Inquiry-based science enhances critical thinking and deepens understanding by encouraging students to ask questions, explore, and experiment. This hands-on approach fosters curiosity and develops essential problem-solving skills through active engagement with scientific concepts. Discover how inquiry-based methods can transform your learning experience and boost scientific literacy in the full article.
Table of Comparison
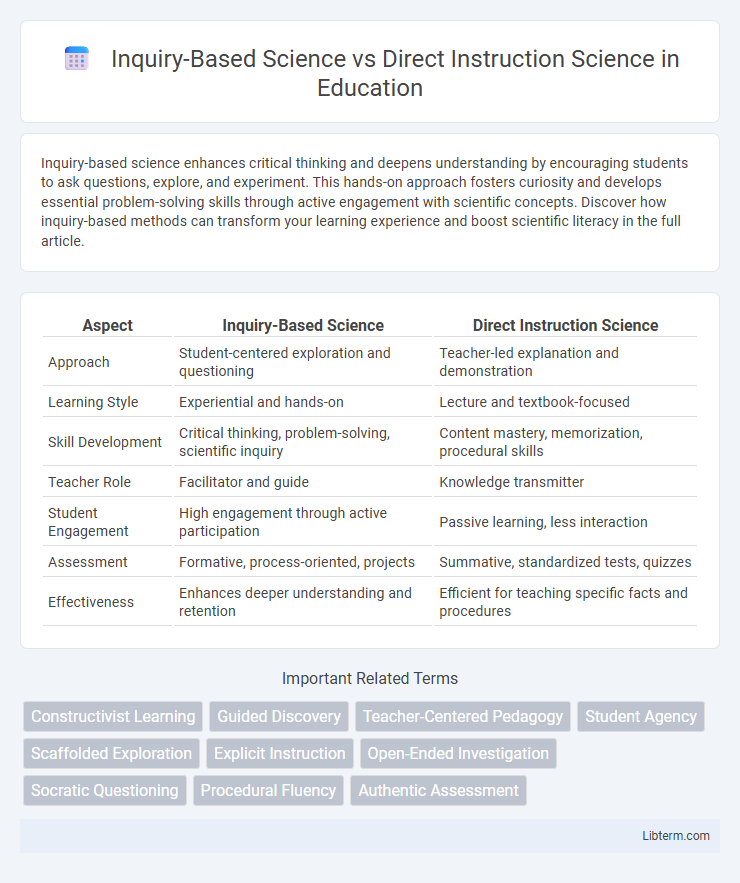
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Science | Direct Instruction Science |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Student-centered exploration and questioning | Teacher-led explanation and demonstration |
| Learning Style | Experiential and hands-on | Lecture and textbook-focused |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, problem-solving, scientific inquiry | Content mastery, memorization, procedural skills |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and guide | Knowledge transmitter |
| Student Engagement | High engagement through active participation | Passive learning, less interaction |
| Assessment | Formative, process-oriented, projects | Summative, standardized tests, quizzes |
| Effectiveness | Enhances deeper understanding and retention | Efficient for teaching specific facts and procedures |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based and Direct Instruction Science
Inquiry-Based Science emphasizes hands-on exploration and student-driven questioning to foster critical thinking and deeper understanding of scientific concepts. Direct Instruction Science relies on structured lessons with clear objectives, teacher-led explanations, and step-by-step guidance to ensure mastery of foundational knowledge. Both approaches address different learning needs, with Inquiry-Based promoting discovery and Direct Instruction emphasizing clarity and efficiency.
Defining Inquiry-Based Science: Key Principles
Inquiry-Based Science emphasizes student-driven exploration, where learners actively formulate questions, conduct experiments, and analyze data to construct knowledge. This approach prioritizes critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and scientific reasoning by engaging students in hands-on investigations reflective of real-world scientific processes. Key principles include fostering curiosity, promoting collaborative learning, and encouraging evidence-based conclusions through iterative inquiry cycles.
Understanding Direct Instruction Science: Core Features
Direct Instruction Science emphasizes a structured, teacher-led approach where lessons follow a clear sequence designed to build foundational knowledge efficiently. Core features include explicit teaching of scientific concepts, systematic practice, and frequent assessments to monitor student understanding and provide immediate feedback. This method aims to reduce misconceptions and enhance mastery through guided learning and reinforcement of key principles.
Learning Outcomes: Inquiry vs Direct Instruction
Inquiry-based science learning promotes critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and conceptual understanding by engaging students in hands-on experiments and investigations. Direct instruction science often results in higher short-term retention of specific facts and procedural knowledge due to structured, teacher-led explanations. Research indicates inquiry-based approaches improve long-term comprehension and application of scientific concepts, while direct instruction may be more effective for foundational knowledge acquisition.
Student Engagement and Motivation in Both Approaches
Inquiry-based science fosters higher student engagement by encouraging curiosity and hands-on exploration, leading to increased intrinsic motivation and active participation. Direct instruction science provides structured guidance and clear expectations, which can support motivation through predictable outcomes and mastery of foundational concepts. Research indicates that combining inquiry-based methods with direct instruction can optimize both engagement and motivation by balancing exploration with explicit teaching.
Teacher Roles in Inquiry-Based and Direct Instruction Classrooms
Teacher roles in inquiry-based science classrooms emphasize facilitating student exploration, guiding questioning, and supporting critical thinking to promote active learning. In contrast, direct instruction science classrooms position teachers as primary knowledge transmitters, delivering structured content and step-by-step explanations to ensure mastery of foundational concepts. Effective science education balances these approaches by adapting teacher roles to foster both conceptual understanding and process skills.
Assessment Strategies: Inquiry-Based vs Direct Instruction
Inquiry-based science assessment strategies prioritize formative evaluation through observation, student reflections, and performance tasks that gauge critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Direct instruction science assessments rely heavily on summative methods such as quizzes and standardized tests to measure content retention and factual knowledge. Integrating authentic assessments in inquiry-based learning fosters deeper understanding, while direct instruction emphasizes efficiency in evaluating specific learning objectives.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Teaching Method
Inquiry-based science promotes critical thinking and problem-solving by engaging students in hands-on experiments and exploration, fostering deeper conceptual understanding and long-term retention; however, it can be time-consuming and may require more classroom resources and teacher expertise. Direct instruction science offers clear, structured guidance with efficient coverage of essential content and consistent assessment outcomes, beneficial for foundational knowledge but often limits student creativity and independent thinking. Balancing both methods addresses diverse learning needs, optimizing student engagement and mastery in science education.
When to Use Inquiry-Based or Direct Instruction Science
Inquiry-based science is most effective when students need to develop critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deep conceptual understanding by exploring scientific phenomena through experimentation and questioning. Direct instruction science is ideal for introducing foundational knowledge, specific facts, and step-by-step procedures where clarity and accuracy are essential for mastery. Balancing both methods allows educators to tailor instruction based on learning objectives, student readiness, and the complexity of the content.
Integrating Both Approaches: Best Practices for Effective Science Teaching
Integrating Inquiry-Based Science and Direct Instruction Science enhances student engagement and conceptual understanding by combining hands-on exploration with clear, structured guidance. Effective science teaching incorporates scaffolded questioning during inquiry activities and explicit teaching of scientific methods and facts, fostering critical thinking alongside foundational knowledge. Data indicates that a blended approach improves retention and application of scientific concepts, supporting diverse learning styles and promoting deeper cognitive development.
Inquiry-Based Science Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com