Thematic analysis is a method used to identify, analyze, and report patterns within qualitative data, providing deep insights into complex phenomena. It helps you organize data into meaningful themes that capture the essence of participants' experiences and perspectives. Explore the rest of this article to understand how thematic analysis can enhance your research and interpretation skills.
Table of Comparison
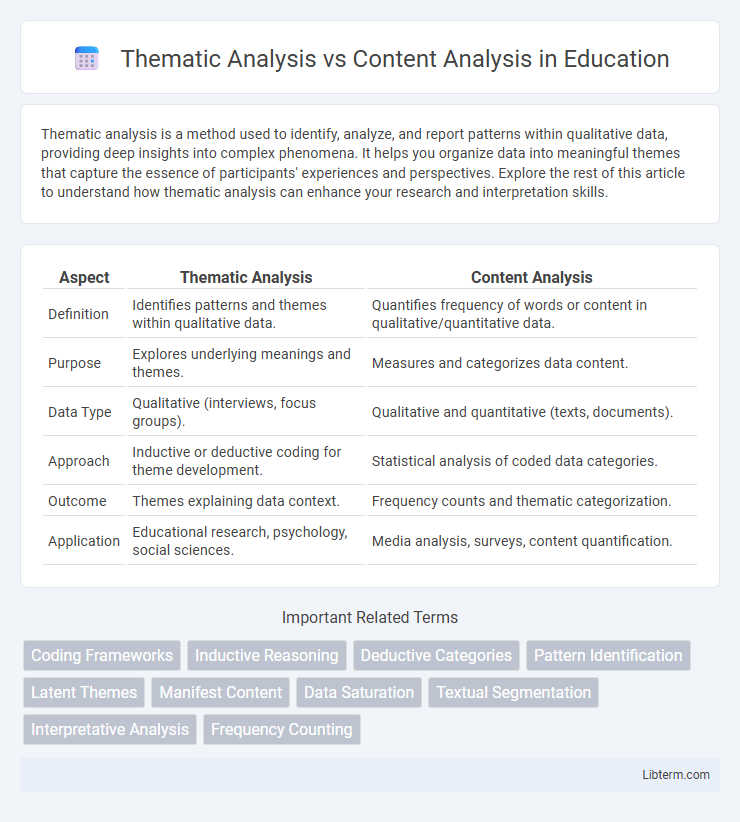
| Aspect | Thematic Analysis | Content Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifies patterns and themes within qualitative data. | Quantifies frequency of words or content in qualitative/quantitative data. |
| Purpose | Explores underlying meanings and themes. | Measures and categorizes data content. |
| Data Type | Qualitative (interviews, focus groups). | Qualitative and quantitative (texts, documents). |
| Approach | Inductive or deductive coding for theme development. | Statistical analysis of coded data categories. |
| Outcome | Themes explaining data context. | Frequency counts and thematic categorization. |
| Application | Educational research, psychology, social sciences. | Media analysis, surveys, content quantification. |
Introduction to Thematic Analysis and Content Analysis
Thematic Analysis systematically identifies, analyzes, and interprets patterns of meaning within qualitative data, enabling researchers to understand underlying themes across a dataset. Content Analysis quantitatively examines the presence, frequency, and relationships of specific words, phrases, or concepts within texts to reveal communication patterns. Both methods serve as essential tools in qualitative research, with Thematic Analysis emphasizing depth and context, while Content Analysis focuses on measurable content characteristics.
Defining Thematic Analysis
Thematic Analysis is a qualitative research method focused on identifying, analyzing, and interpreting patterns or themes within textual data. It goes beyond simply quantifying content by exploring underlying meanings and conceptual frameworks in participants' responses. Unlike Content Analysis, which often emphasizes frequency counts of predefined categories, Thematic Analysis provides a flexible approach to uncover nuanced insights across diverse datasets.
Defining Content Analysis
Content Analysis is a systematic research method used to quantify and analyze the presence, meanings, and relationships of certain words, themes, or concepts within qualitative data. It involves coding text into manageable categories based on explicit rules to detect patterns and frequencies of communication content. Unlike Thematic Analysis, which explores underlying themes and interpretations, Content Analysis emphasizes measurable and replicable data extraction from textual material.
Key Differences Between Thematic and Content Analysis
Thematic analysis identifies patterns or themes within qualitative data, focusing on interpreting underlying meanings, while content analysis quantifies the presence of specific words or phrases to analyze communication trends. Thematic analysis is more flexible and subjective, emphasizing context and depth, whereas content analysis is systematic and objective, prioritizing frequency and categorization. Key differences include thematic analysis's focus on latent themes versus content analysis's emphasis on manifest content and measurable data.
Data Collection Procedures
Thematic analysis involves collecting qualitative data through interviews, focus groups, or open-ended survey questions to identify patterns and themes within the dataset. Content analysis typically uses structured data sources, such as documents, media texts, or social media posts, applying systematic coding procedures to quantify the presence of specific words, phrases, or concepts. Both methods require rigorous sampling techniques and data preparation to ensure reliability and validity in interpreting textual or verbal information.
Coding and Categorization Techniques
Thematic Analysis employs inductive coding to identify patterns and themes within qualitative data, allowing nuanced interpretation of underlying meanings. Content Analysis utilizes both deductive and inductive coding methods to quantify the presence of specific words, phrases, or concepts, enabling statistical analysis of textual content. Categorization in Thematic Analysis is flexible and emergent, while Content Analysis relies on predefined categories for systematic classification and measurement.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Approach
Thematic Analysis excels in identifying and interpreting patterns within qualitative data, offering flexibility to explore complex, nuanced themes but may lack quantifiable rigor and can be subjective depending on researcher interpretation. Content Analysis provides systematic, quantifiable analysis of textual data, enabling objective measurement and frequency counts of predefined categories but may overlook deeper contextual meanings and latent themes. Both approaches require careful consideration of research goals, with Thematic Analysis suited for exploratory studies and Content Analysis favoring hypothesis-driven or large-scale data examination.
When to Use Thematic vs. Content Analysis
Thematic analysis is most effective when exploring patterns and underlying themes within qualitative data to understand deeper meanings, often used in psychology and social sciences. Content analysis suits quantitative evaluation of text frequency and presence, ideal for large datasets or media monitoring where statistical analysis is required. Choosing between them depends on research goals: thematic analysis for subjective interpretation and richness, content analysis for objective, systematic categorization.
Applications Across Research Fields
Thematic analysis excels in qualitative research by identifying patterns and themes within complex data sets, making it highly effective in psychology, sociology, and health studies for exploring experiences and perceptions. Content analysis quantifies data, frequently applied in media studies, communication, and marketing research to analyze frequency of specific words, phrases, or concepts in large text corpora. Both methodologies support diverse research objectives but differ in their analytical focus--interpretative depth for thematic analysis versus statistical relevance for content analysis.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Study
Thematic Analysis excels in identifying patterns and themes within qualitative data, ideal for exploratory and interpretive studies aiming to understand underlying meanings. Content Analysis quantifies the presence of specific words or concepts, suitable for large datasets requiring objective measurement and frequency analysis. Selecting the right method depends on your research goals: use Thematic Analysis for in-depth thematic insights and Content Analysis for systematic content quantification.
Thematic Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com