Project-based learning promotes hands-on experience by engaging you directly in real-world tasks, enhancing problem-solving and critical thinking skills. This approach fosters collaboration and creativity, preparing individuals for dynamic work environments. Discover how project-based methods can transform your educational or professional journey in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
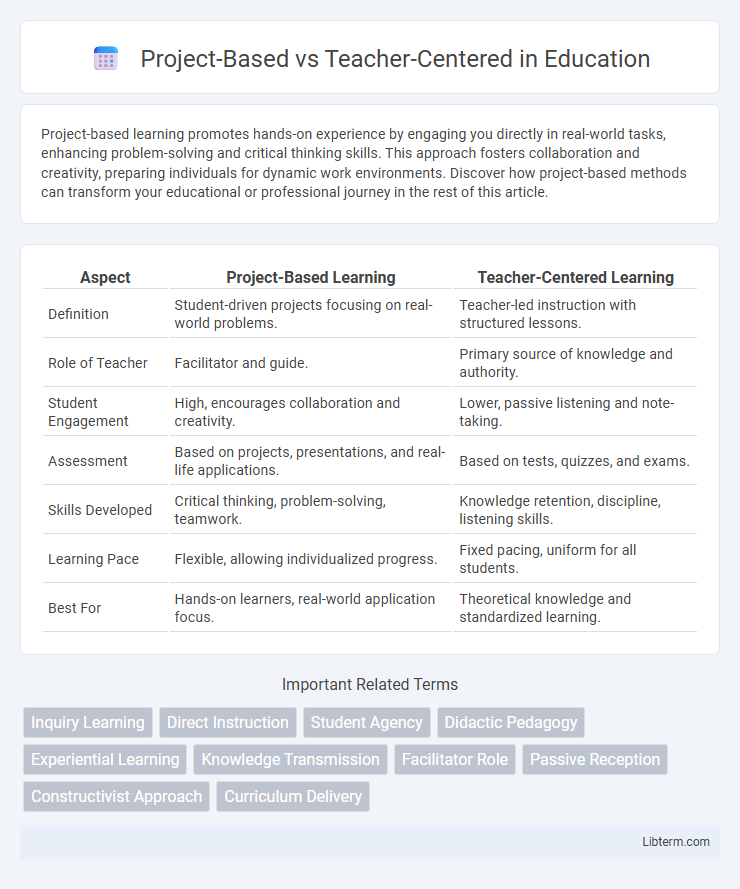
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning | Teacher-Centered Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-driven projects focusing on real-world problems. | Teacher-led instruction with structured lessons. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide. | Primary source of knowledge and authority. |
| Student Engagement | High, encourages collaboration and creativity. | Lower, passive listening and note-taking. |
| Assessment | Based on projects, presentations, and real-life applications. | Based on tests, quizzes, and exams. |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, problem-solving, teamwork. | Knowledge retention, discipline, listening skills. |
| Learning Pace | Flexible, allowing individualized progress. | Fixed pacing, uniform for all students. |
| Best For | Hands-on learners, real-world application focus. | Theoretical knowledge and standardized learning. |
Understanding Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes student engagement through real-world projects that foster critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Unlike Teacher-Centered approaches where instruction is primarily lecture-based and content delivery depends on the teacher, PBL promotes active learning by allowing students to explore and apply knowledge autonomously. Research shows that PBL enhances deeper understanding and retention by connecting academic concepts to practical applications.
Defining Teacher-Centered Approach
The teacher-centered approach emphasizes direct instruction where educators control the learning environment, delivering content through lectures and structured lessons. This method prioritizes memorization and standardized assessments, focusing on curriculum coverage rather than student exploration. It contrasts with project-based learning by limiting student autonomy and encouraging passive knowledge reception.
Key Differences Between the Two Methods
Project-based learning emphasizes student engagement through hands-on activities, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem solving. Teacher-centered methods rely on direct instruction where the teacher controls content delivery, pacing, and assessment to ensure mastery of specific knowledge. The fundamental difference lies in student autonomy and active participation in project-based learning versus structured guidance and passive reception in teacher-centered approaches.
Benefits of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging students in real-world tasks that promote active exploration. It fosters collaboration and communication, encouraging learners to work in teams and develop interpersonal skills essential for future careers. PBL also increases student motivation and retention by making education relevant and hands-on, contrasting with the passive reception typical of teacher-centered approaches.
Advantages of Teacher-Centered Teaching
Teacher-centered teaching offers structured content delivery, allowing educators to efficiently manage classroom time and ensure consistent coverage of curriculum standards. This approach provides clear guidance and immediate feedback, which helps students grasp fundamental concepts and fosters discipline. Additionally, it enables easier assessment of individual student performance through standardized evaluations.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Project-based learning boosts student engagement by fostering hands-on, collaborative experiences that enhance creativity and critical thinking. Teacher-centered approaches often limit motivation by emphasizing passive listening and rote memorization, reducing opportunities for active participation. Research shows project-based methods lead to higher intrinsic motivation and deeper understanding, improving overall academic performance.
Assessment Strategies: Comparing Approaches
Project-based assessment strategies prioritize authentic evaluation through real-world tasks, emphasizing student collaboration, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. Teacher-centered assessments often rely on standardized tests and quizzes to measure individual knowledge retention and comprehension, providing structured and objective data. Balancing both approaches can enhance a comprehensive understanding of student performance by integrating formative feedback with summative evaluation.
Real-World Application and Skills Development
Project-based learning emphasizes real-world application by engaging students in hands-on tasks that simulate practical challenges, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Teacher-centered approaches typically focus on knowledge transmission, often limiting opportunities for students to develop collaboration, creativity, and adaptability necessary for modern workplaces. Prioritizing project-based methods enhances skill development by aligning educational experiences with actual industry demands and future career competencies.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Project-Based learning often faces challenges like time-intensive planning, resource constraints, and difficulty in assessing individual contributions, which can hinder consistent implementation. Teacher-Centered methods struggle with limited student engagement, reduced critical thinking opportunities, and may not address diverse learning styles effectively. Both approaches require balancing structure and flexibility to maximize student outcomes while managing the inherent limitations of their instructional models.
Choosing the Best Approach for Your Classroom
Project-based learning enhances student engagement through hands-on activities that promote critical thinking and real-world problem solving, making it ideal for classrooms prioritizing active participation. Teacher-centered instruction offers structured guidance and clear expectations, benefiting learners who require direct support and a more controlled environment. Evaluating student needs, curriculum goals, and available resources helps educators select the most effective approach tailored to their unique classroom dynamics.
Project-Based Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com