A self-contained classroom is designed to provide specialized instruction to students with diverse learning needs within a structured environment. These classrooms offer tailored support, individualized teaching strategies, and focused resources to help students thrive academically and socially. Explore this article to learn how a self-contained classroom can benefit Your child's educational journey.
Table of Comparison
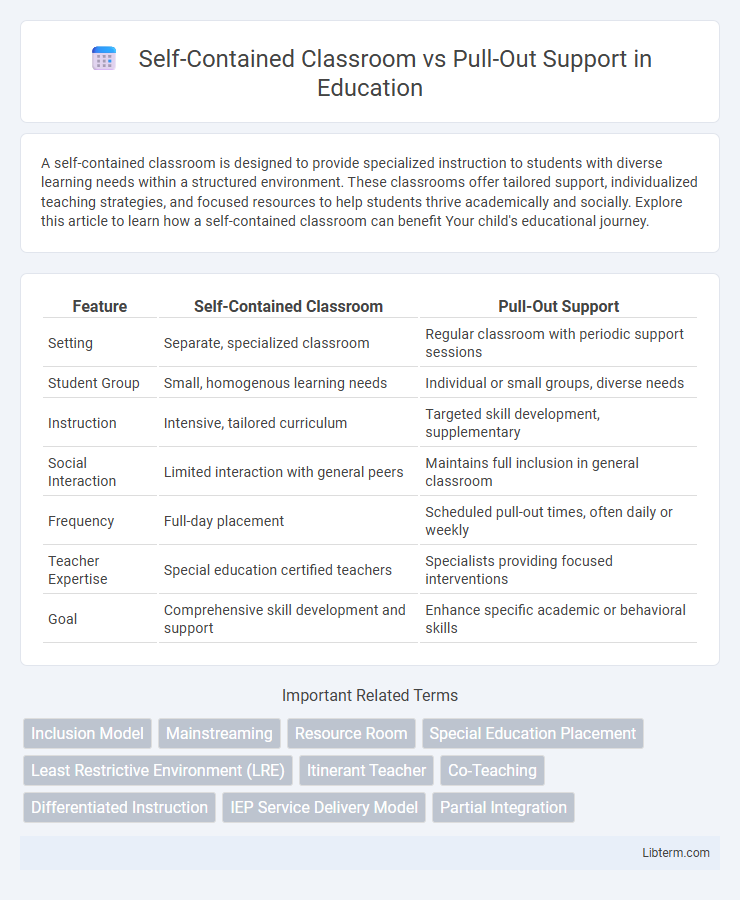
| Feature | Self-Contained Classroom | Pull-Out Support |
|---|---|---|
| Setting | Separate, specialized classroom | Regular classroom with periodic support sessions |
| Student Group | Small, homogenous learning needs | Individual or small groups, diverse needs |
| Instruction | Intensive, tailored curriculum | Targeted skill development, supplementary |
| Social Interaction | Limited interaction with general peers | Maintains full inclusion in general classroom |
| Frequency | Full-day placement | Scheduled pull-out times, often daily or weekly |
| Teacher Expertise | Special education certified teachers | Specialists providing focused interventions |
| Goal | Comprehensive skill development and support | Enhance specific academic or behavioral skills |
Introduction to Self-Contained Classrooms and Pull-Out Support
Self-contained classrooms provide students with specialized instruction within a dedicated classroom setting, focusing on individualized support for those with significant learning or behavioral needs. Pull-out support involves temporarily removing students from general education classrooms to receive targeted interventions or therapies, allowing integration with peers for most of the day. Both approaches aim to tailor educational experiences to meet diverse student needs while balancing inclusion and specialized assistance.
Defining Self-Contained Classrooms
Self-contained classrooms are specialized educational settings where students with similar learning needs receive instruction exclusively within one room, promoting tailored teaching methods and consistent support. These classrooms typically serve students with moderate to severe disabilities, offering a structured environment with a low student-to-teacher ratio to enhance individual learning. The focused approach contrasts with pull-out support, which involves periodic removal from general education classes for specific interventions.
Understanding Pull-Out Support Programs
Pull-out support programs provide targeted instruction by temporarily removing students from their general education classrooms to focus on specific skills or interventions. These programs are designed to offer specialized assistance in areas such as reading, math, or language development, tailored to individual student needs. Pull-out support allows for personalized attention while enabling students to reintegrate into the general classroom for the majority of their day.
Key Differences Between Self-Contained and Pull-Out Models
Self-contained classrooms provide specialized instruction within a dedicated classroom where students with similar learning needs remain for the majority of the school day, fostering a consistent, controlled environment. Pull-out support involves temporarily removing students from general education classrooms to receive targeted interventions, allowing them to participate in mainstream academic and social settings for most of the day. Key differences include the degree of inclusion, with self-contained models offering intensive, continuous support versus pull-out models emphasizing integration and short-term, focused assistance.
Benefits of Self-Contained Classrooms
Self-contained classrooms provide a structured environment tailored to students with significant learning differences, offering individualized instruction and consistent routines that enhance focus and academic progress. These settings enable specialized teachers to deliver targeted interventions, fostering social skills and independence within a controlled group. Research shows improved behavioral outcomes and academic gains in self-contained settings due to smaller class sizes and concentrated support designed to meet diverse educational needs.
Advantages of Pull-Out Support
Pull-out support offers personalized instruction tailored to students' specific needs, facilitating targeted skill development in a less restrictive environment. This approach enables students to engage with the general education curriculum and peers while receiving specialized attention from experts. Enhanced flexibility and individualized pacing in pull-out settings contribute to improved academic outcomes and social integration.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Self-contained classrooms often face challenges related to social isolation and limited exposure to typically developing peers, which can hinder social skill development and inclusion. Pull-out support presents limitations such as fragmented learning experiences and potential stigma, as students frequently transition between general and special education settings. Both approaches require careful coordination and individualized planning to address diverse learner needs without compromising academic progress or emotional well-being.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Model
When selecting between self-contained classrooms and pull-out support, factors such as the student's individual learning needs, social integration goals, and intensity of required support are critical. Academic progress should be weighed against opportunities for peer interaction and inclusion in the general education environment. Additionally, considerations include available resources, teacher expertise, and the student's behavioral and emotional profile to determine the most effective setting.
Impact on Student Academic and Social Outcomes
Self-contained classrooms provide consistent instructional support within a stable environment, often leading to improved academic gains for students with moderate to severe disabilities by allowing tailored, individualized teaching. Pull-out support facilitates specialized interventions while enabling students to participate in general education settings, promoting social integration and peer interaction essential for developing social skills and adaptive behaviors. Research indicates that combining both approaches optimizes academic achievement and social competency, balancing individualized instruction with opportunities for inclusive experiences.
Best Practices for Supporting Diverse Learners
Implementing best practices for supporting diverse learners involves tailoring instruction within Self-Contained Classrooms to provide individualized, intensive support while fostering social-emotional growth through consistent routines and small class sizes. Pull-Out Support models complement inclusion settings by offering targeted skill-building sessions that address specific academic or behavioral needs without isolating students from their general education peers. Effective collaboration between special educators and general teachers, alongside ongoing progress monitoring, ensures seamless transitions and maximizes student engagement and achievement.
Self-Contained Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com