The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) serves as a foundational federal law aiming to improve educational opportunities for all students, particularly those from disadvantaged backgrounds. It provides essential funding for schools, supports academic standards, and promotes equity in education across states. Explore the rest of the article to discover how the ESEA impacts your child's learning environment and shapes educational policy nationwide.
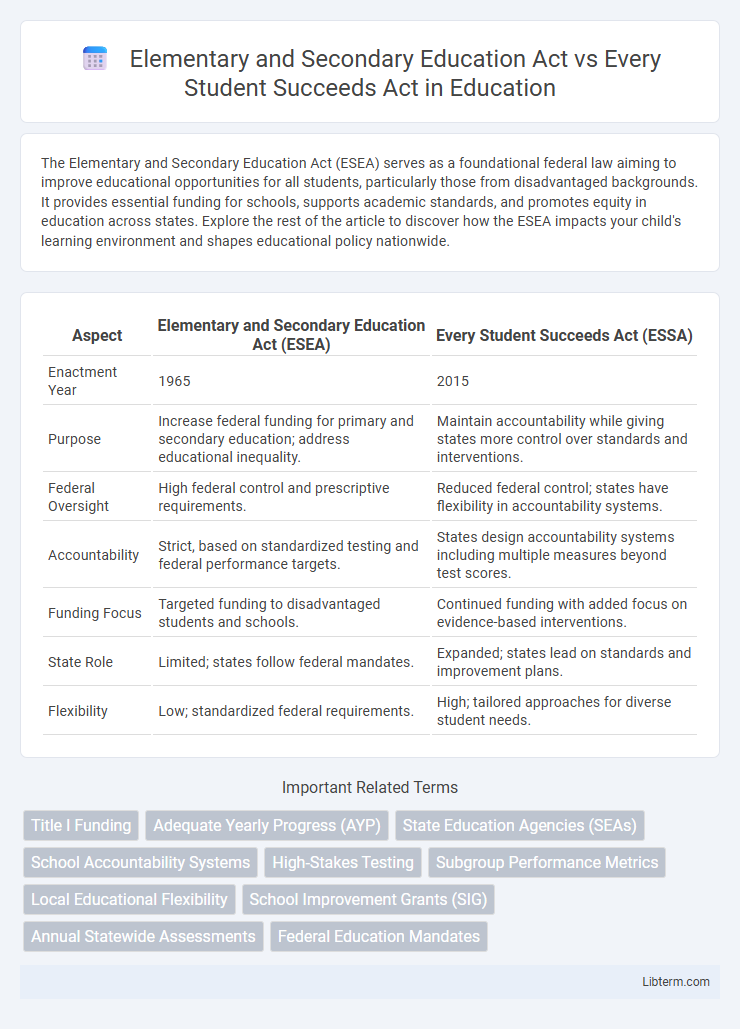
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) | Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) |
|---|---|---|
| Enactment Year | 1965 | 2015 |
| Purpose | Increase federal funding for primary and secondary education; address educational inequality. | Maintain accountability while giving states more control over standards and interventions. |
| Federal Oversight | High federal control and prescriptive requirements. | Reduced federal control; states have flexibility in accountability systems. |
| Accountability | Strict, based on standardized testing and federal performance targets. | States design accountability systems including multiple measures beyond test scores. |
| Funding Focus | Targeted funding to disadvantaged students and schools. | Continued funding with added focus on evidence-based interventions. |
| State Role | Limited; states follow federal mandates. | Expanded; states lead on standards and improvement plans. |
| Flexibility | Low; standardized federal requirements. | High; tailored approaches for diverse student needs. |
Overview of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA)
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA), enacted in 1965, is a landmark federal law designed to provide equal access to quality education, particularly for disadvantaged students. It established foundational funding for primary and secondary education, targeting resources to low-income schools and emphasizing accountability through standardized testing. ESEA's ongoing reauthorizations, including the shift from No Child Left Behind to the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA), reflect evolving strategies to balance federal oversight with state flexibility.
Introduction to the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA), enacted in 2015, replaced the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) to provide states with greater flexibility in setting educational standards while maintaining federal oversight on accountability and student achievement. ESSA emphasizes state-driven assessments, accountability plans, and interventions for underperforming schools, aiming to improve educational outcomes and equity. The act balances federal guidance with local control to address diverse student needs across the United States.
Historical Context and Legislative Background
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) of 1965 was enacted during President Lyndon B. Johnson's administration as a central part of his "War on Poverty," aiming to provide equal educational opportunities and federal funding to disadvantaged students. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA), signed into law in 2015 under President Barack Obama, replaced the No Child Left Behind Act and shifted greater accountability and decision-making power from the federal government back to states and local districts. ESSA maintains the focus on high academic standards and standardized testing but offers states more flexibility in designing interventions and educational programs.
Key Goals and Objectives: ESEA vs ESSA
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) primarily aimed to close achievement gaps by providing federal funds to support disadvantaged students and improve educational equity. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) shifted focus towards increased state and local control over accountability, emphasizing flexible, data-driven strategies to enhance student outcomes and school performance. ESSA maintains core goals of ESEA but expands objectives to include comprehensive support for diverse learners through evidence-based interventions and broader stakeholder involvement.
Funding Mechanisms and Resource Allocation
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) primarily provided federal funding through Title I grants to support disadvantaged students, emphasizing strict compliance and accountability measures. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) retains Title I funding but shifts resource allocation decisions to states and local districts, allowing more flexibility in addressing educational needs. ESSA mandates that funds be used to support high-quality education while promoting equitable access and targeted interventions based on state-developed accountability plans.
Accountability Systems and Student Assessment
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) emphasized strict federal accountability systems with annual standardized testing in reading and math for grades 3-8 and once in high school, tying results to school performance and consequences. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) maintains annual testing requirements but shifts accountability control from the federal government to states, allowing them to design systems that include multiple indicators such as graduation rates, academic achievement, and school climate. Student assessment under ESSA also encourages diverse measures beyond standardized tests, promoting a more holistic approach to evaluating student and school performance.
Federal vs State Roles in Education Policy
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) established a strong federal role in education by setting national standards and accountability measures through programs like Title I funding. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) shifted significant control back to states, granting them authority to develop tailored accountability systems and education policies while still requiring federal oversight for equity and essential protections. This transition emphasizes state flexibility in addressing local educational needs within a framework of federal guidelines to promote student success.
Impact on Teachers and School Districts
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) imposed strict federal mandates emphasizing standardized testing and accountability, often limiting teacher autonomy and increasing administrative burdens on school districts. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) shifted accountability to states and local districts, granting educators greater flexibility in curriculum choices and assessment methods to better address diverse student needs. ESSA's emphasis on local control has empowered school districts to develop more tailored professional development programs, improving teacher effectiveness and retention.
Equity and Support for Disadvantaged Students
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA), established in 1965, emphasized federal funding to improve educational equity and support for disadvantaged students through targeted programs like Title I, which allocates resources to high-poverty schools. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) of 2015 reauthorized ESEA, shifting greater accountability and decision-making power to states while maintaining a strong focus on equity by requiring interventions for struggling schools and support for disadvantaged student groups, including low-income, English learners, and students with disabilities. ESSA enhances flexibility in achieving equity goals but retains federal mandates to close achievement gaps and provide comprehensive support to vulnerable populations.
Long-Term Outcomes and Future Policy Directions
The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) initially prioritized standardized testing and federal accountability measures, which influenced educational outcomes by emphasizing short-term performance metrics. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA), as the ESEA's reauthorization, shifts focus toward broader long-term outcomes such as college and career readiness, equity in resource allocation, and local control over accountability systems. Future policy directions under ESSA emphasize data-driven interventions, support for marginalized student groups, and flexibility in state-designed accountability frameworks to promote sustained educational improvements.
Elementary and Secondary Education Act Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com