Selective admission processes prioritize candidates based on specific criteria, ensuring institutions maintain high academic standards and diversity. This approach helps you stand out by showcasing your unique skills and achievements during the application process. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to navigate selective admissions and enhance your chances of acceptance.
Table of Comparison
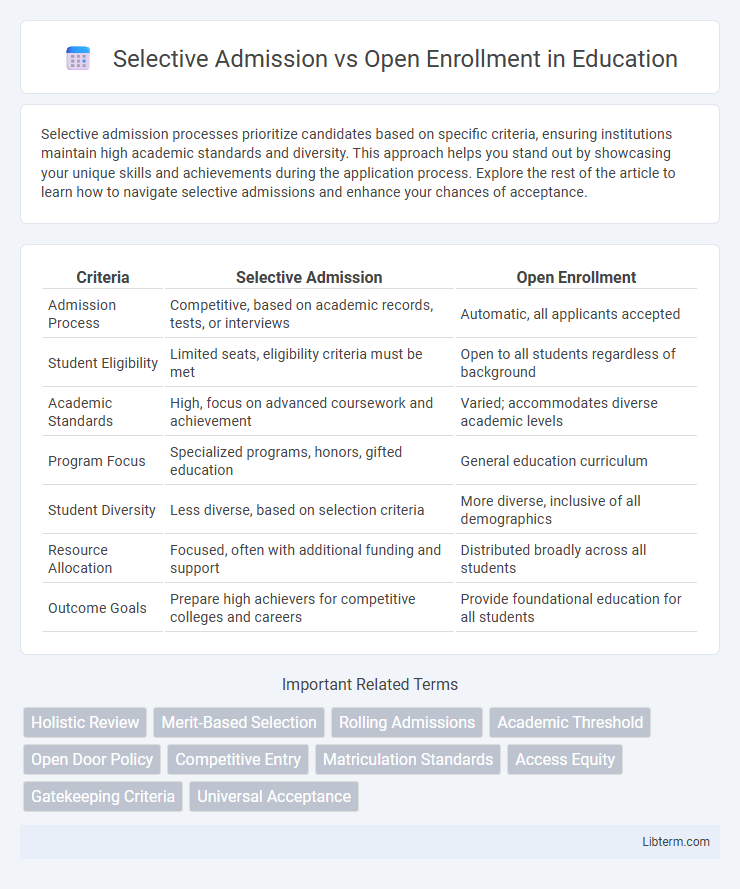
| Criteria | Selective Admission | Open Enrollment |
|---|---|---|
| Admission Process | Competitive, based on academic records, tests, or interviews | Automatic, all applicants accepted |
| Student Eligibility | Limited seats, eligibility criteria must be met | Open to all students regardless of background |
| Academic Standards | High, focus on advanced coursework and achievement | Varied; accommodates diverse academic levels |
| Program Focus | Specialized programs, honors, gifted education | General education curriculum |
| Student Diversity | Less diverse, based on selection criteria | More diverse, inclusive of all demographics |
| Resource Allocation | Focused, often with additional funding and support | Distributed broadly across all students |
| Outcome Goals | Prepare high achievers for competitive colleges and careers | Provide foundational education for all students |
Understanding Selective Admission Policies
Selective admission policies prioritize criteria such as academic achievements, test scores, and extracurricular activities to evaluate prospective students, ensuring a competitive and high-achieving student body. These policies often require applicants to submit transcripts, letters of recommendation, and personal statements for a comprehensive review process. Understanding selective admission involves recognizing its emphasis on merit-based evaluation and the intent to maintain rigorous academic standards within the institution.
Defining Open Enrollment in Education
Open enrollment in education refers to policies that allow students to attend public schools outside their designated residential zones without requiring competitive admission criteria. This system promotes equal access by enabling families to choose schools based on preference rather than academic performance or selection processes. Open enrollment enhances diversity and flexibility within school districts by removing barriers to entry typically associated with selective admission policies.
Key Differences Between Selective and Open Enrollment
Selective admission requires applicants to meet specific academic or extracurricular criteria, ensuring a competitive and merit-based selection process. Open enrollment, in contrast, allows all students to register regardless of qualifications, promoting inclusivity and broader access. The key difference lies in the admission criteria, with selective admission prioritizing achievement and aptitude, while open enrollment emphasizes accessibility and diversity.
Advantages of Selective Admission Systems
Selective admission systems enhance educational quality by ensuring that students meet specific academic criteria, fostering a more motivated and capable student body. These systems often lead to higher graduation rates and better resource allocation, as institutions can tailor programs to students with proven skills and readiness. By maintaining rigorous standards, selective admissions also boost the institution's reputation and attract competitive faculty and funding opportunities.
Benefits of Open Enrollment Approaches
Open enrollment offers increased accessibility to education by allowing all students to attend public schools without stringent entry requirements, promoting diversity and equal opportunity. This approach fosters a more inclusive learning environment by reducing barriers related to academic performance or selective criteria. Schools benefit from open enrollment by receiving broader community support and increased funding tied to student attendance.
Impact on Student Diversity and Inclusion
Selective admission policies often result in less diverse student populations due to stringent academic and extracurricular criteria that may favor privileged backgrounds, potentially limiting opportunities for underrepresented groups. Open enrollment promotes greater diversity and inclusion by allowing broader access regardless of prior academic performance, supporting a more varied student body in terms of socioeconomic status, ethnicity, and learning abilities. These enrollment approaches significantly shape campus cultural dynamics and influence institutional commitments to equity and inclusivity.
Academic Outcomes: Selective Admission vs Open Enrollment
Selective admission policies often result in higher academic outcomes as they allow institutions to admit students based on merit, ensuring a population with strong academic preparation and motivation. Open enrollment policies increase access but can create greater diversity in academic readiness, which may challenge maintaining uniformly high academic standards and outcomes. Studies show selective admission schools tend to report higher graduation rates, standardized test scores, and postgraduate success compared to open enrollment institutions.
Accessibility and Equity in Higher Education
Selective admission policies often create barriers for underrepresented and marginalized groups, limiting accessibility to higher education by prioritizing academic metrics that may reflect systemic inequalities. Open enrollment promotes equity by providing broader access regardless of prior academic performance, fostering diversity and inclusion among students. Institutions with open enrollment policies tend to support non-traditional learners and offer remedial programs to bridge educational gaps, enhancing overall social mobility.
Navigating Application Processes: Tips for Students
Selective admission requires meeting specific academic criteria and submitting detailed applications, so students should focus on showcasing strong grades, test scores, and extracurricular achievements. Open enrollment typically allows for easier application with fewer requirements, making timely submission and accurate completion crucial. Researching deadlines, understanding individual school policies, and preparing necessary documents early improve the chances of acceptance in both systems.
Future Trends in Admissions Policies
Future trends in admissions policies indicate a growing emphasis on inclusive criteria beyond standardized test scores, as selective admission processes integrate holistic evaluations to promote diversity. Open enrollment models are evolving with enhanced support systems and digital tools to accommodate a broader student population while maintaining academic standards. Data-driven decision-making and AI-powered assessments are expected to shape adaptive admission frameworks that balance accessibility with quality education outcomes.
Selective Admission Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com