Experiential learning immerses you in real-world challenges, fostering deeper understanding through active participation rather than passive absorption. Engaging directly with tasks enhances critical thinking, adaptability, and retention of knowledge. Discover how embracing experiential learning can transform your education by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
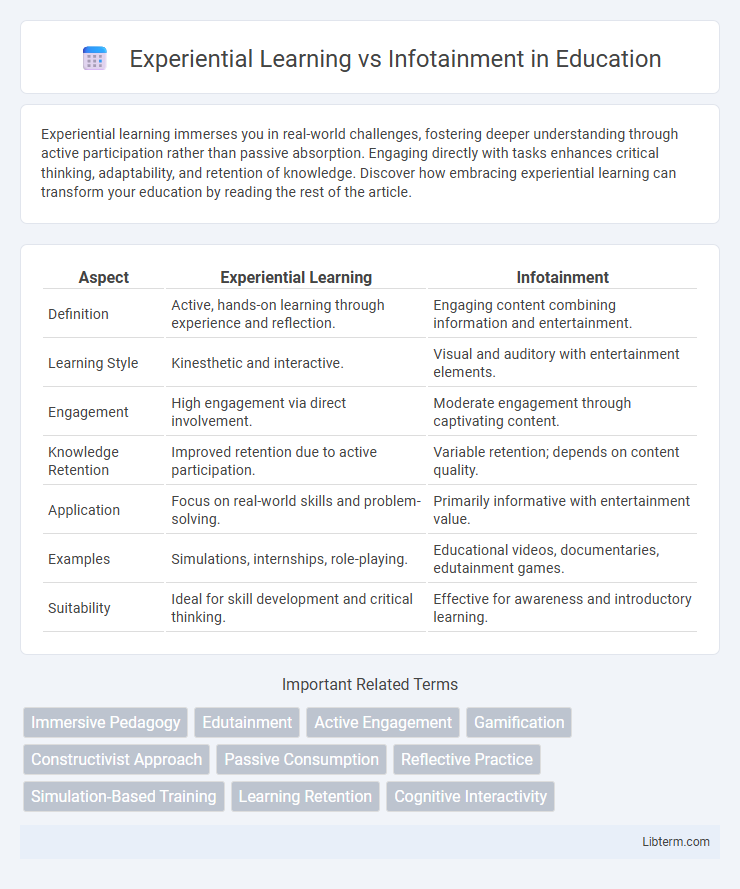
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Infotainment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active, hands-on learning through experience and reflection. | Engaging content combining information and entertainment. |
| Learning Style | Kinesthetic and interactive. | Visual and auditory with entertainment elements. |
| Engagement | High engagement via direct involvement. | Moderate engagement through captivating content. |
| Knowledge Retention | Improved retention due to active participation. | Variable retention; depends on content quality. |
| Application | Focus on real-world skills and problem-solving. | Primarily informative with entertainment value. |
| Examples | Simulations, internships, role-playing. | Educational videos, documentaries, edutainment games. |
| Suitability | Ideal for skill development and critical thinking. | Effective for awareness and introductory learning. |
Understanding Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes active participation and real-world experience, allowing learners to construct knowledge through direct engagement and reflection, which results in deeper understanding and retention. This approach contrasts with infotainment, which focuses on entertaining content delivery that may prioritize engagement over meaningful learning outcomes. Effective experiential learning leverages hands-on activities, immediate feedback, and contextual problem-solving to promote critical thinking and skill development.
Defining Infotainment
Infotainment blends information and entertainment to engage audiences while delivering educational content, often through multimedia formats like videos, games, or interactive presentations. This approach prioritizes audience engagement and enjoyment, making learning more accessible but sometimes less deep than experiential learning, which emphasizes hands-on, practical experiences. Infotainment is effective for introducing concepts and maintaining attention but may lack the immersive, skill-building elements essential to experiential learning.
Key Differences Between Experiential Learning and Infotainment
Experiential learning emphasizes active participation and real-world experiences to foster deep understanding and skill development, whereas infotainment combines informative content with entertainment to engage audiences without necessarily promoting hands-on involvement. The key difference lies in the learning outcome, as experiential learning aims for practical knowledge application, while infotainment prioritizes audience engagement and enjoyment. Experiential learning strategies involve immersive activities, simulations, and reflection, contrasting with infotainment's focus on captivating visuals, storytelling, and simplified information delivery.
Cognitive Impact: Deep Learning vs Passive Consumption
Experiential learning fosters deep cognitive engagement by involving learners in active problem-solving and critical thinking, which enhances retention and understanding of complex concepts. Infotainment primarily promotes passive consumption, leading to superficial processing and limited long-term knowledge retention. Studies show active learning methods significantly improve cognitive skills compared to infotainment-based approaches, emphasizing the value of immersive experiences in education.
Role of Engagement in Learning Outcomes
Experiential learning enhances retention and understanding by immersing learners in active, hands-on experiences that foster deeper cognitive engagement. Infotainment captures attention through entertaining and informative content but may prioritize short-term interest over sustained learning outcomes. Engagement in experiential learning drives meaningful skill acquisition and critical thinking, whereas infotainment often focuses on passive consumption with limited impact on long-term knowledge retention.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies and Examples
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on engagement with real-world scenarios, utilizing case studies such as medical simulations or business internships to deepen practical understanding and skill acquisition. Infotainment combines entertainment and information delivery, often through interactive multimedia or gamified content, enhancing learner motivation but occasionally sacrificing depth of application. Case studies like NASA's virtual reality training programs illustrate the intersection, demonstrating how immersive infotainment tools can support experiential learning by providing realistic, impactful experiences.
Long-Term Retention and Transferability
Experiential learning enhances long-term retention by engaging learners in active, hands-on activities that reinforce understanding through real-world application, fostering deeper cognitive connections. Infotainment often leads to short-term engagement but may result in superficial knowledge, limiting transferability to practical contexts. Emphasizing experiential methods promotes durable memory and adaptable skills essential for effective knowledge transfer across varied situations.
Challenges in Embracing Experiential Learning
Experiential learning faces challenges such as high resource demands, including time, skilled facilitators, and appropriate environments, which many organizations find difficult to provide consistently. Adapting experiential learning to diverse learner needs and measuring its impact compared to infotainment's immediate engagement can complicate implementation. Resistance to change from traditional infotainment methods also hampers acceptance, limiting the potential benefits of immersive, hands-on educational experiences.
When Is Infotainment Useful in Education?
Infotainment is useful in education when engaging students with complex or unfamiliar topics that benefit from a captivating, multimedia approach. It enhances retention by combining information with entertainment elements such as videos, animations, and storytelling, making learning more accessible and enjoyable. This method is particularly effective for introducing foundational concepts and sparking curiosity, before deeper, hands-on experiential learning takes place.
Choosing the Right Approach for Lasting Impact
Experiential learning fosters deeper retention by engaging learners in hands-on activities, promoting active problem-solving and real-world application of knowledge. Infotainment combines information with entertainment to capture attention but often lacks long-term cognitive impact due to its passive consumption. Selecting experiential learning enhances lasting impact by transforming theoretical concepts into meaningful experiences, making it the preferred approach for durable skill development and behavioral change.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com