Explicit curriculum clearly defines learning objectives, instructional content, and assessment methods to ensure systematic knowledge acquisition. It focuses on transparency in what is taught, allowing educators to align teaching strategies with desired outcomes effectively. Discover how implementing an explicit curriculum can enhance Your educational success by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
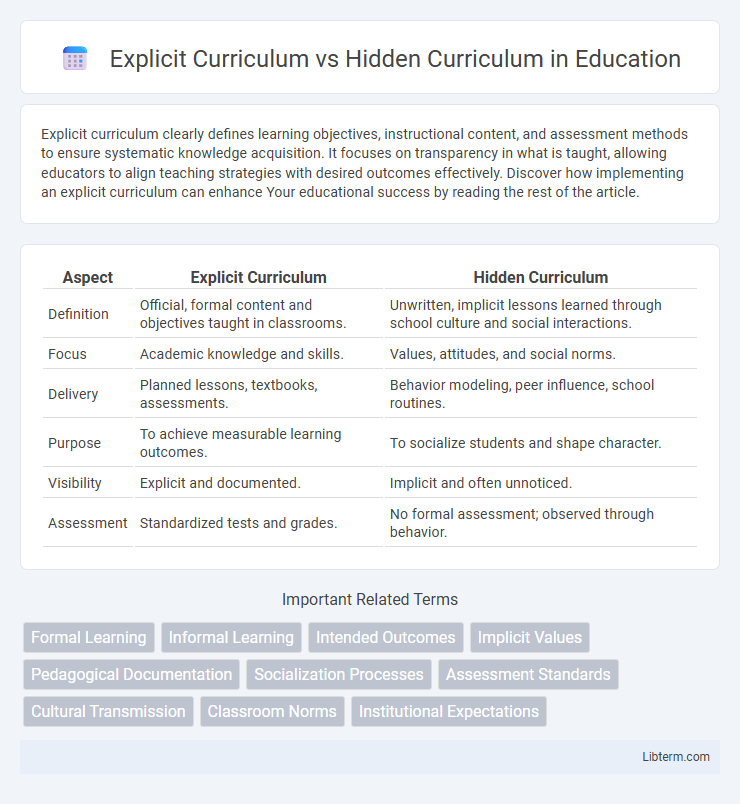
| Aspect | Explicit Curriculum | Hidden Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official, formal content and objectives taught in classrooms. | Unwritten, implicit lessons learned through school culture and social interactions. |
| Focus | Academic knowledge and skills. | Values, attitudes, and social norms. |
| Delivery | Planned lessons, textbooks, assessments. | Behavior modeling, peer influence, school routines. |
| Purpose | To achieve measurable learning outcomes. | To socialize students and shape character. |
| Visibility | Explicit and documented. | Implicit and often unnoticed. |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and grades. | No formal assessment; observed through behavior. |
Introduction to Explicit and Hidden Curriculum
Explicit curriculum consists of formal educational content and objectives clearly outlined in lesson plans, textbooks, and standardized assessments, ensuring structured learning experiences. Hidden curriculum refers to the implicit lessons, values, and norms conveyed through classroom interactions, school culture, and teacher attitudes that influence students' social and moral development. Both forms of curriculum shape student learning, with explicit curriculum targeting academic skills and hidden curriculum addressing socialization processes.
Defining Explicit Curriculum
Explicit curriculum refers to the formal, structured educational content and learning objectives outlined by educational institutions or authorities, including syllabi, textbooks, lesson plans, and assessments. It encompasses the specific skills, knowledge, and competencies that students are officially expected to learn during a course or program. This clearly articulated curriculum serves as the foundation for teaching and evaluating academic progress, contrasting with the implicit lessons conveyed through school culture or social interactions.
Understanding Hidden Curriculum
Hidden curriculum refers to the implicit lessons, values, and perspectives that students learn in school beyond the formal explicit curriculum, such as social norms, beliefs, and behaviors. Understanding hidden curriculum is crucial because it shapes students' attitudes, social skills, and cultural understanding, often influencing their future interactions and success. Educators must recognize and address these unspoken elements to create more equitable and inclusive learning environments.
Key Differences Between Explicit and Hidden Curriculum
Explicit curriculum encompasses the formal, structured educational content and learning objectives outlined by schools, including textbooks, lesson plans, and standardized assessments. Hidden curriculum refers to the implicit lessons, values, and social norms conveyed through classroom interactions, school culture, and institutional practices that are not formally documented. Key differences lie in their visibility and intent: explicit curriculum is intentionally designed and assessed, while hidden curriculum is informal, subconscious, and shapes students' social behaviors and attitudes.
The Role of Teachers in Both Curriculums
Teachers play a pivotal role in delivering the explicit curriculum through structured lessons, clear objectives, and formal assessments that ensure students grasp defined knowledge and skills. In the hidden curriculum, educators influence social norms, values, and behaviors by modeling attitudes, reinforcing school culture, and managing classroom interactions often unconsciously. Effective teaching requires awareness of both curricula to foster academic success while promoting positive social development and ethical citizenship.
Impact on Student Learning and Development
Explicit curriculum provides structured knowledge and skills aligned with academic standards, directly influencing student achievement and cognitive development. Hidden curriculum, encompassing implicit social norms and values, shapes students' attitudes, behaviors, and interpersonal skills critical for holistic growth and socialization. Both curricula collectively impact student learning by balancing formal instruction with essential life competencies.
Examples of Explicit vs Hidden Curriculum in Schools
Explicit curriculum in schools includes structured lessons like math problem-solving exercises, science lab experiments, and history lectures with clear learning objectives. Hidden curriculum involves the implicit messages students receive, such as understanding social hierarchies through classroom seating arrangements or learning teamwork and cooperation during group projects not formally outlined in the syllabus. Examples illustrate that while explicit curriculum targets academic skills, hidden curriculum shapes social behaviors and cultural norms within the school environment.
Challenges and Controversies
Explicit curriculum presents clear, structured learning objectives, but challenges arise when its rigid framework limits critical thinking and creativity. Hidden curriculum, encompassing implicit social norms and values taught through school culture, faces controversies related to reinforcing inequalities and perpetuating biases unconsciously. Balancing both requires addressing how unspoken lessons impact student identity and inclusivity within diverse educational environments.
Strategies to Address Hidden Curriculum
Strategies to address the hidden curriculum involve fostering open communication between educators and students to identify implicit biases and unspoken norms within the learning environment. Implementing reflective teaching practices and culturally responsive pedagogy helps educators recognize and challenge unintended messages conveyed through school culture and interactions. Developing transparent policies and promoting inclusivity ensures that the implicit lessons align with the explicit curriculum's goals for equity and social justice.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap in Education
Bridging the gap between explicit curriculum and hidden curriculum enhances holistic student development by aligning formal educational goals with social and cultural learning. Integrating awareness of hidden curriculum influences supports equitable teaching practices and fosters critical thinking, empathy, and ethical behavior. Prioritizing this synergy prepares students to navigate complex social environments and succeed beyond academic achievement.
Explicit Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com