Technical expertise is essential for mastering complex systems and solving intricate problems efficiently. By developing a strong foundation in relevant tools and methodologies, you can enhance your capacity to innovate and improve performance. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of technical skills and their practical applications.
Table of Comparison
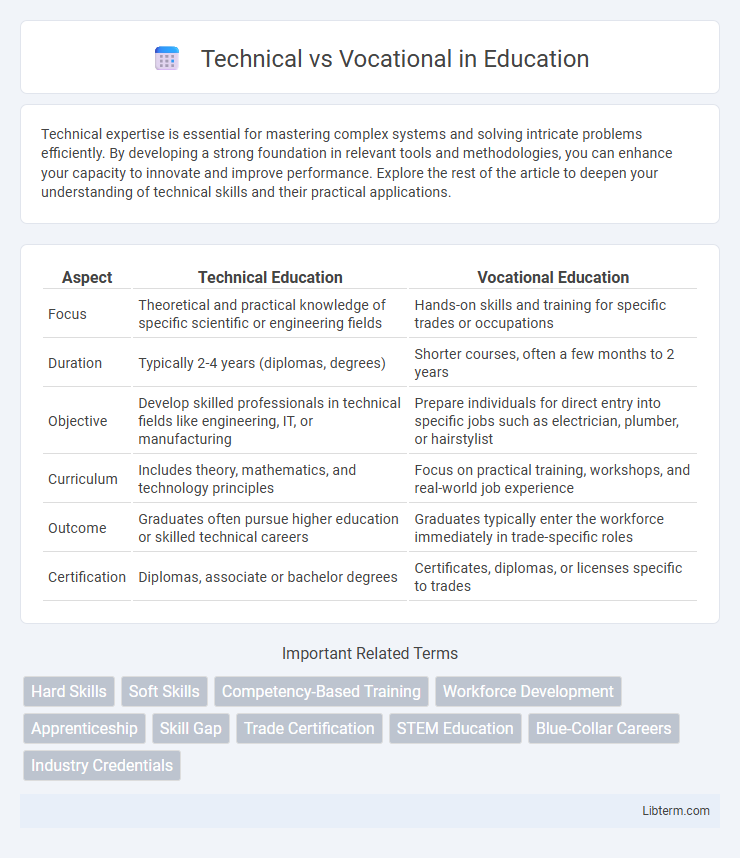
| Aspect | Technical Education | Vocational Education |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Theoretical and practical knowledge of specific scientific or engineering fields | Hands-on skills and training for specific trades or occupations |
| Duration | Typically 2-4 years (diplomas, degrees) | Shorter courses, often a few months to 2 years |
| Objective | Develop skilled professionals in technical fields like engineering, IT, or manufacturing | Prepare individuals for direct entry into specific jobs such as electrician, plumber, or hairstylist |
| Curriculum | Includes theory, mathematics, and technology principles | Focus on practical training, workshops, and real-world job experience |
| Outcome | Graduates often pursue higher education or skilled technical careers | Graduates typically enter the workforce immediately in trade-specific roles |
| Certification | Diplomas, associate or bachelor degrees | Certificates, diplomas, or licenses specific to trades |
Understanding Technical Education
Technical education emphasizes practical skills and theoretical knowledge in fields such as engineering, IT, and applied sciences, preparing students for specialized careers requiring problem-solving and technical proficiency. Vocational education focuses on hands-on training in trades like carpentry, plumbing, and cosmetology, aiming to equip learners with immediate, job-ready competencies. Understanding technical education involves recognizing its role in bridging academic concepts with real-world applications to enhance workforce readiness.
Defining Vocational Education
Vocational education emphasizes practical skills and hands-on training tailored to specific trades or occupations, preparing learners for direct entry into the workforce. Unlike broader technical education, which may incorporate theoretical knowledge and advanced technologies, vocational programs focus on job-ready competencies in fields such as carpentry, automotive repair, or culinary arts. These programs often include apprenticeships or work-based learning experiences to ensure proficiency and industry readiness.
Historical Development: Technical vs Vocational
The historical development of technical education traces back to the Industrial Revolution, where formal institutions emerged to meet the growing demand for skilled engineers and technicians in manufacturing and infrastructure. Vocational education, on the other hand, originated from apprenticeship traditions and trade guilds, evolving to provide practical, hands-on training for specific occupations such as carpentry, plumbing, and electrical work. Over time, both systems have integrated elements of each other, but technical education emphasizes theoretical knowledge and technological proficiency, while vocational education prioritizes skill acquisition and direct workplace readiness.
Curriculum Differences
Technical education curriculum emphasizes theoretical knowledge and principles in fields like engineering, computer science, and applied mathematics, preparing students for roles requiring strong analytical skills. Vocational education curriculum centers on hands-on training and practical skills in trades such as carpentry, plumbing, and cosmetology, aimed at immediate job readiness. While technical programs often include laboratory work and advanced concepts, vocational programs prioritize experiential learning and skill mastery for specific occupations.
Skill Sets Acquired
Technical education primarily develops analytical and problem-solving skills through theoretical knowledge in fields like engineering, IT, and sciences, enabling learners to design, analyze, and innovate. Vocational education emphasizes practical, hands-on skills tailored to specific trades such as carpentry, plumbing, or culinary arts, equipping students with job-ready abilities for immediate employment. Both pathways foster specialized competencies but differ in depth of theoretical grounding versus applied expertise.
Career Opportunities and Pathways
Technical education emphasizes specialized knowledge and skills in fields such as engineering, IT, and healthcare, leading to careers that often require strong analytical and problem-solving abilities. Vocational training focuses on hands-on experience in trades like carpentry, plumbing, and automotive repair, offering direct pathways to skilled labor positions with high demand. Both pathways provide valuable career opportunities, with technical education typically facilitating advancement in professional and technological sectors, while vocational training supports rapid entry into practical, essential jobs.
Industry Relevance and Demand
Technical education emphasizes theoretical knowledge and engineering principles, equipping students for careers in fields like IT, manufacturing, and telecommunications with a foundation in problem-solving and innovation. Vocational training focuses on practical skills tailored to specific trades such as plumbing, welding, or automotive repair, aligning closely with immediate labor market demands and hands-on job requirements. Industry relevance and demand drive vocational programs to rapidly adapt curricula to evolving technologies, while technical programs often prepare students for long-term professional growth and specialized roles within engineering and technology sectors.
Duration and Learning Methods
Technical education programs typically last from six months to two years, emphasizing theoretical knowledge alongside practical applications through classroom instruction and laboratory work. Vocational training usually spans a shorter period, ranging from a few weeks to a year, focusing primarily on hands-on experience and skill development in real-world work environments or apprenticeships. Both learning methods cater to specific career goals, with technical courses offering in-depth understanding while vocational programs prioritize immediate job readiness through experiential learning.
Accreditation and Certification
Technical education emphasizes theoretical knowledge and is often accredited by national education bodies ensuring academic standards, while vocational training focuses on practical skills and is certified by industry-specific organizations validating job readiness. Accreditation in technical programs often leads to recognized degrees or diplomas, whereas vocational certifications provide competency-based credentials tailored to specific trades. Both accreditation and certification serve as quality assurance mechanisms but differ in scope and application depending on the educational or professional context.
Choosing the Right Path: Key Considerations
Choosing the right path between technical and vocational education depends on career goals, skill acquisition, and industry demand. Technical education emphasizes theoretical knowledge and advanced technical skills for engineering, IT, or scientific fields, while vocational training focuses on hands-on experience and practical skills for trades like plumbing, carpentry, or cosmetology. Evaluating job market trends, personal interests, and long-term career growth are essential in making an informed decision.
Technical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com