Lecture-based learning remains a foundational teaching method that effectively delivers structured information to large groups, promoting knowledge acquisition through expert instruction. This approach facilitates focused content delivery, allowing students to absorb key concepts and theories essential for their academic progress. Discover how lecture-based learning can enhance Your educational experience by exploring its benefits and strategies in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
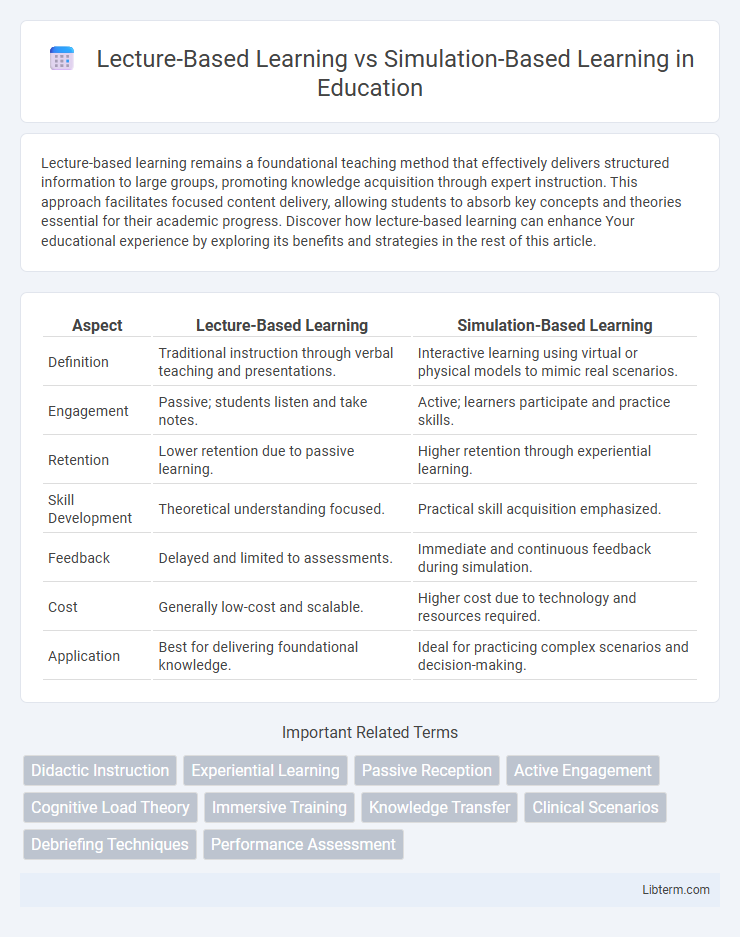
| Aspect | Lecture-Based Learning | Simulation-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional instruction through verbal teaching and presentations. | Interactive learning using virtual or physical models to mimic real scenarios. |
| Engagement | Passive; students listen and take notes. | Active; learners participate and practice skills. |
| Retention | Lower retention due to passive learning. | Higher retention through experiential learning. |
| Skill Development | Theoretical understanding focused. | Practical skill acquisition emphasized. |
| Feedback | Delayed and limited to assessments. | Immediate and continuous feedback during simulation. |
| Cost | Generally low-cost and scalable. | Higher cost due to technology and resources required. |
| Application | Best for delivering foundational knowledge. | Ideal for practicing complex scenarios and decision-making. |
Overview of Lecture-Based Learning
Lecture-Based Learning delivers content through structured presentations, emphasizing expert knowledge transmission to large groups. It relies on verbal explanation and visual aids to provide foundational understanding of concepts, often in a fixed timeframe. This method prioritizes passive learning, where student interaction is limited, focusing on information absorption and note-taking.
Overview of Simulation-Based Learning
Simulation-Based Learning utilizes interactive, immersive environments to replicate real-world scenarios, enhancing critical thinking and practical skills. This method engages learners in hands-on experiences through virtual reality, role-playing, or computer-based simulations, enabling risk-free experimentation and immediate feedback. Research shows simulation-based approaches improve knowledge retention and learner confidence compared to traditional lecture-based instruction.
Historical Development of Both Methods
Lecture-based learning originated in ancient Greece, becoming formalized through medieval universities where oral transmission of knowledge was dominant. Simulation-based learning emerged in the 20th century, initially used in military training during World War II to replicate real-world scenarios for enhanced experiential learning. Over time, advances in technology have expanded simulation-based methods across fields like medicine and aviation, promoting active learning beyond traditional didactic lectures.
Key Features of Lecture-Based Learning
Lecture-Based Learning centers on instructor-led presentations that convey foundational knowledge through verbal explanations and visual aids such as slides or charts. This method emphasizes passive information absorption, with limited student interaction and real-time feedback. It efficiently covers large amounts of theoretical content, making it suitable for introducing complex concepts to large groups.
Core Principles of Simulation-Based Learning
Simulation-based learning centers on immersive, experiential training using realistic scenarios to replicate clinical or professional environments. Core principles include deliberate practice with immediate feedback, safe error exploration, and skill repetition to enhance competence and confidence. This method promotes active learning and critical thinking, contrasting the passive reception typical of lecture-based approaches.
Comparative Effectiveness in Knowledge Retention
Simulation-based learning significantly enhances knowledge retention by providing immersive, hands-on experiences that facilitate active engagement and practical application. Lecture-based learning primarily delivers theoretical knowledge, which may lead to lower long-term retention compared to experiential learning methods. Studies indicate that learners retain complex concepts more effectively through simulation due to improved cognitive processing and memory consolidation.
Impact on Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
Lecture-based learning delivers foundational knowledge but often limits active engagement, which can restrict development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Simulation-based learning immerses students in realistic scenarios that require analysis, decision-making, and application of knowledge, significantly enhancing these cognitive abilities. Studies show simulation-based approaches foster deeper understanding and improved transfer of skills to real-world contexts compared to traditional lectures.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Lecture-based learning often results in passive student engagement due to its one-way communication style, which can limit motivation and retention. Simulation-based learning actively immerses students in realistic scenarios, fostering higher engagement and intrinsic motivation by encouraging problem-solving and critical thinking. Research shows that simulation-based approaches increase student participation rates by up to 45% compared to traditional lectures, enhancing overall learning outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Lecture-based learning often faces challenges such as limited student engagement, passive knowledge absorption, and difficulties in addressing diverse learning paces. Simulation-based learning, while enhancing practical skills and experiential understanding, encounters limitations including high costs, resource intensity, and the potential for technology-related issues. Both approaches require careful integration to balance theoretical knowledge with interactive, hands-on experiences for effective educational outcomes.
Future Trends in Educational Methods
Future trends in educational methods indicate a significant shift towards simulation-based learning, leveraging virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to create immersive, interactive experiences that enhance student engagement and retention. While lecture-based learning remains foundational, hybrid models integrating real-time simulations with traditional lectures are increasingly adopted to develop practical skills and critical thinking in fields like medicine, engineering, and business. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) further personalize simulation scenarios, adapting difficulty and feedback to individual learner needs, thereby optimizing educational outcomes.
Lecture-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com