A curriculum-centered approach prioritizes structured content and systematic delivery to ensure comprehensive coverage of educational objectives. This method focuses on the teacher as the primary source of knowledge, guiding students through predetermined materials and assessments. Discover how adopting a curriculum-centered strategy can enhance Your teaching effectiveness in the full article.
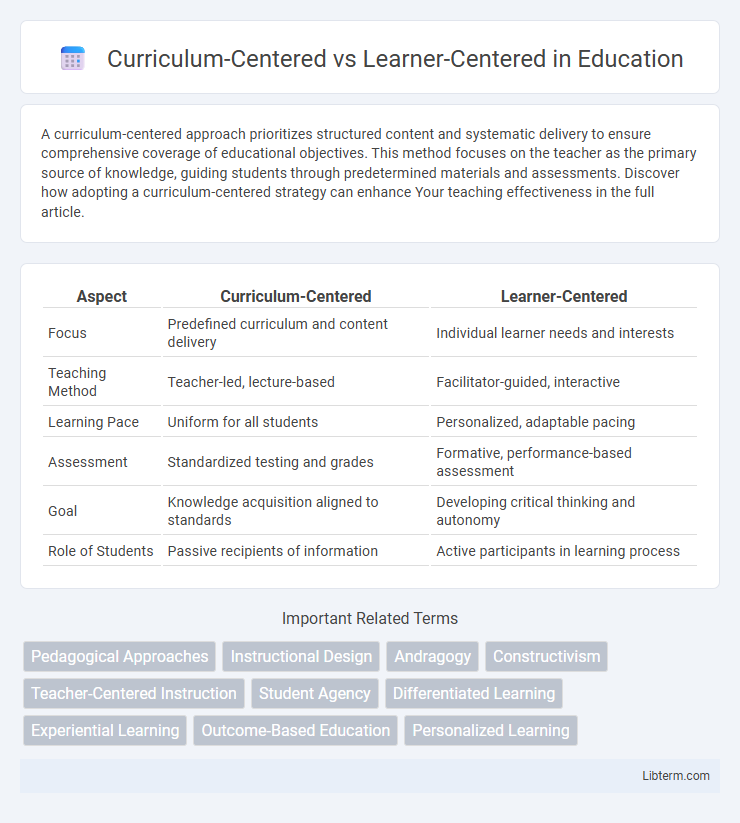
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Curriculum-Centered | Learner-Centered |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Predefined curriculum and content delivery | Individual learner needs and interests |
| Teaching Method | Teacher-led, lecture-based | Facilitator-guided, interactive |
| Learning Pace | Uniform for all students | Personalized, adaptable pacing |
| Assessment | Standardized testing and grades | Formative, performance-based assessment |
| Goal | Knowledge acquisition aligned to standards | Developing critical thinking and autonomy |
| Role of Students | Passive recipients of information | Active participants in learning process |
Introduction to Curriculum-Centered and Learner-Centered Approaches
Curriculum-centered approaches emphasize structured content delivery based on predetermined objectives, ensuring standardized knowledge acquisition across learners. Learner-centered approaches prioritize individual student needs, experiences, and active engagement to foster deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. Both methods shape educational strategies, affecting instructional design, assessment, and classroom interaction dynamics.
Core Principles of Curriculum-Centered Education
Curriculum-centered education prioritizes a structured syllabus emphasizing content mastery, standardized assessments, and teacher-led instruction to ensure uniform knowledge delivery across students. This approach centers on a predefined curriculum aligned with academic standards, promoting consistent learning outcomes through sequenced objectives and measurable benchmarks. Core principles include subject-specific expertise, content coverage, and teacher control over the learning process to maintain educational rigor and coherence.
Key Characteristics of Learner-Centered Pedagogy
Learner-centered pedagogy emphasizes active student engagement, personalized learning experiences, and the development of critical thinking skills, contrasting with rigid curriculum-centered approaches focused on content delivery. Key characteristics include fostering autonomy, encouraging collaboration, and adapting teaching strategies to meet diverse learning needs. This approach prioritizes student motivation and meaningful understanding over rote memorization, enhancing long-term retention and application.
Roles of Teachers in Each Approach
In curriculum-centered education, teachers serve as primary knowledge transmitters, focusing on delivering a pre-defined syllabus and ensuring content mastery. In learner-centered approaches, teachers act as facilitators and guides, supporting students' individual learning processes and fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This shift emphasizes personalized instruction and active student engagement over standardized content delivery.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Curriculum-centered approaches emphasize structured content delivery, which can limit student engagement by prioritizing standardized goals over individual interests, often resulting in passive learning. Learner-centered strategies prioritize student choice and active participation, fostering intrinsic motivation through personalized and meaningful learning experiences. Research shows that learner-centered environments boost engagement by addressing diverse learning styles and promoting autonomy, ultimately enhancing academic achievement and motivation.
Assessment Methods in Both Models
Curriculum-centered assessment methods primarily use standardized tests and fixed criteria to evaluate student mastery of predetermined content, emphasizing uniformity and measurable outcomes. Learner-centered assessment employs formative approaches such as portfolios, self-assessments, and project-based evaluations that prioritize individual growth, critical thinking, and student reflection. The contrast highlights curriculum-centered models' focus on summative evaluation versus learner-centered models' emphasis on ongoing, personalized feedback and skill development.
Flexibility and Adaptability of the Curriculum
Curriculum-centered education emphasizes a fixed syllabus with predetermined content and sequencing, limiting flexibility in addressing diverse learner needs. Learner-centered approaches prioritize adaptability, allowing curriculum customization based on students' interests, abilities, and learning paces to enhance engagement and outcomes. Flexible curricula support differentiated instruction and continuous adjustments, fostering personalized learning experiences aligned with individual growth trajectories.
Impact on Learning Outcomes
Curriculum-centered approaches emphasize structured content delivery, often leading to consistent but rigid learning outcomes focused on knowledge acquisition. Learner-centered methods prioritize individual student needs and active engagement, resulting in improved critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and higher retention rates. Research indicates learner-centered environments foster greater motivation and adaptability, positively impacting overall academic achievement and lifelong learning capabilities.
Challenges and Limitations
Curriculum-centered approaches often face challenges such as rigid structure, limited adaptability to individual learner needs, and potential disengagement due to standardized content delivery. Learner-centered methods encounter limitations including increased demand on instructor flexibility, variable learning paces complicating progress tracking, and resource intensiveness for personalized support. Balancing curriculum goals with learner autonomy remains a critical challenge in optimizing educational outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Curriculum-centered approaches emphasize structured content delivery, ensuring consistency and alignment with educational standards, which benefits learners needing clear guidance and measurable outcomes. Learner-centered strategies prioritize individual needs, preferences, and active engagement, fostering critical thinking and personalized growth ideal for diverse learners with varied backgrounds. Selecting the right approach involves assessing learner profiles, educational goals, and context to balance curriculum requirements with adaptability for inclusive, effective learning experiences.
Curriculum-Centered Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com