Mainstream education provides a standardized curriculum designed to accommodate the majority of students within traditional school settings. It often emphasizes core subjects such as mathematics, science, language arts, and social studies to build foundational knowledge and skills. Discover how mainstream education shapes learning experiences and impacts your child's development by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
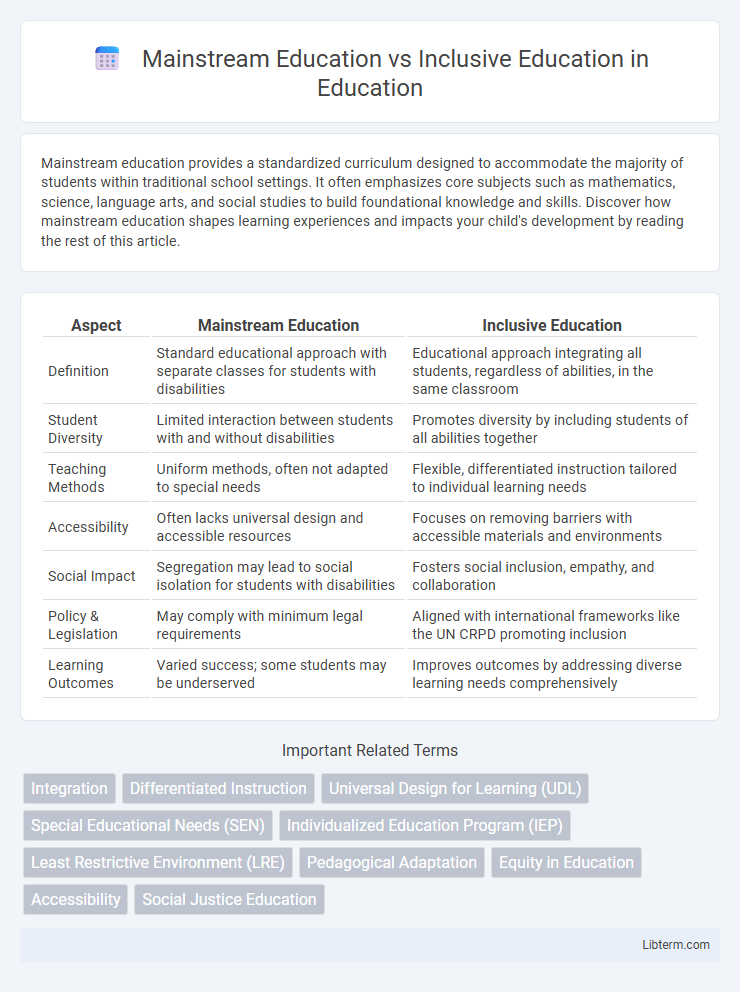
| Aspect | Mainstream Education | Inclusive Education |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standard educational approach with separate classes for students with disabilities | Educational approach integrating all students, regardless of abilities, in the same classroom |
| Student Diversity | Limited interaction between students with and without disabilities | Promotes diversity by including students of all abilities together |
| Teaching Methods | Uniform methods, often not adapted to special needs | Flexible, differentiated instruction tailored to individual learning needs |
| Accessibility | Often lacks universal design and accessible resources | Focuses on removing barriers with accessible materials and environments |
| Social Impact | Segregation may lead to social isolation for students with disabilities | Fosters social inclusion, empathy, and collaboration |
| Policy & Legislation | May comply with minimum legal requirements | Aligned with international frameworks like the UN CRPD promoting inclusion |
| Learning Outcomes | Varied success; some students may be underserved | Improves outcomes by addressing diverse learning needs comprehensively |
Defining Mainstream Education
Mainstream education refers to the traditional system where students with and without disabilities learn together in general classrooms, following a standardized curriculum. It emphasizes uniform instruction designed for the majority of students, often with limited adaptations for those with special needs. This approach aims to integrate all students but may not fully address diverse learning requirements or provide individualized support.
Understanding Inclusive Education
Inclusive education ensures all students, including those with disabilities or diverse learning needs, participate fully in mainstream classrooms to promote equity and social integration. This approach adapts teaching methods, curricula, and environments to accommodate individual differences, fostering an accessible and supportive learning atmosphere. Emphasizing collaboration among educators, families, and specialists enhances personalized support, improving academic and social outcomes for every student.
Historical Development of Both Approaches
Mainstream education originated in the 19th century with standardized curricula designed for the majority of students, often excluding those with disabilities or special needs. Inclusive education emerged in the late 20th century as a response to segregation, promoting the integration of all learners regardless of ability within general education classrooms. The shift towards inclusive education was influenced by global movements like the Salamanca Statement (1994) and legislative changes such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) in the United States.
Key Differences Between Mainstream and Inclusive Education
Mainstream education typically educates all students in a uniform classroom setting, often without specialized support for students with disabilities, whereas inclusive education integrates students with diverse learning needs within the general education environment, providing tailored accommodations and support services. Key differences include the level of individualization, with inclusive education emphasizing personalized learning plans and collaboration among educators, specialists, and families, compared to the standardized curriculum delivery in mainstream settings. Inclusive education promotes social integration and equal access to learning opportunities, while mainstream education may unintentionally contribute to segregation of students with special educational needs.
Benefits of Mainstream Education
Mainstream education offers students access to standardized curricula and well-established resources, promoting academic rigor and social integration with typically developing peers. It fosters exposure to diverse perspectives, preparing students for real-world interactions and collaboration. This environment often enhances communication skills and encourages higher expectations, contributing to overall student development and future opportunities.
Advantages of Inclusive Education
Inclusive education fosters equal access to learning opportunities for students with diverse abilities, promoting social integration and reducing stigma. It enhances academic outcomes by addressing individual needs through personalized teaching strategies and collaborative support. Inclusive settings also develop empathy and acceptance among all students, preparing them for inclusive societies and diverse workplaces.
Challenges Facing Mainstream Education
Mainstream education faces challenges such as limited resources to support diverse learning needs and insufficient teacher training for inclusive practices. Overcrowded classrooms often hinder personalized attention, negatively impacting students with disabilities or learning difficulties. Systemic rigidity and standardized curricula contribute to exclusion, preventing equitable access and participation for all learners.
Barriers to Implementing Inclusive Education
Barriers to implementing inclusive education include inadequate teacher training, limited resources, and inflexible curricula that fail to accommodate diverse learning needs. Physical infrastructure challenges, such as inaccessible classrooms, and societal attitudes toward disability also hinder effective inclusion. Addressing these obstacles requires policy reforms, increased funding, and awareness programs to foster an inclusive educational environment for all students.
Impact on Student Learning and Socialization
Mainstream education often provides structured academic environments that support standardized learning objectives but may overlook individual learning differences, potentially hindering students with special needs from fully engaging. Inclusive education fosters diverse classrooms where tailored teaching strategies enhance learning outcomes for all students, promoting empathy and collaboration among peers. Research indicates inclusive settings significantly improve social skills, reduce stigma, and encourage positive interactions, resulting in holistic development for students across varying abilities.
Future Trends in Education: Mainstream vs. Inclusive Models
Future trends in education emphasize a growing shift from traditional mainstream education models towards inclusive education frameworks that prioritize diversity and accessibility for all students. Inclusive education integrates students with varied learning needs into general classrooms, utilizing adaptive technologies and individualized support to enhance learning outcomes. Advancements in digital tools and policy reforms are driving this evolution, promoting equity and fostering collaboration between educators, families, and communities.
Mainstream Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com