Mastering social skills enhances your ability to communicate effectively, build meaningful relationships, and navigate diverse social situations with confidence. These essential skills include active listening, empathy, and clear verbal expression, which collectively improve personal and professional interactions. Explore the rest of this article to uncover practical tips and strategies to refine your social skills.
Table of Comparison
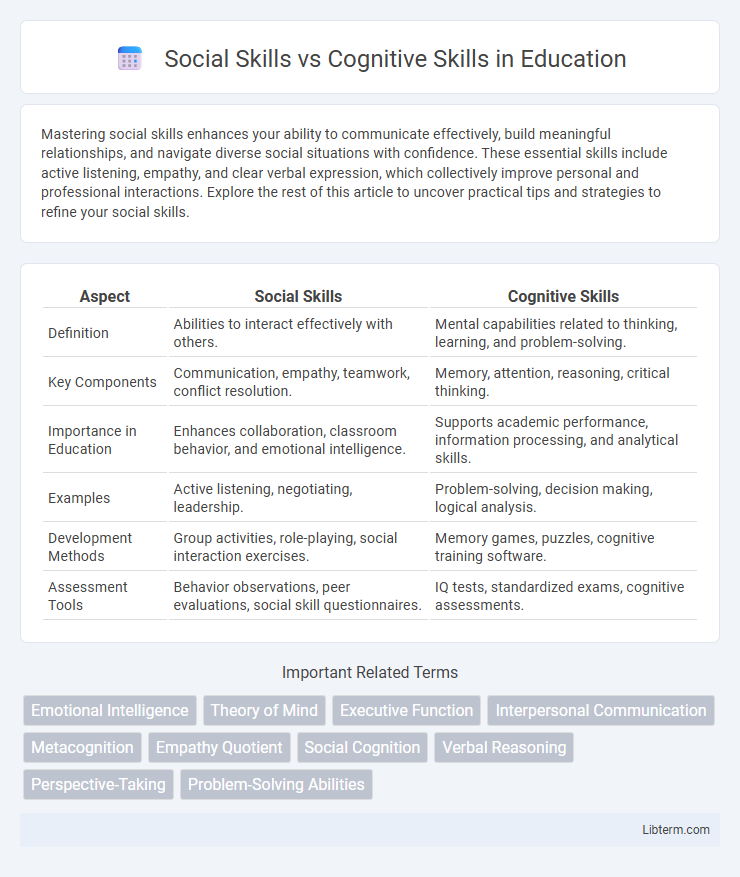
| Aspect | Social Skills | Cognitive Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Abilities to interact effectively with others. | Mental capabilities related to thinking, learning, and problem-solving. |
| Key Components | Communication, empathy, teamwork, conflict resolution. | Memory, attention, reasoning, critical thinking. |
| Importance in Education | Enhances collaboration, classroom behavior, and emotional intelligence. | Supports academic performance, information processing, and analytical skills. |
| Examples | Active listening, negotiating, leadership. | Problem-solving, decision making, logical analysis. |
| Development Methods | Group activities, role-playing, social interaction exercises. | Memory games, puzzles, cognitive training software. |
| Assessment Tools | Behavior observations, peer evaluations, social skill questionnaires. | IQ tests, standardized exams, cognitive assessments. |
Understanding Social Skills: Definition and Importance
Social skills encompass the ability to communicate, cooperate, and build relationships effectively within diverse social environments, underpinning successful interpersonal interactions. Mastery of skills such as empathy, active listening, and conflict resolution is essential for personal and professional growth, influencing teamwork and leadership capabilities. Developing strong social skills contributes significantly to emotional intelligence, which is linked to improved mental health, job performance, and social adaptability.
Defining Cognitive Skills: Core Components
Cognitive skills encompass essential mental capabilities such as attention, memory, reasoning, and problem-solving that enable effective information processing and decision-making. Core components include working memory, which allows temporary information manipulation; executive functions, responsible for planning and cognitive flexibility; and processing speed, facilitating quick understanding and response to stimuli. These foundational cognitive skills directly impact learning, comprehension, and complex task execution across diverse environments.
Social Skills vs Cognitive Skills: Key Differences
Social skills involve the ability to interact effectively with others, including communication, empathy, and teamwork, while cognitive skills refer to mental processes such as memory, problem-solving, and attention. The key differences lie in their application: social skills are behaviorally oriented and crucial for relationship-building, whereas cognitive skills underpin intellectual tasks and learning capacity. Developing both skill sets enhances overall personal and professional effectiveness, with social skills fostering collaboration and cognitive skills driving analytical thinking.
The Interplay Between Social and Cognitive Development
Social skills and cognitive skills are deeply interconnected, with social interactions enhancing cognitive functions such as problem-solving, memory, and attention. The development of theory of mind, a key cognitive ability, relies heavily on social experiences and communication. Neuroscientific studies show that neural networks involved in social cognition overlap with those responsible for executive functions, underscoring the dynamic interplay between social and cognitive development.
Real-Life Examples of Social and Cognitive Skills
Social skills, such as effective communication, empathy, and teamwork, are essential for building relationships and resolving conflicts in both personal and professional environments. Cognitive skills involve critical thinking, problem-solving, and memory, which are crucial for tasks like analyzing data, making decisions, and learning new concepts. Examples include leading a group project (social skill) and interpreting complex information to develop a strategy (cognitive skill).
Impact on Academic and Workplace Success
Social skills, including communication, teamwork, and emotional intelligence, significantly enhance academic performance by facilitating collaboration and effective interaction with peers and educators. Cognitive skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and memory are foundational for understanding complex concepts and achieving high academic standards. In the workplace, the integration of strong social skills and cognitive abilities drives productivity, leadership, and adaptability, directly influencing career advancement and organizational success.
Enhancing Social Skills: Effective Strategies
Enhancing social skills involves practicing active listening, maintaining eye contact, and developing empathy to improve interpersonal interactions and build stronger relationships. Role-playing scenarios and group activities facilitate the application of learned behaviors in real-life settings, fostering confidence and communication abilities. Consistent feedback and mindfulness techniques help individuals recognize social cues and adjust responses effectively, promoting emotional intelligence and social adaptability.
Boosting Cognitive Skills: Proven Techniques
Boosting cognitive skills involves targeted exercises such as memory training, problem-solving tasks, and brain games that enhance neural plasticity and executive function. Research highlights the effectiveness of consistent practice in activities like puzzles, strategy-based games, and mindfulness meditation to improve attention, processing speed, and working memory. Nutritional support with omega-3 fatty acids and adequate sleep further optimizes cognitive performance by supporting brain health and cognitive resilience.
The Role of Parents and Educators in Skill Development
Parents and educators play a crucial role in developing social skills by modeling effective communication, empathy, and collaboration in daily interactions. Cognitive skills are nurtured through structured learning activities, critical thinking exercises, and problem-solving tasks facilitated both at home and in educational settings. Prioritizing a balanced approach that integrates social-emotional learning with cognitive challenges supports holistic child development and long-term success.
Balancing Social and Cognitive Skills for Lifelong Success
Balancing social skills such as communication, empathy, and collaboration with cognitive skills including critical thinking, problem-solving, and memory enhances overall effectiveness in personal and professional life. Mastery of both skill sets fosters adaptability, emotional intelligence, and decision-making capabilities crucial for lifelong success. Integrating social and cognitive competencies leads to improved relationships, career advancement, and sustained mental agility.
Social Skills Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com