Online learning offers flexible access to education anytime and anywhere, enhancing your ability to balance study with personal and professional commitments. Interactive platforms and diverse multimedia resources create engaging, personalized learning experiences that cater to different learning styles. Explore the rest of the article to discover how online learning can transform your educational journey and boost your skills effectively.
Table of Comparison
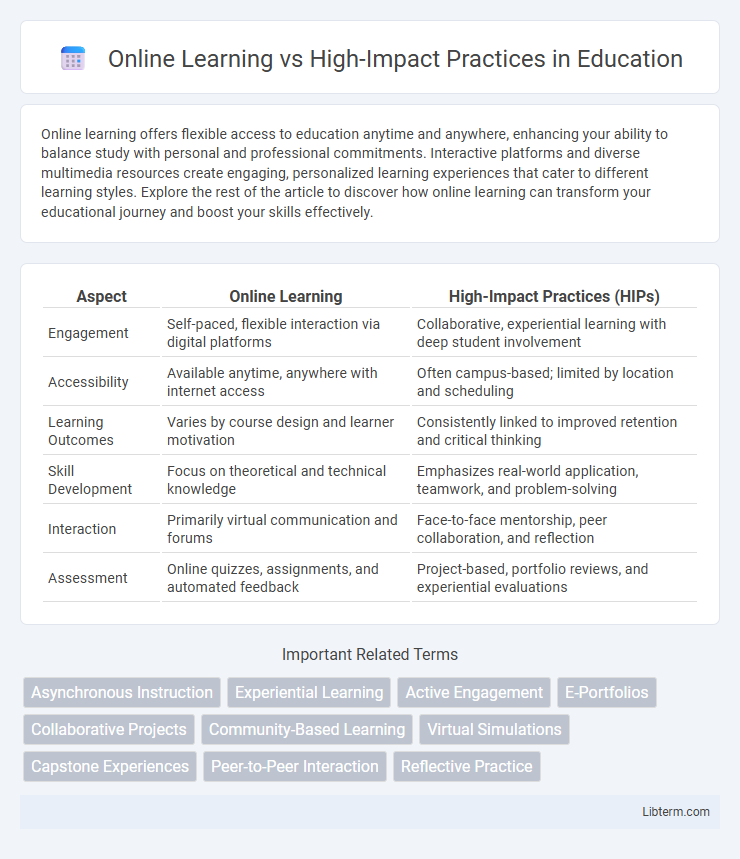
| Aspect | Online Learning | High-Impact Practices (HIPs) |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement | Self-paced, flexible interaction via digital platforms | Collaborative, experiential learning with deep student involvement |
| Accessibility | Available anytime, anywhere with internet access | Often campus-based; limited by location and scheduling |
| Learning Outcomes | Varies by course design and learner motivation | Consistently linked to improved retention and critical thinking |
| Skill Development | Focus on theoretical and technical knowledge | Emphasizes real-world application, teamwork, and problem-solving |
| Interaction | Primarily virtual communication and forums | Face-to-face mentorship, peer collaboration, and reflection |
| Assessment | Online quizzes, assignments, and automated feedback | Project-based, portfolio reviews, and experiential evaluations |
Introduction to Online Learning and High-Impact Practices
Online learning leverages digital platforms to provide flexible access to educational content, enabling students to engage with course materials anytime and anywhere. High-Impact Practices (HIPs), such as collaborative projects, service learning, and undergraduate research, are pedagogical strategies designed to enhance student engagement, deepen learning, and improve retention. Integrating online learning with HIPs can create dynamic, interactive experiences that promote critical thinking, practical skills, and meaningful student-faculty interactions.
Defining Online Learning: Features and Modalities
Online learning encompasses digital education methods that deliver instruction via the internet, enabling flexible access to courses across various devices. Key features include synchronous and asynchronous modalities, which allow real-time interaction and self-paced study respectively, enhancing learner engagement and accessibility. Popular formats involve video lectures, discussion forums, virtual simulations, and interactive assessments designed to replicate or complement traditional classroom experiences.
Understanding High-Impact Practices in Education
High-Impact Practices (HIPs) in education are teaching and learning activities that have been empirically demonstrated to significantly enhance student engagement, retention, and learning outcomes. These practices include undergraduates participating in collaborative projects, service learning, internships, and capstone courses, which foster deep learning and critical thinking skills. Online learning integrates many HIPs by leveraging digital tools to provide interactive, experiential opportunities that promote active participation and meaningful educational experiences.
Accessibility and Flexibility: Online vs High-Impact Approaches
Online learning offers unparalleled accessibility and flexibility, enabling students to engage with course materials anytime and anywhere, accommodating diverse schedules and learning paces. High-impact practices, such as collaborative projects and internships, provide immersive, experiential learning that fosters deep skill development but often require fixed times and locations, limiting flexibility. Balancing online learning's convenience with the transformational benefits of high-impact practices can optimize educational outcomes and inclusivity.
Student Engagement and Interaction: A Comparative View
Online learning platforms leverage interactive multimedia, real-time discussions, and virtual collaboration tools to foster student engagement, while high-impact practices (HIPs) such as undergraduate research, service learning, and internships emphasize experiential, hands-on interaction in real-world settings. Research shows that HIPs significantly boost student retention and deep learning by promoting active participation and meaningful mentorship, whereas effective online learning environments rely heavily on well-designed asynchronous and synchronous activities to maintain interaction quality. Combining digital tools with the immersive nature of HIPs can enhance student engagement by bridging flexibility and experiential depth.
Learning Outcomes: Measuring Success Across Modalities
Learning outcomes in online learning and high-impact practices (HIPs) reveal distinct efficacy patterns, with HIPs such as undergraduate research and service learning consistently promoting deeper critical thinking and retention. Online learning platforms leverage adaptive technologies and data analytics to personalize instruction and assess competency, often demonstrating comparable knowledge acquisition to traditional methods when active engagement is integrated. Measuring success across these modalities requires longitudinal studies incorporating standardized assessment tools and direct measures of learning, such as portfolios and performance tasks, to capture both cognitive gains and practical skill development.
Equity and Inclusion: Addressing Diverse Learner Needs
Online learning environments can enhance equity and inclusion by providing flexible access to diverse learners, including those with disabilities, geographic constraints, or socioeconomic challenges. High-Impact Practices (HIPs) such as collaborative projects and service learning foster deeper engagement but may require adaptation to be accessible and inclusive in virtual settings. Combining online learning with thoughtfully modified HIPs ensures diverse learner needs are met, promoting equitable outcomes and meaningful participation across varied student populations.
Technology Integration and Support Systems
Technology integration in online learning enhances accessibility and personalization through advanced platforms, adaptive software, and real-time analytics that support student engagement and performance. High-impact practices benefit from robust support systems such as virtual mentorship, collaborative tools, and integrated feedback mechanisms, which foster deeper learning interactions and community building. Effective alignment of these technological resources with pedagogical goals ensures optimized learning outcomes and sustained academic success.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Online learning faces challenges such as limited hands-on experience, reduced peer interaction, and potential technological barriers that can hinder engagement and effective knowledge retention. High-impact practices (HIPs), while fostering deep learning through collaborative and experiential activities, may be constrained by resource availability, scalability issues, and accessibility limitations for diverse student populations. Both approaches require addressing these drawbacks to maximize educational outcomes and inclusivity.
Future Trends: Blending Online Learning with High-Impact Practices
Future trends in education emphasize the integration of online learning platforms with high-impact practices such as collaborative projects, undergraduate research, and service learning. This blended approach leverages digital tools to enhance student engagement, foster critical thinking, and improve retention rates. Institutions investing in technology infrastructure and faculty training are positioned to deliver more personalized and experiential learning experiences that align with workforce demands.
Online Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com