Retention rate measures the percentage of customers or employees who remain loyal or stay over a specific period, reflecting the stability and satisfaction within a business or organization. A high retention rate indicates strong engagement and effectiveness in meeting needs, which directly impacts growth and profitability. Explore the article to learn strategies that can improve your retention rate and drive long-term success.
Table of Comparison
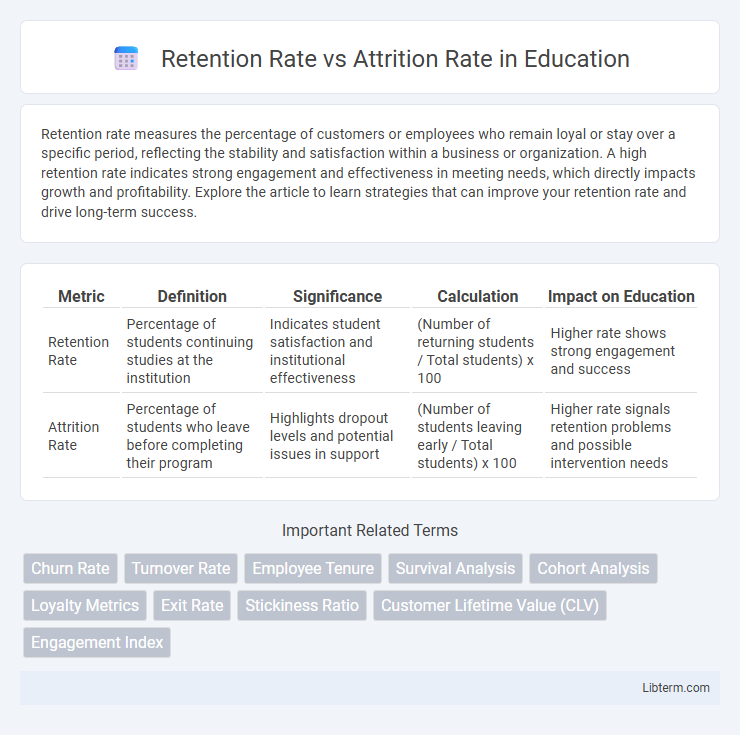
| Metric | Definition | Significance | Calculation | Impact on Education |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retention Rate | Percentage of students continuing studies at the institution | Indicates student satisfaction and institutional effectiveness | (Number of returning students / Total students) x 100 | Higher rate shows strong engagement and success |
| Attrition Rate | Percentage of students who leave before completing their program | Highlights dropout levels and potential issues in support | (Number of students leaving early / Total students) x 100 | Higher rate signals retention problems and possible intervention needs |
Understanding Retention Rate
Retention rate measures the percentage of customers or employees who remain engaged or employed over a specific period, reflecting loyalty and satisfaction. High retention rates indicate effective management and positive experiences, which contribute to sustainable growth and reduced recruitment costs. Understanding retention rate helps businesses identify successful strategies and areas needing improvement to enhance long-term stability.
Defining Attrition Rate
Attrition rate, also known as employee turnover rate, measures the percentage of employees who leave an organization over a specific period, reflecting workforce stability and organizational health. A high attrition rate can indicate issues such as employee dissatisfaction, poor management, or lack of growth opportunities, impacting productivity and increasing recruitment costs. Understanding attrition rate helps businesses develop targeted retention strategies to maintain talent and improve overall employee engagement.
Key Differences Between Retention and Attrition
Retention rate measures the percentage of employees or customers who stay with an organization over a specific period, reflecting stability and satisfaction. Attrition rate indicates the proportion of individuals who leave voluntarily or involuntarily, highlighting turnover challenges and potential issues in engagement or management. Key differences lie in their focus: retention emphasizes loyalty and ongoing participation, while attrition centers on loss and the reasons behind departures.
Importance of Tracking Retention and Attrition
Tracking retention and attrition rates provides crucial insights into employee satisfaction and organizational health, directly impacting workforce stability and productivity. High retention rates indicate effective management and positive work environments, while elevated attrition rates signal potential issues requiring strategic intervention. Consistent monitoring of these metrics enables informed decision-making for talent management, reducing turnover costs and fostering long-term business success.
Calculating Retention Rate
Retention rate is calculated by dividing the number of customers or employees who remain over a specific period by the total number at the start, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. High retention rates indicate strong loyalty and satisfaction, while attrition rate is the complement, representing the percentage lost. Accurately measuring retention helps businesses identify growth opportunities and reduce churn by improving engagement strategies.
Calculating Attrition Rate
Calculating attrition rate involves dividing the number of employees who leave an organization during a specific period by the average number of employees during that period, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. This metric provides critical insight into workforce stability and helps identify retention challenges. Human resources departments use attrition rate to strategize employee engagement and reduce turnover costs.
Factors Influencing Retention and Attrition
Employee retention rates are influenced by factors such as job satisfaction, competitive compensation, opportunities for career advancement, and positive workplace culture. In contrast, attrition rates often rise due to poor management, lack of growth prospects, inadequate recognition, and work-life imbalance. Understanding these drivers helps organizations implement targeted strategies to enhance retention and reduce turnover.
Strategies to Improve Retention Rate
Retention rate improvements rely on effective employee engagement programs, career development opportunities, and competitive compensation packages. Implementing regular feedback mechanisms and fostering a positive workplace culture directly reduce attrition rate by addressing employee dissatisfaction early. Data-driven strategies, including predictive analytics, help identify at-risk employees to tailor personalized retention initiatives.
Reducing Attrition Rate: Best Practices
Reducing attrition rate involves implementing targeted employee engagement strategies, such as personalized career development plans and competitive compensation packages, to enhance job satisfaction and loyalty. Regular feedback loops and transparent communication foster a supportive work environment that addresses employee concerns proactively. Leveraging data analytics to identify early signs of disengagement enables timely interventions, significantly improving retention rates and overall organizational performance.
Impact of Retention and Attrition on Business Performance
High retention rates enhance business performance by reducing recruitment costs and maintaining institutional knowledge, leading to increased productivity and customer satisfaction. Conversely, elevated attrition rates disrupt operations, increase training expenses, and lower employee morale, which can result in decreased revenue and weakened competitive advantage. Focusing on retention strategies ensures sustainable growth and stronger organizational stability.
Retention Rate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com