Choosing a private school offers personalized education, smaller class sizes, and access to specialized programs that can enhance Your child's academic and social development. These institutions often provide a safe and nurturing environment with dedicated faculty committed to student success. Explore the rest of the article to learn how a private school can meet Your family's unique educational needs.
Table of Comparison
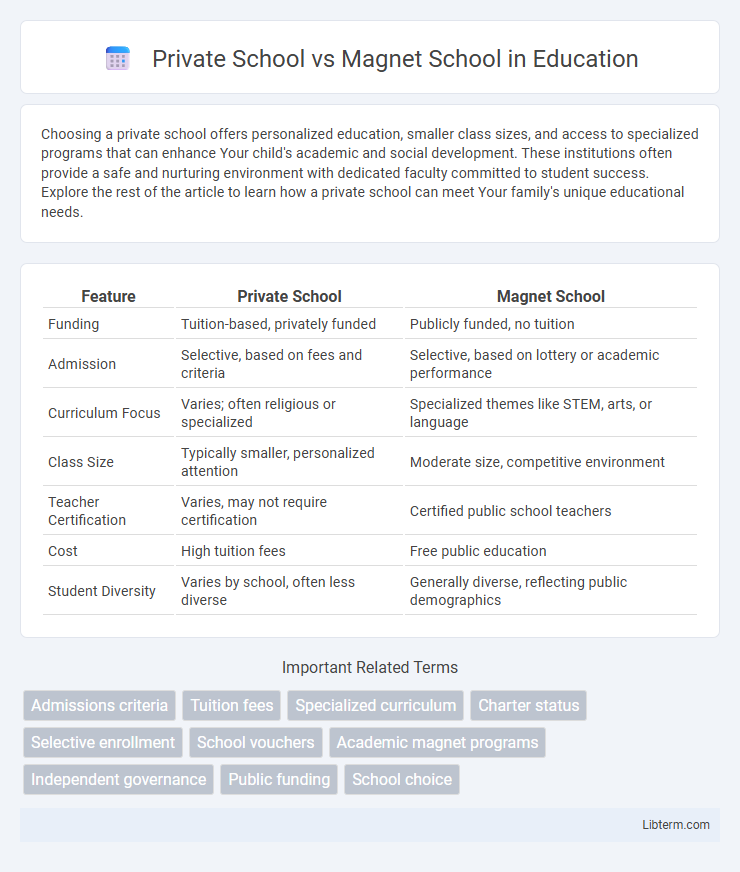
| Feature | Private School | Magnet School |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Tuition-based, privately funded | Publicly funded, no tuition |
| Admission | Selective, based on fees and criteria | Selective, based on lottery or academic performance |
| Curriculum Focus | Varies; often religious or specialized | Specialized themes like STEM, arts, or language |
| Class Size | Typically smaller, personalized attention | Moderate size, competitive environment |
| Teacher Certification | Varies, may not require certification | Certified public school teachers |
| Cost | High tuition fees | Free public education |
| Student Diversity | Varies by school, often less diverse | Generally diverse, reflecting public demographics |
Overview: Understanding Private and Magnet Schools
Private schools operate independently of public funding, relying on tuition fees, donations, and endowments to provide specialized curricula, smaller class sizes, and unique extracurricular opportunities. Magnet schools are publicly funded institutions within the public school system, designed to attract diverse students through specialized programs in areas such as science, technology, performing arts, or languages. Both school types offer tailored educational experiences but differ significantly in funding, governance, and admission criteria.
Admission Criteria: Selection Processes Compared
Private schools typically use selective admission criteria including entrance exams, interviews, and previous academic records, emphasizing holistic evaluation. Magnet schools require applicants to demonstrate specialized talents or academic achievement through tests, auditions, or portfolios, targeting specific fields such as STEM or the arts. Both institutions prioritize merit-based selection, but magnet schools often align criteria with their specialized curricula, while private schools assess broader academic and personal qualifications.
Tuition and Fees: Cost Differences Explained
Private schools typically require tuition payments ranging from $10,000 to over $40,000 annually, depending on location and facilities, while magnet schools are publicly funded and offer free education to students who qualify through a lottery or specific admission criteria. Private school fees often include additional costs such as uniforms, extracurricular activities, and technology fees, whereas magnet schools may have minimal or no extra charges, making them a cost-effective alternative for specialized programs. Families considering educational options should evaluate the comprehensive financial commitment of private schools versus the accessible tuition-free model of magnet schools while factoring in potential transportation and resource expenses.
Curriculum Focus: Academic Offerings and Specializations
Private schools often offer a broad curriculum with diverse academic offerings tailored to college preparation and specialized interests such as arts, sciences, or religious studies. Magnet schools emphasize specialized curricula centered on STEM, performing arts, or international studies to attract students with specific talents or career goals. Both types prioritize rigorous academic programs, but magnet schools integrate focused themes into public education, whereas private schools provide customizable education driven by independent governance.
Teaching Staff: Qualifications and Approaches
Private schools often employ teaching staff with advanced degrees and specialized certifications, emphasizing individualized instruction and innovative pedagogical methods. Magnet schools typically recruit educators with expertise aligned to their specialized curricula, integrating project-based learning and collaborative teaching approaches. Both school types prioritize highly qualified teachers but differ in instructional focus and staff recruitment strategies.
Class Size and Student-Teacher Ratio
Private schools typically offer smaller class sizes, often ranging from 10 to 15 students per class, fostering individualized attention and personalized instruction. Magnet schools, while public, usually maintain moderate class sizes around 20 to 25 students, balancing specialized curricula with resource availability. The student-teacher ratio in private schools averages about 8:1, significantly lower than the 16:1 ratio commonly found in magnet schools, influencing the level of direct teacher engagement and support.
Diversity and Student Demographics
Private schools often have less diverse student demographics due to selective admissions and higher tuition fees, which can limit access for underrepresented groups. Magnet schools, funded by public education systems, typically emphasize diversity by drawing students from a wider geographic area and implementing specialized programs that attract a heterogeneous student body. Research shows magnet schools can foster greater racial, socioeconomic, and cultural diversity compared to many private institutions.
Extracurricular Activities and Enrichment Programs
Private schools typically offer a broad range of extracurricular activities and enrichment programs funded through tuition and private resources, allowing for specialized arts, advanced sports, and unique clubs. Magnet schools, often focused on specific themes such as science, technology, or the arts, provide targeted extracurriculars designed to complement their specialized curricula, including specialized competitions, workshops, and mentorship programs. Both school types emphasize enriching students' educational experiences, but private schools offer more variety due to flexibility in funding, while magnet schools excel in theme-based program depth.
Parental Involvement and Community Engagement
Parental involvement in private schools typically includes active participation in fundraising, school governance, and tailored support for student activities, fostering a closely-knit community. Magnet schools emphasize community engagement through specialized programs that attract diverse student populations, encouraging collaboration between parents, local organizations, and educators. Both school types benefit from strong parental support, but private schools often see more direct financial contributions, while magnet schools focus on partnerships that enhance educational resources and cultural experiences.
Outcomes: Academic Performance and College Readiness
Private schools consistently demonstrate higher academic performance with smaller class sizes and individualized instruction, leading to elevated standardized test scores and GPA averages. Magnet schools emphasize specialized curricula and rigorous coursework, fostering advanced critical thinking and STEM proficiency, which enhances college readiness indicators such as AP exam success and college admission rates. Both schooling options contribute positively to student outcomes, but private schools often show stronger college matriculation results due to robust counseling and alumni networks.
Private School Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com