The International Baccalaureate (IB) offers a rigorous, internationally recognized curriculum designed to develop critical thinking, intercultural understanding, and independent research skills. It prepares students for success in higher education and global careers by fostering intellectual, personal, and emotional growth. Explore this article to discover how the IB program can elevate your academic journey and future opportunities.
Table of Comparison
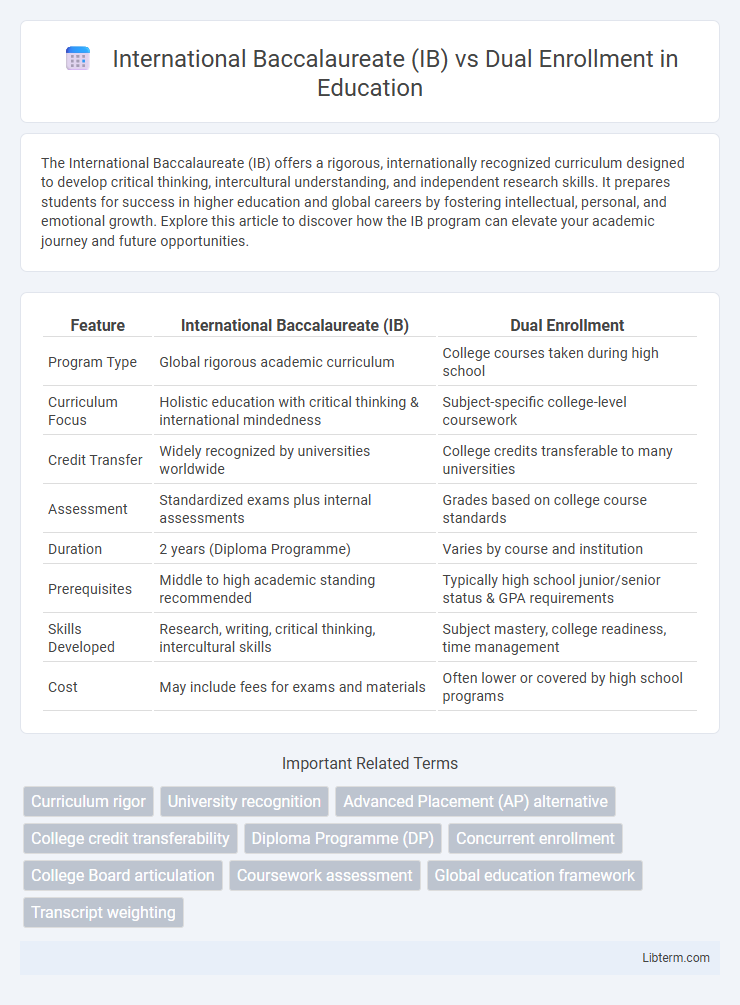
| Feature | International Baccalaureate (IB) | Dual Enrollment |
|---|---|---|
| Program Type | Global rigorous academic curriculum | College courses taken during high school |
| Curriculum Focus | Holistic education with critical thinking & international mindedness | Subject-specific college-level coursework |
| Credit Transfer | Widely recognized by universities worldwide | College credits transferable to many universities |
| Assessment | Standardized exams plus internal assessments | Grades based on college course standards |
| Duration | 2 years (Diploma Programme) | Varies by course and institution |
| Prerequisites | Middle to high academic standing recommended | Typically high school junior/senior status & GPA requirements |
| Skills Developed | Research, writing, critical thinking, intercultural skills | Subject mastery, college readiness, time management |
| Cost | May include fees for exams and materials | Often lower or covered by high school programs |
Overview of International Baccalaureate (IB) and Dual Enrollment
The International Baccalaureate (IB) is a globally recognized educational program emphasizing critical thinking, intercultural understanding, and rigorous academic standards across six subject groups. Dual Enrollment allows high school students to take college-level courses for credit, providing a flexible pathway to earn both high school and college credits simultaneously. Both programs aim to enhance college readiness but differ in structure, with IB offering a holistic curriculum and Dual Enrollment focusing on college coursework integration.
Key Differences Between IB and Dual Enrollment
International Baccalaureate (IB) offers a globally recognized curriculum emphasizing critical thinking, research skills, and a holistic education, while Dual Enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits by taking courses directly from a partnering college or university. IB programs require completion of core components such as Theory of Knowledge, Extended Essay, and CAS (Creativity, Activity, Service), contrasting with Dual Enrollment's focus on college-level coursework without a standardized curriculum. IB diploma provides worldwide college recognition, whereas Dual Enrollment credits depend on the transfer policies of individual institutions.
Curriculum Structure and Academic Rigor
The International Baccalaureate (IB) program features a globally standardized curriculum emphasizing critical thinking, interdisciplinary learning, and a core comprising Theory of Knowledge, Extended Essay, and Creativity, Activity, Service components, demanding comprehensive academic rigor. Dual Enrollment allows high school students to take college-level courses at local higher education institutions, providing specialized, credit-earning coursework tailored to individual academic or career goals, with variable rigor depending on the college and subject. IB's holistic and integrated approach contrasts with Dual Enrollment's flexibility and course-level specificity, offering distinct paths to academic advancement and college preparation.
College Credit and University Recognition
International Baccalaureate (IB) offers college credit through higher-level (HL) exam scores, recognized by many universities worldwide for advanced placement and course waivers. Dual Enrollment provides direct college credit by completing actual college courses in high school, with credits typically accepted by the institution granting them and often transferable to other universities. University recognition varies, as IB credits depend on exam scores and school policies, while Dual Enrollment credits depend on articulation agreements between colleges and universities.
Program Accessibility and Eligibility Requirements
International Baccalaureate (IB) programs typically require students to attend schools authorized by the IB Organization and meet specific academic standards for enrollment, which can limit accessibility based on geographic location and school availability. Dual enrollment programs are generally more accessible, allowing high school students to take college-level courses at local colleges or through online institutions, with eligibility often based on minimum GPA and standardized test scores. Eligibility for IB focuses on rigorous academic readiness and school selection, while dual enrollment prioritizes meeting college course prerequisites and maintaining academic performance.
Impact on College Admissions
International Baccalaureate (IB) programs showcase a rigorous, globally recognized curriculum that often strengthens college applications by demonstrating a student's ability to handle challenging academic work. Dual Enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits through accredited institutions, providing tangible evidence of college-level achievement and readiness. Both approaches can positively impact college admissions, but IB's holistic emphasis on critical thinking and global perspectives may appeal more to highly selective universities.
Student Experience and Workload
The International Baccalaureate (IB) program offers a rigorous curriculum with a global perspective, requiring students to complete extended essays, Theory of Knowledge courses, and Creativity, Activity, Service projects, which intensifies the academic workload and fosters critical thinking. Dual Enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits through enrolling in local college courses, providing flexibility and exposure to college-level coursework but demands strong time-management skills to balance both high school and college responsibilities. Student experience in IB is structured with a cohort-based environment and extensive teacher support, whereas Dual Enrollment offers more independence, often requiring self-motivation and proactive communication with college instructors.
Cost and Financial Considerations
International Baccalaureate (IB) programs typically involve exam fees ranging from $119 to $151 per subject, with additional costs for course materials and potential school fees, making the overall expense moderate but consistent annually. Dual Enrollment often offers a more cost-effective option by allowing high school students to earn college credits at reduced tuition rates or even free through partnerships with local colleges, significantly lowering post-secondary education expenses. Families should evaluate long-term savings and financial aid eligibility, as Dual Enrollment can reduce the total cost of college by shortening degree timelines, while IB's fees are generally limited to the high school years.
Pros and Cons of IB vs Dual Enrollment
International Baccalaureate (IB) offers a rigorous, globally recognized curriculum that develops critical thinking and research skills, but it demands a significant time commitment and can be challenging to balance with other activities. Dual Enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits early, reducing future tuition costs and easing the transition to higher education, yet course availability depends on local college partnerships and may lack the holistic approach of IB. IB's emphasis on international-mindedness contrasts with Dual Enrollment's focus on college credit accumulation, making each option suitable for different academic goals and learning styles.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right path between International Baccalaureate (IB) and Dual Enrollment depends on academic goals, learning style, and college credit preferences. IB offers a rigorous, globally recognized curriculum emphasizing critical thinking and holistic education, while Dual Enrollment provides direct college credit through local colleges, often with more flexible course selection. Factors such as college acceptance policies, program availability, and workload balance should guide the decision for maximizing future academic and career opportunities.
International Baccalaureate (IB) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com