Inquiry-based teaching promotes active learning by encouraging students to explore questions and problems deeply, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This student-centered approach empowers learners to construct knowledge through investigation and reflection, making education more engaging and meaningful. Discover how inquiry-based teaching can transform your classroom and enhance student success in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
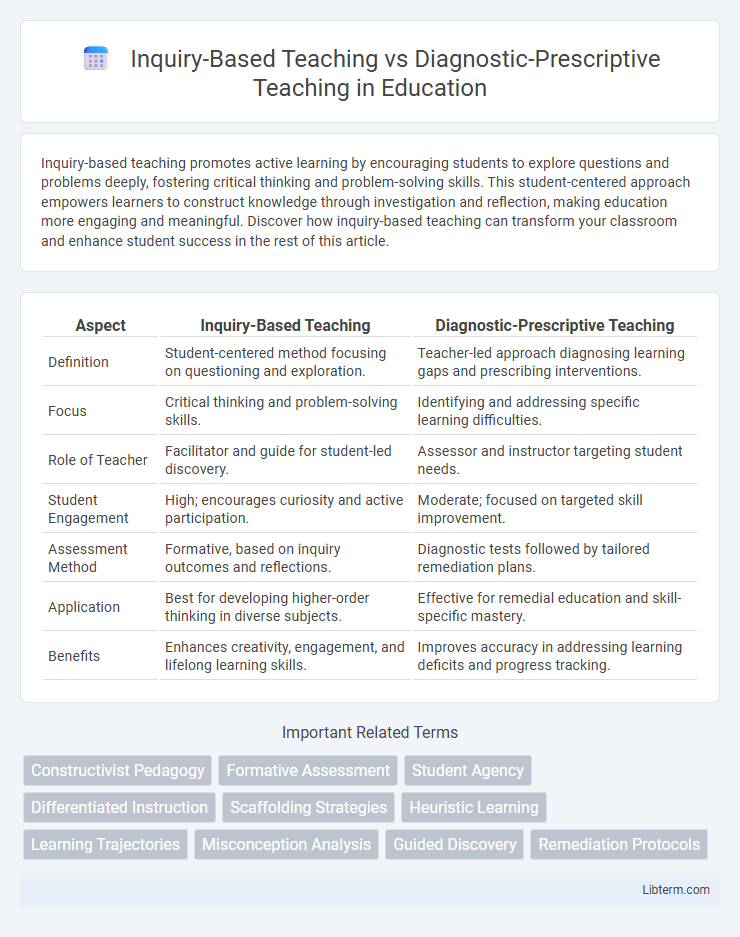
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Teaching | Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered method focusing on questioning and exploration. | Teacher-led approach diagnosing learning gaps and prescribing interventions. |
| Focus | Critical thinking and problem-solving skills. | Identifying and addressing specific learning difficulties. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide for student-led discovery. | Assessor and instructor targeting student needs. |
| Student Engagement | High; encourages curiosity and active participation. | Moderate; focused on targeted skill improvement. |
| Assessment Method | Formative, based on inquiry outcomes and reflections. | Diagnostic tests followed by tailored remediation plans. |
| Application | Best for developing higher-order thinking in diverse subjects. | Effective for remedial education and skill-specific mastery. |
| Benefits | Enhances creativity, engagement, and lifelong learning skills. | Improves accuracy in addressing learning deficits and progress tracking. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based Teaching and Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching
Inquiry-Based Teaching emphasizes student-centered exploration, fostering critical thinking through questioning, investigation, and problem-solving activities. Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching relies on assessing learners' current knowledge to identify gaps and tailor instruction to address specific learning needs. Both approaches aim to enhance educational outcomes but differ in methodology, with inquiry-based promoting discovery and diagnostic-prescriptive focusing on targeted intervention.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Teaching
Inquiry-based teaching centers on student-driven exploration, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving through questioning, investigation, and reflection. Core principles include promoting curiosity, facilitating active learning, and encouraging learners to construct knowledge by engaging with real-world problems. This approach contrasts diagnostic-prescriptive teaching, which emphasizes identifying student difficulties and providing targeted interventions based on assessments.
Core Principles of Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching
Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching centers on identifying individual learner difficulties through detailed assessment and tailoring instruction to address specific gaps, ensuring targeted skill development. Core principles include continuous diagnosis of student understanding, personalized intervention strategies, and ongoing adjustment based on measurable progress. This approach contrasts with Inquiry-Based Teaching by emphasizing structured diagnostics and customized corrective actions to optimize educational outcomes.
Historical Background and Development
Inquiry-Based Teaching emerged from progressive education theories in the early 20th century, emphasizing student-centered learning and critical thinking as advocated by John Dewey. Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching developed later, gaining traction in the mid-20th century through the influence of educational psychology and special education, focusing on identifying learners' deficits and tailoring interventions. Both approaches evolved through empirical research, with Inquiry-Based teaching aligning with constructivist paradigms and Diagnostic-Prescriptive methods grounded in behaviorist and cognitive diagnostic frameworks.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Inquiry-Based Teaching centers on student-driven exploration and critical thinking, encouraging learners to formulate questions and investigate solutions independently. Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching emphasizes identifying individual student learning gaps through assessments and tailoring instruction to address specific weaknesses. The primary difference lies in Inquiry-Based Teaching fostering autonomous discovery, while Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching provides targeted interventions based on diagnostic evaluation.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Teaching
Inquiry-based teaching enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to explore questions and investigate solutions independently. This method fosters deeper understanding and retention of knowledge compared to diagnostic-prescriptive teaching, which often centers on teacher-led diagnosis and targeted correction. Inquiry-based learning also promotes student engagement and motivation by making learning more relevant and personalized.
Advantages of Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching
Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching offers precise identification of students' learning gaps through systematic assessment, enabling targeted interventions that enhance individual academic progress. This method fosters personalized learning paths, addressing specific weaknesses and building foundational skills more efficiently than broad inquiry-based approaches. By focusing on measurable outcomes and tailored instruction, Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching improves mastery of content and accelerates remediation in diverse educational settings.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Inquiry-Based Teaching often faces challenges such as limited student readiness for open-ended exploration and the potential for misconceptions without proper guidance. Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching encounters limitations in its time-consuming assessment process and the risk of overly focusing on deficits rather than fostering broader critical thinking skills. Both methods require skilled educators to balance structure and flexibility to maximize learning outcomes effectively.
Best Practices and Implementation Strategies
Inquiry-based teaching fosters student curiosity through open-ended questions and hands-on exploration, promoting critical thinking and deeper understanding in STEM subjects. Diagnostic-prescriptive teaching relies on ongoing assessments to identify learning gaps and tailor instruction, optimizing individualized student support for improved academic outcomes. Combining formative assessments with collaborative, student-centered activities ensures effective implementation of both methods, enhancing engagement and addressing diverse learning needs.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Inquiry-Based Teaching fosters critical thinking and active learning by encouraging students to explore and question concepts, making it ideal for diverse learners who thrive in interactive environments. Diagnostic-Prescriptive Teaching precisely identifies individual learning gaps through assessments and customizes instruction to address specific needs, supporting students requiring targeted intervention. Selecting the right approach depends on learner profiles, with inquiry methods enhancing engagement and diagnostic-prescriptive strategies optimizing personalized skill development.
Inquiry-Based Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com