The SMOG Index is a readability formula that estimates the years of education a person needs to understand a piece of writing. It focuses on the number of complex words within a set of sentences to determine text difficulty, making it a reliable tool for assessing health information and educational materials. Explore the rest of the article to learn how applying the SMOG Index can enhance your writing clarity and accessibility.
Table of Comparison
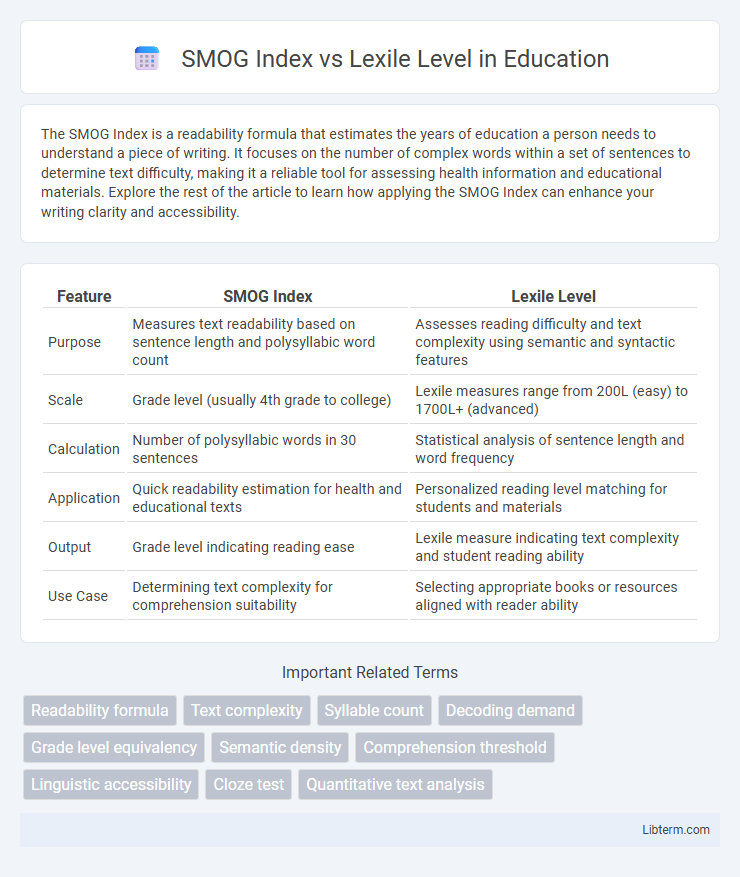
| Feature | SMOG Index | Lexile Level |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures text readability based on sentence length and polysyllabic word count | Assesses reading difficulty and text complexity using semantic and syntactic features |
| Scale | Grade level (usually 4th grade to college) | Lexile measures range from 200L (easy) to 1700L+ (advanced) |
| Calculation | Number of polysyllabic words in 30 sentences | Statistical analysis of sentence length and word frequency |
| Application | Quick readability estimation for health and educational texts | Personalized reading level matching for students and materials |
| Output | Grade level indicating reading ease | Lexile measure indicating text complexity and student reading ability |
| Use Case | Determining text complexity for comprehension suitability | Selecting appropriate books or resources aligned with reader ability |
Introduction to Readability Metrics
Readability metrics like the SMOG Index and Lexile Level provide quantifiable measures of text complexity, aiding educators in selecting appropriate reading materials. The SMOG Index estimates the years of education needed to understand a text based on syllable count in polysyllabic words, emphasizing sentence difficulty. Lexile Levels combine semantic difficulty and syntactic complexity through proprietary algorithms, offering a standardized scale for matching readers with texts at suitable comprehension levels.
What is the SMOG Index?
The SMOG Index is a readability formula that estimates the years of education required to understand a piece of text by analyzing the number of polysyllabic words. It is widely used in health communication to ensure materials are accessible to a broad audience. Unlike the Lexile Level, which measures text complexity based on sentence length and word frequency, the SMOG Index focuses specifically on the prevalence of complex words to assess reading difficulty.
Understanding the Lexile Level
The Lexile Level measures text complexity by analyzing sentence length and word frequency, providing a scale that connects readers with materials matching their reading ability. Unlike the SMOG Index, which estimates readability based solely on polysyllabic word count, Lexile offers a more comprehensive assessment by incorporating both semantic and syntactic features. This allows educators and parents to better select appropriate texts that promote reading growth and comprehension.
Calculation Methods: SMOG Index vs Lexile Level
The SMOG Index calculates readability based on the number of polysyllabic words within a 30-sentence sample, providing an estimate of the years of education needed for comprehension. The Lexile Level employs a psychometric measurement analyzing sentence length and word frequency in extensive corpora, generating a numerical score aligned with reader ability and text complexity. Both metrics offer distinct approaches to assessing text difficulty, with SMOG emphasizing syllable count and Lexile integrating linguistic data for personalized reading assessment.
Key Differences Between SMOG and Lexile
The SMOG Index measures text readability by estimating the years of education required to understand a piece of writing, focusing on the count of polysyllabic words per sentence. In contrast, the Lexile Level assesses both text complexity and reader ability using semantic and syntactic features, producing a numerical score that correlates with reading difficulty. Key differences include SMOG's emphasis on word complexity alone versus Lexile's broader analysis, making Lexile a more comprehensive tool for matching readers with texts.
Strengths and Limitations of the SMOG Index
The SMOG Index effectively estimates the years of education required to understand a text, making it a reliable measure for assessing readability, especially in healthcare and legal documents. Its strength lies in its simplicity and strong correlation with comprehension, but it primarily focuses on sentence length and polysyllabic words, potentially overlooking context and vocabulary difficulty. Limitations include less sensitivity to nuanced language features and difficulty in evaluating texts with complex sentence structures or specialized terminology compared to the Lexile Level system.
Advantages and Drawbacks of the Lexile Level
Lexile Level offers a precise measurement of a reader's ability and text complexity, facilitating personalized reading growth and targeted instructional strategies in educational settings. Its standardized scale enables easy comparison across a wide range of texts and student abilities, promoting tailored learning experiences. However, Lexile Levels may oversimplify text difficulty by focusing mainly on sentence length and word frequency, potentially overlooking nuances like theme, prior knowledge, or text cohesion, which can affect comprehension.
Applications in Education and Publishing
SMOG Index measures text readability by estimating grade level based on sentence length and polysyllabic words, making it practical for educators targeting appropriate reading materials for students. Lexile Level quantifies reading ability and text complexity using a proprietary algorithm, supporting personalized learning by matching readers with texts that optimize comprehension growth. Both metrics inform curriculum design and content development in education and publishing, enhancing accessibility and engagement for diverse audiences.
Choosing the Right Readability Tool
Choosing the right readability tool depends on the target audience and purpose of the text analysis, with the SMOG Index offering a focus on syllable count to estimate years of education needed for comprehension, ideal for health and scientific materials. Lexile Level provides a more comprehensive evaluation by measuring semantic difficulty and sentence length, aligning text complexity with student reading abilities, which is useful for educational settings. Understanding these differences ensures the selection of an appropriate metric to enhance text accessibility and reader engagement.
Conclusion: SMOG Index or Lexile Level?
The SMOG Index provides a quick estimate of text readability based on sentence and word complexity, making it ideal for health communication and simple content. Lexile Level offers a more comprehensive assessment linked to student reading abilities, supporting personalized learning and curriculum alignment. Choose the SMOG Index for straightforward, grade-level readability and Lexile Level for detailed, education-focused text measurement.
SMOG Index Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com