Norm-referenced assessment compares a student's performance against a larger group to determine their relative standing. This type of evaluation highlights how Your abilities rank within a broader context, typically using percentile ranks or standard scores. Explore the rest of this article to understand its benefits, limitations, and practical applications.
Table of Comparison
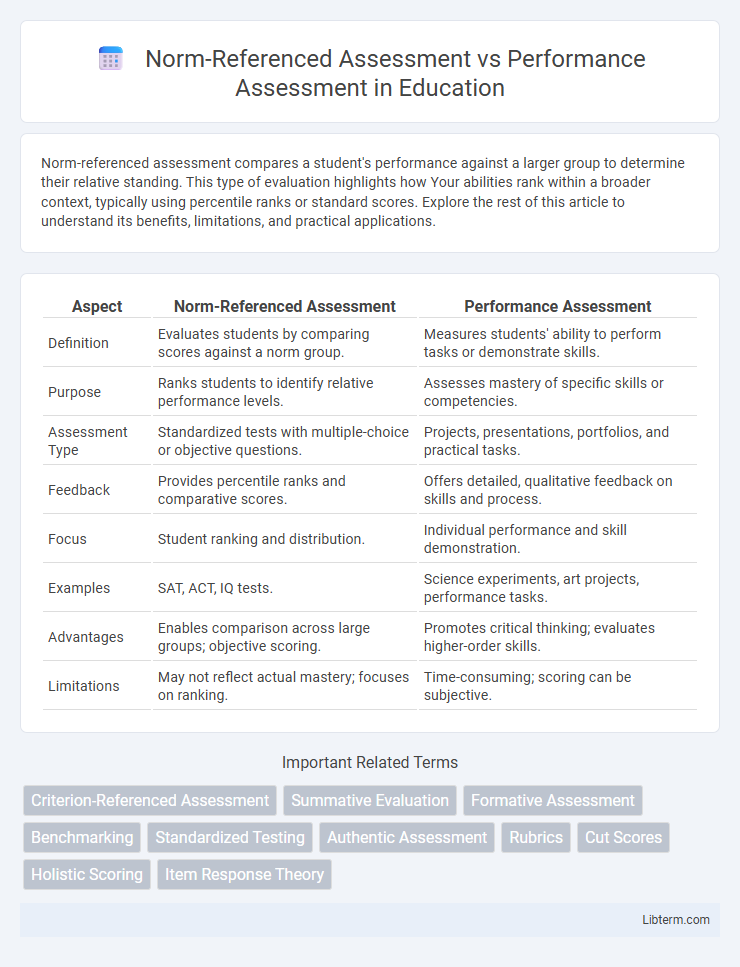
| Aspect | Norm-Referenced Assessment | Performance Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates students by comparing scores against a norm group. | Measures students' ability to perform tasks or demonstrate skills. |
| Purpose | Ranks students to identify relative performance levels. | Assesses mastery of specific skills or competencies. |
| Assessment Type | Standardized tests with multiple-choice or objective questions. | Projects, presentations, portfolios, and practical tasks. |
| Feedback | Provides percentile ranks and comparative scores. | Offers detailed, qualitative feedback on skills and process. |
| Focus | Student ranking and distribution. | Individual performance and skill demonstration. |
| Examples | SAT, ACT, IQ tests. | Science experiments, art projects, performance tasks. |
| Advantages | Enables comparison across large groups; objective scoring. | Promotes critical thinking; evaluates higher-order skills. |
| Limitations | May not reflect actual mastery; focuses on ranking. | Time-consuming; scoring can be subjective. |
Introduction to Assessment Types
Norm-referenced assessment compares a student's performance to a peer group, providing a ranking that highlights relative achievement through standardized tests. Performance assessment evaluates a student's ability to apply skills or knowledge through tasks like projects, presentations, or portfolios, measuring mastery in real-world contexts. These distinct assessment types serve complementary roles in education, informing instructional strategies and student development.
Defining Norm-Referenced Assessment
Norm-Referenced Assessment measures a student's performance by comparing it to a predefined group, establishing relative rankings rather than absolute mastery of content. This method utilizes standardized tests to generate percentile scores that indicate how an individual performs relative to peers. It primarily serves to identify a student's position within a normative sample rather than assessing specific skills or competencies directly.
Understanding Performance Assessment
Performance assessment evaluates students' abilities through real-world tasks and active demonstrations, emphasizing applied skills and critical thinking. Unlike norm-referenced assessments that compare scores across peers, performance assessments focus on individual competency and authentic problem-solving. This approach provides richer insights into student learning by measuring how knowledge is used in practical contexts.
Key Differences Between Assessment Methods
Norm-referenced assessments rank students by comparing their performance to peers using standardized tests, emphasizing relative achievement and percentiles. Performance assessments evaluate students based on their ability to apply skills in real-world tasks, focusing on individual mastery and critical thinking through portfolios or projects. Key differences include the purpose of evaluation--relative ranking versus skill demonstration--and the format, with norm-referenced often relying on multiple-choice questions and performance assessments utilizing open-ended, practical tasks.
Advantages of Norm-Referenced Assessments
Norm-referenced assessments provide the advantage of comparing individual student performance against a larger population, facilitating standardized benchmarking and percentile ranking. These assessments enable educators to identify students who are above or below average, aiding in targeted interventions and resource allocation. The use of norm-referenced data supports consistent measurement across diverse groups, promoting fairness and reliability in evaluating academic achievement.
Benefits of Performance Assessments
Performance assessments provide a more authentic evaluation of students' skills by requiring them to apply knowledge in real-world contexts, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. These assessments offer detailed insights into individual learning processes and competencies, enabling personalized feedback that supports student growth. Unlike norm-referenced assessments, performance assessments encourage deeper understanding and practical application, fostering meaningful engagement and long-term retention.
Limitations and Criticisms
Norm-referenced assessments often face criticism for promoting competition over individual learning by ranking students against peers rather than measuring mastery of content. Performance assessments are sometimes limited by subjective scoring and inconsistencies in evaluator judgment, which can affect reliability and comparability. Both approaches may inadequately address diverse learning styles and fail to provide a comprehensive evaluation of student abilities across different contexts.
Use Cases in Education
Norm-referenced assessments excel in ranking students by comparing individual performance against a larger group, making them ideal for standardized testing and large-scale evaluations. Performance assessments provide valuable insights into students' practical skills and problem-solving abilities, often utilized in project-based learning, portfolio reviews, and competency-based education. Both assessment types serve distinct roles: norm-referenced tests identify achievement gaps across populations, while performance assessments measure mastery in real-world or applied contexts.
Selecting the Right Assessment Type
Selecting the right assessment type depends on the learning objectives and the skills being evaluated. Norm-referenced assessments compare individual performance against a larger group to determine relative ranking, ideal for standardized testing and identifying achievement levels. Performance assessments measure students' ability to apply knowledge through real-world tasks, providing deeper insights into critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical skills.
Conclusion: Making Informed Assessment Choices
Choosing between norm-referenced assessment and performance assessment requires understanding each method's strengths and limitations relative to specific educational goals. Norm-referenced tests effectively measure relative student standing through standardized scoring, while performance assessments evaluate practical skills and authentic problem-solving abilities. Informed decision-making involves aligning assessment types with desired outcomes, ensuring accurate measurement of student learning and fostering targeted instruction.
Norm-Referenced Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com