Auditing involves a systematic examination of financial records and processes to ensure accuracy, compliance, and accountability within an organization. It enhances transparency and helps identify potential risks or areas for improvement in financial reporting. Explore the rest of the article to understand how auditing can safeguard your business and strengthen financial trust.
Table of Comparison
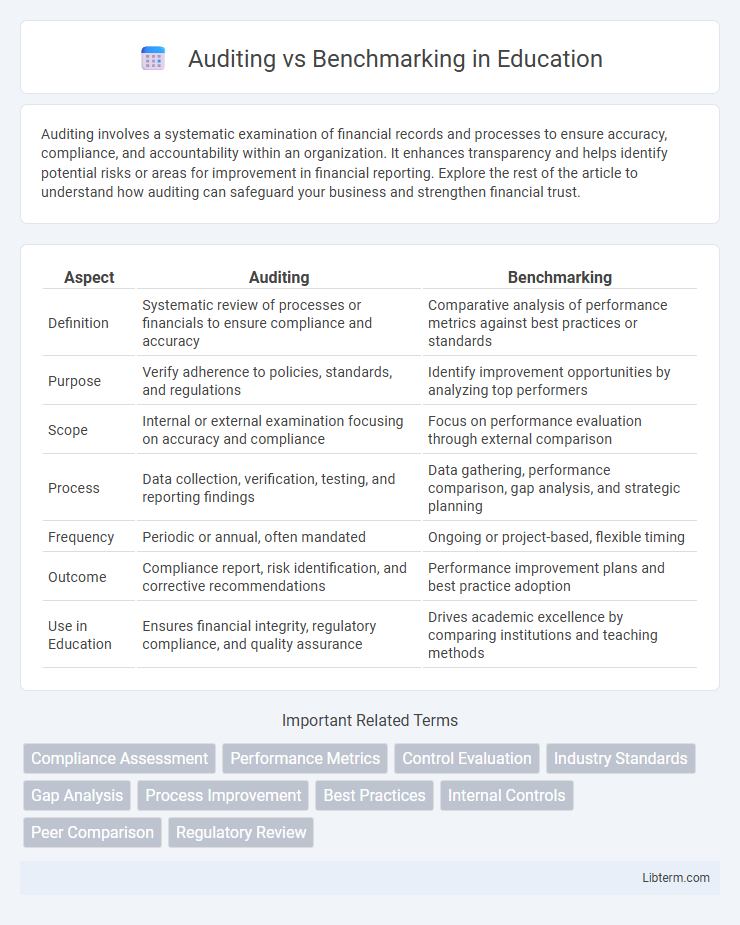
| Aspect | Auditing | Benchmarking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic review of processes or financials to ensure compliance and accuracy | Comparative analysis of performance metrics against best practices or standards |
| Purpose | Verify adherence to policies, standards, and regulations | Identify improvement opportunities by analyzing top performers |
| Scope | Internal or external examination focusing on accuracy and compliance | Focus on performance evaluation through external comparison |
| Process | Data collection, verification, testing, and reporting findings | Data gathering, performance comparison, gap analysis, and strategic planning |
| Frequency | Periodic or annual, often mandated | Ongoing or project-based, flexible timing |
| Outcome | Compliance report, risk identification, and corrective recommendations | Performance improvement plans and best practice adoption |
| Use in Education | Ensures financial integrity, regulatory compliance, and quality assurance | Drives academic excellence by comparing institutions and teaching methods |
Introduction to Auditing and Benchmarking
Auditing involves a systematic examination and evaluation of an organization's processes, controls, and compliance to ensure accuracy and adherence to standards. Benchmarking compares an organization's performance metrics against industry leaders or best practices to identify areas for improvement and drive competitive advantage. Both practices provide valuable insights for operational efficiency, risk management, and strategic development in business environments.
Defining Auditing: Purpose and Scope
Auditing involves the systematic examination and evaluation of an organization's processes, financial records, or systems to ensure accuracy, compliance, and effectiveness. Its purpose is to identify discrepancies, risks, and areas for improvement within the defined scope, which may include financial statements, operational procedures, or regulatory adherence. The scope of auditing is determined by the objectives set by stakeholders and often includes specific time periods, departments, or processes under review.
Understanding Benchmarking: Key Concepts
Benchmarking involves systematically comparing an organization's processes, performance metrics, and practices against industry leaders to identify areas for improvement. It emphasizes learning from best practices by analyzing competitors or top-performing companies to set performance standards and goals. This continuous evaluation fosters innovation and drives strategic enhancements beyond the compliance-focused scope of auditing.
Core Differences Between Auditing and Benchmarking
Auditing evaluates compliance and accuracy by systematically examining internal processes against established standards, ensuring financial and operational integrity. Benchmarking compares an organization's performance metrics with best practices from industry leaders to identify gaps and drive continuous improvement. The core difference lies in auditing's focus on verification and compliance, whereas benchmarking centers on performance enhancement through external comparison.
Objectives of Auditing in Business Operations
Auditing in business operations focuses on systematically evaluating financial records, internal controls, and compliance with regulatory standards to ensure accuracy and accountability. Its objectives include detecting fraud, identifying operational inefficiencies, and verifying adherence to corporate policies. This process enables businesses to safeguard assets, improve risk management, and enhance overall organizational performance.
The Goals of Benchmarking for Performance Improvement
Benchmarking aims to identify best practices and performance standards by comparing an organization's processes and metrics against industry leaders or competitors. The primary goals include uncovering performance gaps, driving continuous improvement, and fostering innovation to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. By systematically analyzing external benchmarks, organizations can set realistic targets and implement strategic changes that lead to sustained competitive advantage.
Methodologies: Auditing vs. Benchmarking Approaches
Auditing methodologies involve systematic, detailed inspections and evaluations of processes, controls, and compliance against predefined standards or regulatory requirements. Benchmarking approaches focus on comparing organizational performance metrics, best practices, and processes against industry leaders or competitors to identify areas for improvement. While auditing emphasizes adherence and accuracy, benchmarking prioritizes performance optimization through external comparisons.
Benefits and Challenges of Auditing
Auditing provides critical benefits such as ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, identifying financial discrepancies, and enhancing organizational transparency, which boosts stakeholder confidence. Challenges of auditing include resource intensiveness, potential disruption to operational workflows, and the need for highly skilled auditors to accurately interpret complex data. While auditing focuses on internal verification, benchmarking offers comparative analysis against industry standards for performance improvement.
Advantages and Limitations of Benchmarking
Benchmarking offers advantages such as providing measurable performance standards, facilitating continuous improvement, and uncovering industry best practices that drive competitive advantage. Its limitations include the risk of imitating competitors without innovation, potential data confidentiality issues, and the challenge of finding truly comparable benchmarks across different organizations or sectors. Effective benchmarking requires careful selection of criteria and adaptation to unique business contexts to maximize relevance and impact.
Choosing Between Auditing and Benchmarking: Strategic Considerations
Choosing between auditing and benchmarking requires evaluating the strategic goals of an organization, where auditing provides a comprehensive assessment of compliance and internal controls, while benchmarking offers comparative performance insights against industry standards. Auditing is ideal for identifying risks and ensuring regulatory adherence, whereas benchmarking drives continuous improvement by highlighting performance gaps and best practices. Effective decision-making depends on whether the priority is risk management or competitive performance enhancement.
Auditing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com