Ensuring NCLB compliance is crucial for schools to meet federal education standards and secure essential funding. Adhering to these mandates helps improve student achievement and accountability in your educational institution. Explore the rest of the article to understand key strategies for maintaining NCLB compliance effectively.
Table of Comparison
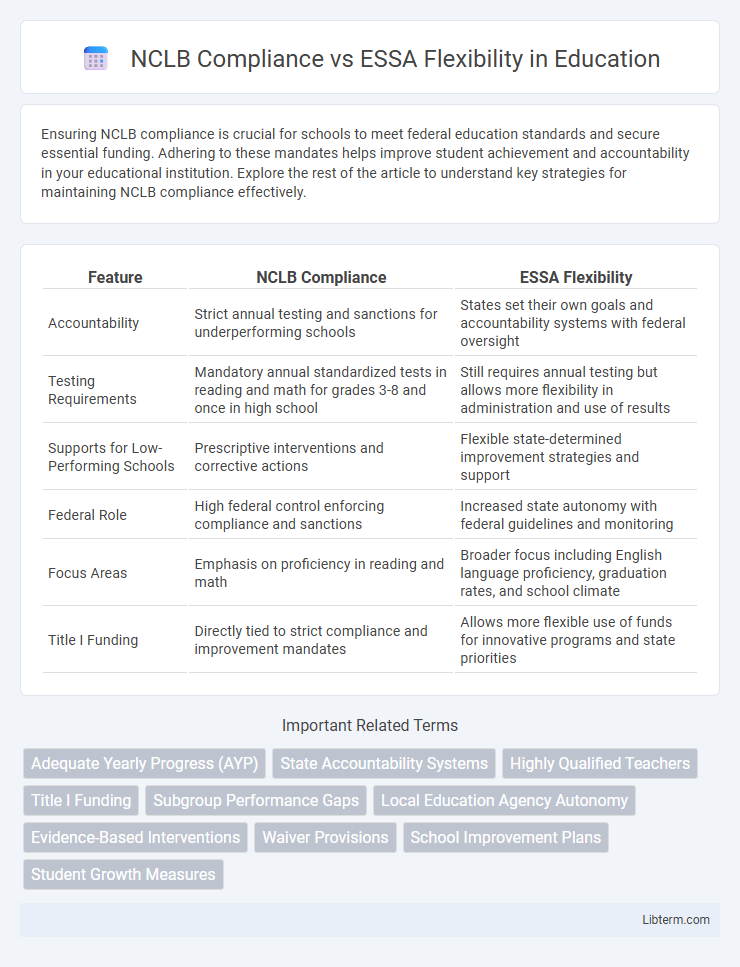
| Feature | NCLB Compliance | ESSA Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
| Accountability | Strict annual testing and sanctions for underperforming schools | States set their own goals and accountability systems with federal oversight |
| Testing Requirements | Mandatory annual standardized tests in reading and math for grades 3-8 and once in high school | Still requires annual testing but allows more flexibility in administration and use of results |
| Supports for Low-Performing Schools | Prescriptive interventions and corrective actions | Flexible state-determined improvement strategies and support |
| Federal Role | High federal control enforcing compliance and sanctions | Increased state autonomy with federal guidelines and monitoring |
| Focus Areas | Emphasis on proficiency in reading and math | Broader focus including English language proficiency, graduation rates, and school climate |
| Title I Funding | Directly tied to strict compliance and improvement mandates | Allows more flexible use of funds for innovative programs and state priorities |
Introduction to NCLB and ESSA
The No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB) established strict federal accountability standards aimed at improving student performance through standardized testing and adequate yearly progress measures. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) replaced NCLB with a more flexible framework, granting states greater authority to design their accountability systems while maintaining core commitments to closing achievement gaps. ESSA emphasizes state-driven strategies and innovation, allowing tailored interventions that reflect diverse educational needs and priorities.
Overview of NCLB Compliance Requirements
NCLB compliance mandates annual testing in reading and math for grades 3-8 and once in high school, with schools required to meet Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP) benchmarks to avoid sanctions. Schools must also demonstrate improvements in student proficiency and subgroup performance, ensuring equitable education for all demographics. These strict accountability measures are designed to enforce uniform standards and close achievement gaps across states.
ESSA’s Approach to Educational Flexibility
ESSA (Every Student Succeeds Act) offers greater educational flexibility by allowing states to design tailored accountability systems and intervention strategies based on unique student needs, moving away from NCLB's rigid, one-size-fits-all mandates. States can prioritize multiple indicators of school performance, such as graduation rates and student growth, rather than relying solely on standardized test scores. This flexibility supports innovative approaches to improving education equity and outcomes while maintaining federal oversight to ensure accountability.
Federal vs. State Control in Accountability
NCLB (No Child Left Behind) mandates strict federal control over accountability measures, requiring states to meet specific Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP) targets with standardized testing and sanctions for non-compliance. ESSA (Every Student Succeeds Act) shifts significant autonomy to states, allowing them to design their own accountability systems, including multiple indicators beyond test scores, promoting state-driven flexibility in addressing educational outcomes. This transition reflects a federal-to-state power shift in education policy, balancing national standards with localized decision-making authority.
Testing and Assessment Mandates
NCLB Compliance demanded annual standardized testing in reading and math for grades 3-8 and once in high school, imposing strict accountability measures based on proficiency levels. ESSA Flexibility allows states to design their own assessment systems with broader options, including measures beyond test scores, while maintaining annual testing requirements but encouraging innovation in assessment types. This shift enables states to balance federal mandates with tailored educational strategies that support diverse student needs and reduce high-stakes testing pressures.
Interventions for Underperforming Schools
NCLB compliance mandates strict, federally prescribed interventions for underperforming schools, including staff replacement and restructuring, to ensure accountability and rapid improvement. ESSA offers greater flexibility by allowing states to design tailored intervention strategies, such as targeted support and improvement within locally determined frameworks. This shift enables more context-sensitive approaches that prioritize sustainable school improvement over rigid, one-size-fits-all mandates.
Teacher Qualifications and Professional Development
NCLB Compliance enforces strict Teacher Qualifications by mandating Highly Qualified Teacher status, requiring specific certifications and subject expertise, while ESSA Flexibility allows states to define teacher effectiveness with broader criteria, promoting diverse qualifications. Professional Development under NCLB is highly prescriptive, focusing on remedial training to meet compliance, whereas ESSA encourages personalized growth opportunities tailored to educators' needs and state priorities. The shift from NCLB to ESSA reflects a movement from uniform federal mandates toward adaptive state-led strategies enhancing teacher quality and instructional improvement.
Impact on Achievement Gaps
NCLB compliance focused on strict accountability measures and standardized testing, often narrowing curriculum and disproportionately penalizing underperforming schools, which limited progress in closing achievement gaps. ESSA flexibility permits states to design tailored accountability systems and incorporate multiple measures of student growth, enabling more targeted interventions that address diverse learning needs. This shift supports closing achievement gaps by encouraging innovation and local-level strategies aligned with community contexts.
School Funding and Resource Allocation
NCLB Compliance mandated rigid school funding formulas tied to standardized test performance, limiting districts' flexibility in resource allocation. ESSA Flexibility allows states to design funding strategies that target resources based on local needs, promoting equitable distribution and innovation. This shift facilitates tailored investment in underserved schools, improving overall educational outcomes through adaptive funding models.
Future Directions in Federal Education Policy
Future directions in federal education policy highlight a shift from the rigid mandates of No Child Left Behind (NCLB) compliance towards the increased flexibility allowed under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). ESSA empowers states to develop tailored accountability systems that prioritize student growth and address diverse local needs while maintaining federal oversight to ensure equity. This balance aims to foster innovation in education strategies and promote continuous improvement in student outcomes nationwide.
NCLB Compliance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com