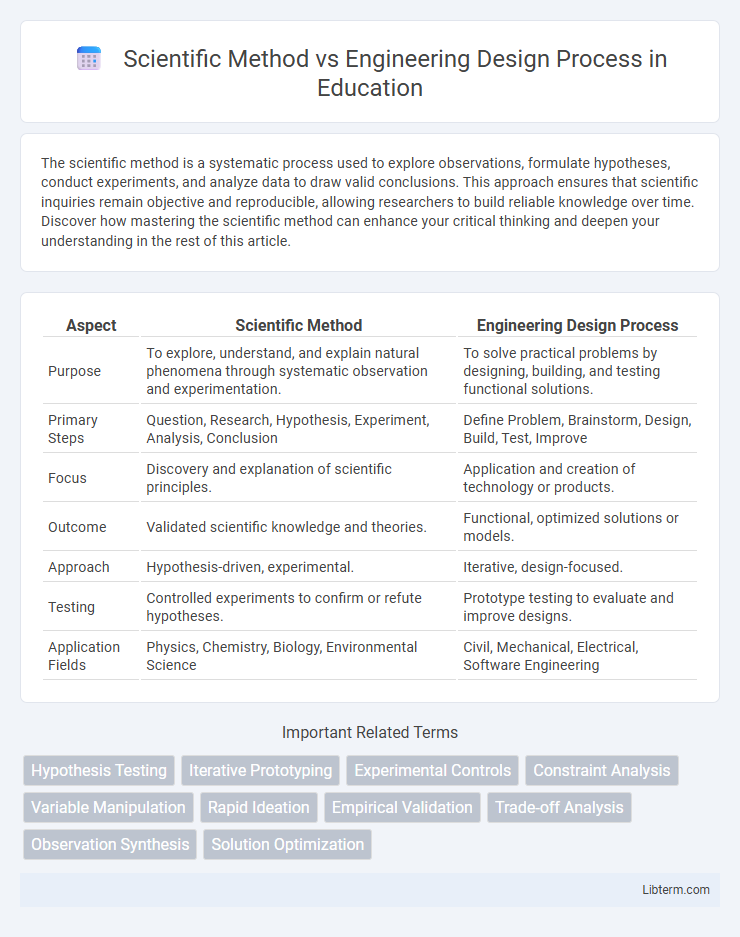
| Aspect | Scientific Method | Engineering Design Process |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To explore, understand, and explain natural phenomena through systematic observation and experimentation. | To solve practical problems by designing, building, and testing functional solutions. |
| Primary Steps | Question, Research, Hypothesis, Experiment, Analysis, Conclusion | Define Problem, Brainstorm, Design, Build, Test, Improve |
| Focus | Discovery and explanation of scientific principles. | Application and creation of technology or products. |
| Outcome | Validated scientific knowledge and theories. | Functional, optimized solutions or models. |
| Approach | Hypothesis-driven, experimental. | Iterative, design-focused. |
| Testing | Controlled experiments to confirm or refute hypotheses. | Prototype testing to evaluate and improve designs. |
| Application Fields | Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Environmental Science | Civil, Mechanical, Electrical, Software Engineering |
Introduction to Scientific Method and Engineering Design Process
The Scientific Method is a systematic approach used to investigate natural phenomena through observation, hypothesis formulation, experimentation, and analysis, aiming to generate reliable and reproducible knowledge. The Engineering Design Process involves iterative steps including defining a problem, researching, brainstorming solutions, prototyping, testing, and refining to develop practical and efficient technological solutions. Both methodologies emphasize problem-solving but differ in focus: the Scientific Method seeks to understand why or how something happens, while the Engineering Design Process concentrates on creating functional products or systems.
Defining the Scientific Method
The Scientific Method involves systematic observation, hypothesis formulation, experimentation, and analysis to acquire empirical knowledge and validate theories. It emphasizes repeatable experiments and objective data to understand natural phenomena, focusing on questions of "why" and "how." This method prioritizes evidential support and logical reasoning to develop scientific laws and models.
Understanding the Engineering Design Process
The Engineering Design Process is a systematic, iterative approach focused on solving practical problems through defining requirements, brainstorming solutions, prototyping, testing, and refining designs. It emphasizes creativity, constraints management, and real-world applicability to develop functional products or systems. Unlike the Scientific Method, which seeks to understand natural phenomena through hypothesis and experimentation, the Engineering Design Process prioritizes creating optimized solutions tailored to specific human needs.
Key Steps in the Scientific Method
The key steps in the Scientific Method include observation, forming a hypothesis, conducting experiments, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. This systematic approach emphasizes empirical evidence and testable predictions to understand natural phenomena. Unlike the Engineering Design Process, which centers on problem-solving and iterative design, the Scientific Method prioritizes experimentation and hypothesis validation.
Core Phases of the Engineering Design Process
The core phases of the Engineering Design Process include defining the problem, conducting background research, generating potential solutions, selecting the best alternative, creating prototypes, testing, and iterating based on feedback. Unlike the Scientific Method, which emphasizes hypothesis testing and experimentation to understand phenomena, the Engineering Design Process focuses on practical problem-solving and creating functional products or systems. This iterative approach ensures continuous improvement and optimization in engineering projects.
Major Differences Between Scientific Method and Engineering Design
The Scientific Method emphasizes hypothesis formation, experimentation, and observation to understand natural phenomena, primarily aiming to generate knowledge and explanations. The Engineering Design Process focuses on defining problems, brainstorming solutions, prototyping, and testing to create functional products or systems that meet specific human needs. Unlike the iterative experimentation in the Scientific Method, the Engineering Design Process prioritizes optimization and real-world constraints such as cost, usability, and safety.
Similarities and Overlapping Elements
Both the Scientific Method and Engineering Design Process emphasize systematic problem-solving through iterative steps such as observation, hypothesis formulation, experimentation, and analysis of results. Both approaches rely on data collection and empirical evidence to refine understanding or improve designs, fostering continuous improvement and innovation. Collaborative teamwork and documentation play pivotal roles in ensuring accuracy, reproducibility, and knowledge sharing across both methodologies.
Practical Applications in Real-World Scenarios
The scientific method drives discovery through hypothesis testing, observation, and experimentation, enabling advancements in fields like medicine and environmental science. The engineering design process applies iterative problem-solving, prototyping, and optimization to create functional products and systems used in industries such as aerospace and software development. Both methodologies foster innovation by addressing complex challenges, with the scientific method emphasizing understanding and the engineering design process focusing on practical implementation.
Choosing the Right Approach: Science vs Engineering
Choosing the right approach depends on the goal: the scientific method focuses on forming hypotheses and conducting experiments to gain knowledge, while the engineering design process emphasizes problem-solving through iterative design, testing, and optimization. Science seeks to understand natural phenomena by generating evidence-based conclusions, whereas engineering applies scientific principles to create functional solutions that meet specific needs or constraints. Selecting between these methods hinges on whether the objective is discovery or practical application.
Conclusion: Integrating Science and Engineering for Innovation
The conclusion emphasizes that integrating the Scientific Method and the Engineering Design Process fosters innovation by combining hypothesis-driven research with practical problem-solving. Scientific inquiry generates fundamental knowledge, while engineering applies this knowledge to develop functional solutions, accelerating technological advancement. This synergy enhances creativity and efficiency in addressing complex challenges across diverse fields.
Scientific Method Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com