Peer observation models foster collaborative learning by allowing educators to observe and provide constructive feedback to one another, enhancing teaching strategies and student engagement. This approach encourages reflective practice, professional growth, and the sharing of effective techniques within educational communities. Discover how implementing a peer observation model can transform your teaching experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
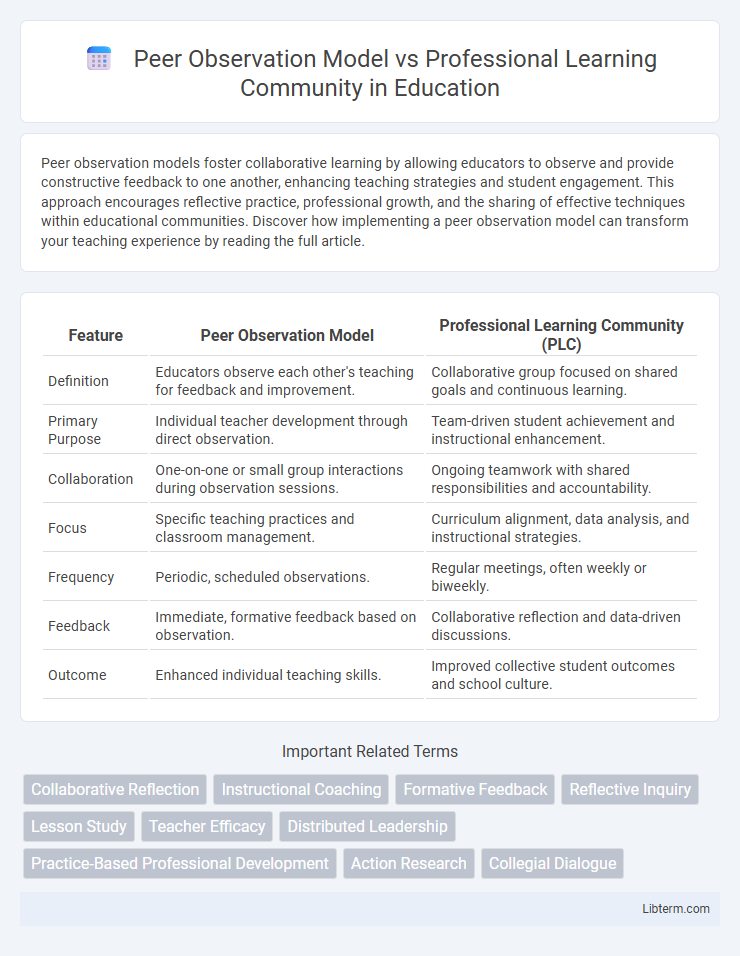
| Feature | Peer Observation Model | Professional Learning Community (PLC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Educators observe each other's teaching for feedback and improvement. | Collaborative group focused on shared goals and continuous learning. |
| Primary Purpose | Individual teacher development through direct observation. | Team-driven student achievement and instructional enhancement. |
| Collaboration | One-on-one or small group interactions during observation sessions. | Ongoing teamwork with shared responsibilities and accountability. |
| Focus | Specific teaching practices and classroom management. | Curriculum alignment, data analysis, and instructional strategies. |
| Frequency | Periodic, scheduled observations. | Regular meetings, often weekly or biweekly. |
| Feedback | Immediate, formative feedback based on observation. | Collaborative reflection and data-driven discussions. |
| Outcome | Enhanced individual teaching skills. | Improved collective student outcomes and school culture. |
Introduction to Peer Observation Model and Professional Learning Community
The Peer Observation Model involves educators observing each other's teaching practices to provide constructive feedback, fostering reflective improvement and collaboration. Professional Learning Communities (PLCs) consist of groups of educators working collaboratively to share expertise, analyze student data, and implement instructional strategies aimed at enhancing student achievement. Both models emphasize continuous professional development but differ in structure, with peer observation focusing on one-on-one feedback and PLCs prioritizing group collaboration and collective responsibility.
Defining Peer Observation Model
The Peer Observation Model is a structured process where educators observe each other's teaching practices to provide constructive feedback aimed at improving instructional techniques. This model emphasizes direct classroom engagement and reflective dialogue to foster professional growth and enhance student learning outcomes. Unlike Professional Learning Communities, which involve collaborative team-based learning and shared goals, the Peer Observation Model centers on individual peer-to-peer interactions and targeted observation cycles.
Understanding Professional Learning Community (PLC)
The Professional Learning Community (PLC) is a collaborative framework where educators engage in collective inquiry, data analysis, and shared decision-making to enhance student outcomes and instructional practices. Unlike the Peer Observation Model, which centers on individual teacher feedback through classroom observations, PLC emphasizes continuous team-based learning, reflection, and mutual accountability across the entire school community. This model fosters a culture of trust and ongoing professional growth by aligning teaching strategies with student needs through collective expertise.
Core Objectives and Goals Comparison
The Peer Observation Model centers on enhancing individual teacher performance through systematic feedback and reflective practice, aiming to improve classroom instruction and student outcomes. In contrast, the Professional Learning Community (PLC) focuses on collaborative teacher teams working collectively to analyze student data and implement evidence-based strategies for school-wide improvement. Both prioritize continuous professional growth, but the Peer Observation Model emphasizes personal development, while PLCs target collective efficacy and shared responsibility for student achievement.
Structure and Implementation Differences
The Peer Observation Model centers on individual teacher interactions with a structured schedule for reciprocal classroom observations and feedback, emphasizing direct, personalized professional growth. The Professional Learning Community (PLC) operates as a collaborative group approach, with regular meetings focused on shared goals, data analysis, and collective problem-solving to enhance overall school performance. Implementation in peer observation requires pairing educators and scheduling observation cycles, while PLCs demand sustained team collaboration, leadership support, and data-driven decision-making frameworks.
Collaboration and Communication Practices
The Peer Observation Model emphasizes one-on-one collaboration where educators engage in reciprocal feedback, fostering individualized professional growth through direct classroom observation and dialogue. Professional Learning Communities (PLCs) expand this interaction to a collective level, promoting continuous communication among teams to analyze student data and co-develop instructional strategies. Both models enhance communication practices, but PLCs institutionalize collaborative decision-making, while the Peer Observation Model provides personalized reflective opportunities.
Impact on Teacher Professional Development
Peer Observation Model enhances teacher professional development by providing real-time feedback, fostering reflective practice, and encouraging collaborative learning tailored to individual needs. Professional Learning Communities (PLCs) promote continuous growth through sustained collaboration, shared goals, and collective problem-solving, leading to improved instructional strategies and student outcomes. Combining Peer Observation with PLCs creates a dynamic framework where personalized feedback and collective expertise drive effective and ongoing teacher development.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Model
Peer Observation Model faces challenges such as resistance from teachers due to fear of judgment and limited time for meaningful observations, which can reduce its effectiveness in fostering genuine professional growth. Professional Learning Communities often struggle with inconsistent participation, lack of administrative support, and difficulty aligning goals, leading to fragmented collaboration and limited impact on teaching practices. Both models require sustained commitment and clear structures to overcome these limitations and achieve successful teacher development.
Best Practices for Effective Implementation
Effective implementation of the Peer Observation Model involves structured, non-evaluative feedback cycles that foster reflective practice and targeted skill improvement among educators. Professional Learning Communities thrive through collaborative inquiry, shared goals, and continuous data-driven discussions that support collective growth and instructional alignment. Integrating clear communication protocols, ongoing training, and alignment with school-wide objectives ensures both models enhance teacher development and student outcomes.
Choosing the Right Model: Key Considerations
Choosing the right model between Peer Observation and Professional Learning Communities involves evaluating goals such as individualized feedback versus collaborative curriculum development. Peer Observation emphasizes real-time classroom insights to enhance teaching techniques, while Professional Learning Communities foster ongoing dialogue and shared accountability among educators. Consider factors like school culture, teacher readiness, and desired outcomes to determine the model that best supports continuous professional growth.
Peer Observation Model Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com