A positive school climate fosters student engagement, promotes safety, and supports academic achievement by creating a respectful and inclusive environment. Effective communication among staff, students, and families plays a crucial role in shaping a nurturing atmosphere where everyone feels valued. Discover how improving your school climate can transform learning experiences throughout the entire article.
Table of Comparison
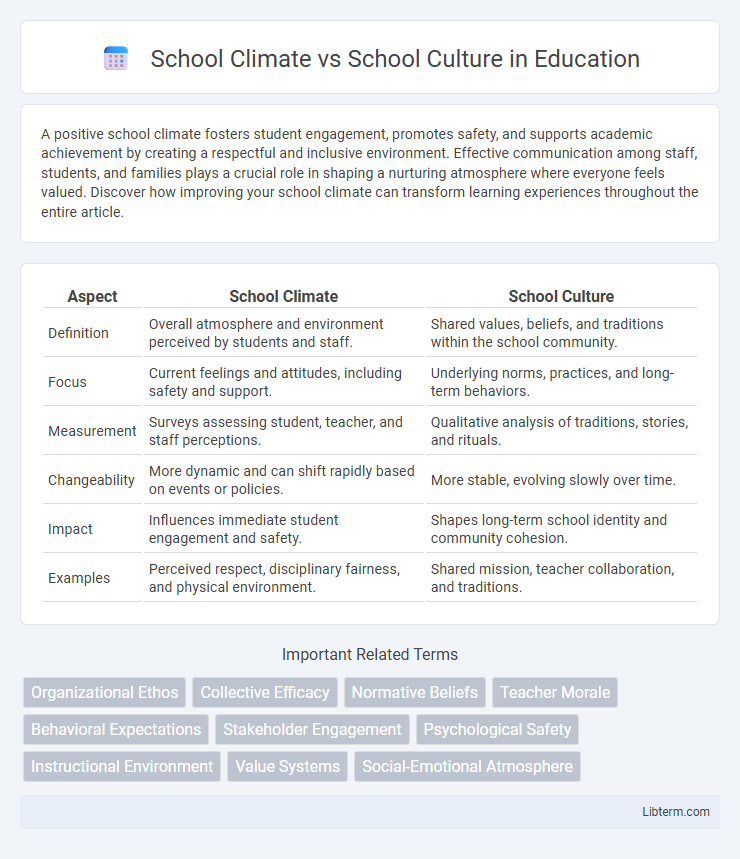
| Aspect | School Climate | School Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overall atmosphere and environment perceived by students and staff. | Shared values, beliefs, and traditions within the school community. |
| Focus | Current feelings and attitudes, including safety and support. | Underlying norms, practices, and long-term behaviors. |
| Measurement | Surveys assessing student, teacher, and staff perceptions. | Qualitative analysis of traditions, stories, and rituals. |
| Changeability | More dynamic and can shift rapidly based on events or policies. | More stable, evolving slowly over time. |
| Impact | Influences immediate student engagement and safety. | Shapes long-term school identity and community cohesion. |
| Examples | Perceived respect, disciplinary fairness, and physical environment. | Shared mission, teacher collaboration, and traditions. |
Defining School Climate
School climate refers to the collective perceptions of students, staff, and parents regarding the safety, relationships, and learning environment within a school. It encompasses factors such as discipline practices, teacher support, and the overall emotional and physical atmosphere that influences student engagement and academic success. A positive school climate promotes respect, inclusivity, and a sense of belonging, directly impacting student motivation and well-being.
Understanding School Culture
School culture embodies the shared beliefs, values, norms, and practices that shape the social and emotional environment of a school community. Understanding school culture involves recognizing its deep-rooted influences on student behavior, teacher collaboration, and overall school identity. A positive school culture fosters trust, inclusivity, and a sense of belonging among students and staff, which directly impacts academic achievement and school improvement efforts.
Key Differences Between School Climate and School Culture
School climate refers to the overall atmosphere and experience within a school, shaped by student, teacher, and staff perceptions of safety, relationships, and support, while school culture encompasses the shared beliefs, values, traditions, and norms that influence behavior and attitudes over time. Key differences include that climate is more about the present environment and how stakeholders feel day-to-day, whereas culture reflects deeper, long-term patterns and collective identity. Measuring climate often involves surveys assessing current perceptions, whereas culture is understood through qualitative analysis of rituals, stories, and institutional practices.
Factors Influencing School Climate
School climate is shaped by factors such as safety, teacher-student relationships, and the overall learning environment, influencing how students and staff perceive their school experience. Elements including school leadership, peer interactions, and classroom management significantly impact the emotional and social atmosphere. Positive school climate fosters engagement, academic success, and well-being by promoting respect, inclusivity, and clear expectations.
Elements Shaping School Culture
Elements shaping school culture include shared values, beliefs, and norms that influence the behavior and attitudes of students, teachers, and staff within the educational environment. Leadership style, traditions, communication patterns, and the school's mission also play crucial roles in defining the overall culture. These components collectively impact the sense of community, trust, and collaboration, distinguishing school culture from the more immediate perceptions addressed by school climate.
Measuring School Climate and Culture
Measuring school climate involves quantifying students' and staff's perceptions of safety, relationships, and instructional support through surveys and observational data. School culture is assessed by evaluating shared values, beliefs, traditions, and behavioral norms using ethnographic methods, focus groups, and qualitative interviews. Combining quantitative climate data with qualitative cultural insights provides a comprehensive understanding of the overall school environment.
Impact of Climate and Culture on Student Outcomes
School climate, characterized by the quality of relationships, safety, and support within a school, directly influences student engagement, academic performance, and mental health. In contrast, school culture, defined by shared beliefs, values, and norms, shapes students' sense of belonging and motivation, fostering long-term educational success. Both positive climate and strong culture collaboratively enhance student outcomes by creating an environment conducive to learning and personal growth.
Strategies to Improve School Climate
Improving school climate requires targeted strategies such as fostering positive relationships among students and staff, implementing consistent disciplinary policies, and promoting a safe, inclusive environment through anti-bullying programs. Schools benefit from engaging families and community members in collaboration efforts, increasing student voice in decision-making processes, and providing professional development on social-emotional learning for educators. Data-driven approaches, including climate surveys and regular feedback loops, enable schools to monitor progress and tailor interventions effectively to enhance overall school climate.
Building a Positive School Culture
Building a positive school culture involves fostering shared values, beliefs, and practices that promote respect, collaboration, and a sense of belonging among students and staff. Unlike school climate, which reflects the current atmosphere or mood perceived by the school community, school culture represents the deeper, enduring foundation influencing behaviors and attitudes. Effective strategies include promoting inclusive leadership, encouraging open communication, and implementing consistent support systems to sustain a nurturing and motivated learning environment.
Integrating Climate and Culture for School Success
Integrating school climate and school culture enhances student achievement and staff collaboration by aligning shared values with a supportive environment. A positive school climate fosters safety and engagement, while a strong culture builds trust and collective responsibility among educators and learners. Combining these elements creates a cohesive framework that drives academic success and long-term school improvement.
School Climate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com