Mastering instructional techniques enhances your ability to convey information clearly and effectively, ensuring learners grasp complex concepts with ease. Utilizing active learning strategies, clear objectives, and timely feedback fosters engagement and retention. Dive into the article to explore practical tips that will transform your instructional approach.
Table of Comparison
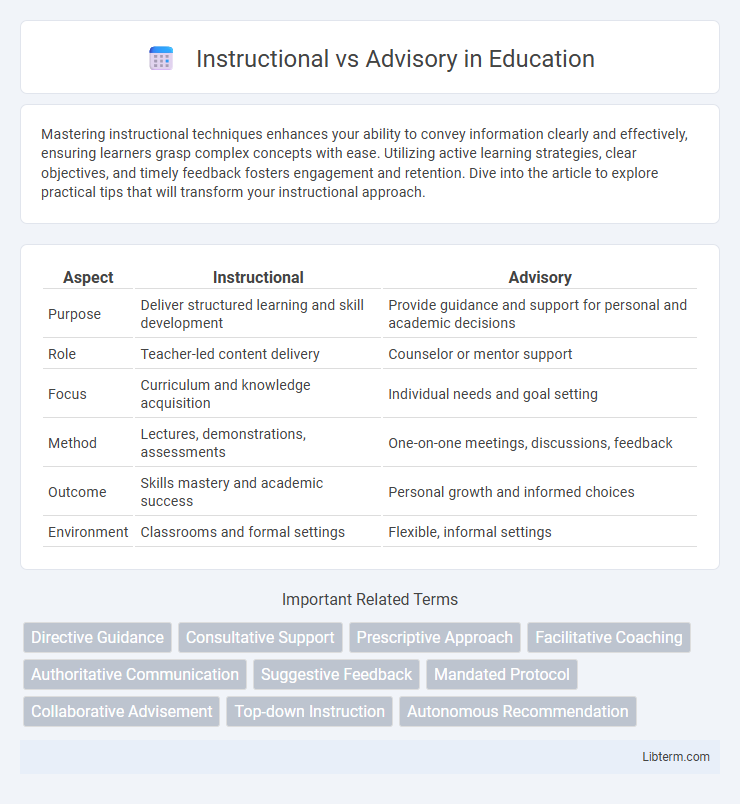
| Aspect | Instructional | Advisory |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Deliver structured learning and skill development | Provide guidance and support for personal and academic decisions |
| Role | Teacher-led content delivery | Counselor or mentor support |
| Focus | Curriculum and knowledge acquisition | Individual needs and goal setting |
| Method | Lectures, demonstrations, assessments | One-on-one meetings, discussions, feedback |
| Outcome | Skills mastery and academic success | Personal growth and informed choices |
| Environment | Classrooms and formal settings | Flexible, informal settings |
Understanding Instructional vs Advisory Approaches
Instructional approaches emphasize direct teaching methods with structured content delivery to enhance learning outcomes, focusing on knowledge transfer and skill development. Advisory approaches prioritize guidance, feedback, and personalized support, aiming to empower learners through collaborative problem-solving and decision-making. Understanding these distinctions helps educators tailor interventions that balance authoritative instruction with learner autonomy for optimal engagement and growth.
Definition of Instructional Strategies
Instructional strategies refer to structured methods and techniques employed by educators to facilitate learning and improve student comprehension, engagement, and retention. These strategies encompass a variety of approaches like direct instruction, cooperative learning, inquiry-based learning, and differentiated instruction tailored to meet diverse learner needs. Advisory strategies, in contrast, primarily focus on guidance, mentorship, and support rather than direct teaching methods.
What Constitutes Advisory Methods
Advisory methods involve providing expert guidance, recommendations, and personalized feedback to support decision-making and problem-solving processes. These methods prioritize collaborative dialogue, empowering individuals or organizations to explore options and develop tailored strategies based on situational analysis. Unlike instructional approaches, advisory techniques emphasize facilitation and consultation rather than direct teaching or prescriptive directives.
Key Differences Between Instructional and Advisory
Instructional roles focus on delivering structured content and facilitating learning through planned lessons and assessments, aiming to develop specific skills or knowledge. Advisory roles emphasize providing guidance, support, and personalized feedback to help individuals make informed decisions or improve performance without direct teaching. Key differences include the instructional role's directive approach versus the advisory role's collaborative and consultative nature.
Benefits of Instructional Techniques
Instructional techniques enhance learning by providing clear, structured guidance that improves knowledge retention and skill acquisition. These methods facilitate active engagement and personalized feedback, leading to higher learner motivation and better performance outcomes. Emphasizing practical application, instructional approaches help bridge the gap between theory and real-world practice more effectively than advisory methods.
Advantages of Advisory Practices
Advisory practices emphasize personalized guidance that adapts to individual needs and promotes critical thinking, fostering long-term skill development. These practices create collaborative environments encouraging active learner engagement and proactive problem-solving. By prioritizing tailored feedback and mentorship, advisory methods enhance motivation and improve overall learning outcomes.
When to Use Instructional vs Advisory
Instructional communication is best used when there is a clear need to guide actions or provide step-by-step directions to achieve specific outcomes, such as in training or technical support contexts. Advisory communication suits situations requiring expert recommendations or opinion sharing without enforcing compliance, commonly applied in consulting or strategic planning fields. Recognizing the goal--whether to direct behavior or offer guidance--determines the choice between instructional and advisory approaches.
Impact on Learner Outcomes
Instructional approaches provide structured content delivery and clear objectives, leading to measurable improvements in learner knowledge retention and skill acquisition. Advisory methods foster personalized guidance and critical thinking, enhancing learner motivation and self-directed problem-solving abilities. Combining both strategies can maximize learner engagement and long-term outcomes by balancing knowledge transfer with adaptive support.
Real-World Examples of Instructional and Advisory Roles
Instructional roles, such as classroom teachers and corporate trainers, involve directly imparting knowledge and skills to learners through structured lessons or training sessions. Advisory roles, exemplified by financial advisors or career counselors, focus on providing expert guidance and personalized recommendations to help individuals make informed decisions. Real-world examples include a math teacher designing curriculum to improve student understanding and a business consultant advising executives on strategic planning.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Instructional approaches deliver structured guidance and clear directives, ideal for learners needing step-by-step support and concrete goals. Advisory methods emphasize collaborative dialogue and expert recommendations, best suited for individuals seeking flexibility and personalized insights. Assess your specific learning objectives, the complexity of the task, and preferred engagement style to determine whether instructional or advisory strategies will maximize effectiveness and outcomes.
Instructional Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com