Cooperative learning in science enhances student understanding by encouraging collaboration, critical thinking, and hands-on experimentation. This approach promotes active engagement, allowing learners to share diverse perspectives and build deeper comprehension of scientific concepts. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for implementing cooperative learning in your science classroom.
Table of Comparison
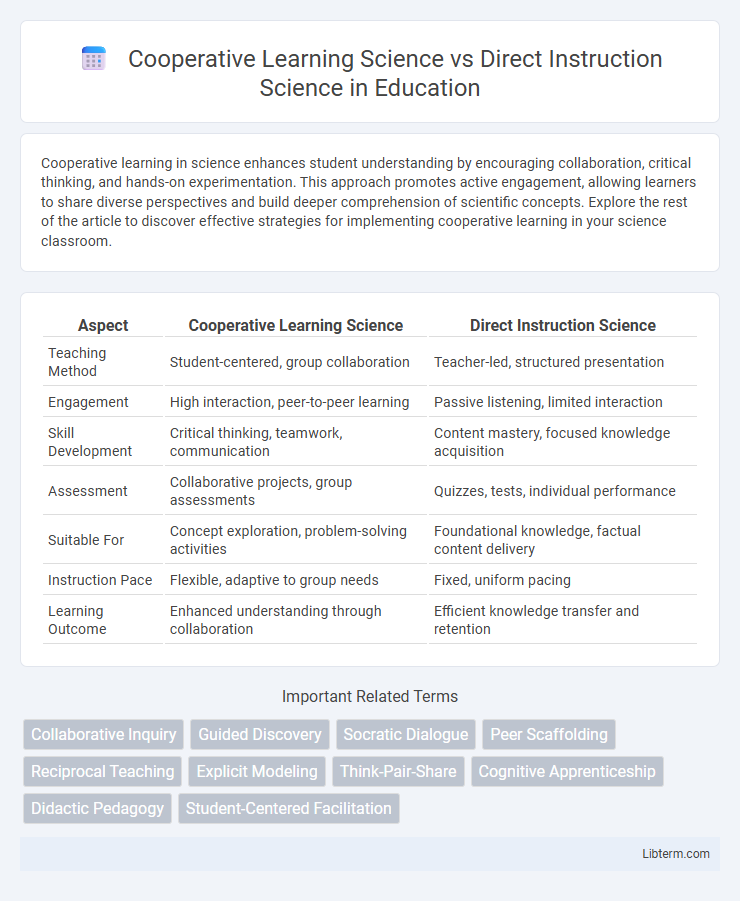
| Aspect | Cooperative Learning Science | Direct Instruction Science |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Method | Student-centered, group collaboration | Teacher-led, structured presentation |
| Engagement | High interaction, peer-to-peer learning | Passive listening, limited interaction |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, teamwork, communication | Content mastery, focused knowledge acquisition |
| Assessment | Collaborative projects, group assessments | Quizzes, tests, individual performance |
| Suitable For | Concept exploration, problem-solving activities | Foundational knowledge, factual content delivery |
| Instruction Pace | Flexible, adaptive to group needs | Fixed, uniform pacing |
| Learning Outcome | Enhanced understanding through collaboration | Efficient knowledge transfer and retention |
Introduction to Cooperative Learning and Direct Instruction in Science
Cooperative Learning in science emphasizes student collaboration through structured group activities that promote critical thinking and practical application of scientific concepts. Direct Instruction in science relies on explicit teaching methods, where educators deliver clear, systematic lessons to ensure mastery of foundational knowledge and skills. Both approaches aim to enhance science comprehension but differ in the balance between student interaction and teacher-led guidance.
Defining Cooperative Learning Science
Cooperative Learning Science is defined as an instructional approach where students work collaboratively in small groups to achieve shared learning goals, fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, and peer interaction. This method emphasizes active engagement, communication, and teamwork to deepen understanding of scientific concepts. Distinct from Direct Instruction Science, which relies on teacher-centered delivery and structured lessons, Cooperative Learning promotes student autonomy and constructivist learning through collaborative exploration.
Understanding Direct Instruction Science
Direct Instruction Science emphasizes clearly structured lessons and explicit teaching methods to enhance student comprehension of scientific concepts. It relies on systematic presentation, guided practice, and immediate feedback to ensure mastery of complex material. Research demonstrates that this approach significantly improves students' retention and application of scientific knowledge compared to more open-ended cooperative learning classrooms.
Key Differences: Cooperative vs Direct Instruction Approaches
Cooperative Learning in science emphasizes student collaboration, interactive group activities, and peer-to-peer engagement to enhance understanding, whereas Direct Instruction relies on teacher-led explanations and structured lessons for content delivery. In Cooperative Learning, students develop critical thinking and communication skills through shared tasks, contrasting with Direct Instruction's focus on mastering factual knowledge via repetition and teacher feedback. The assessment in Cooperative Learning often involves group performance and process evaluation, while Direct Instruction prioritizes individual testing and measurable learning outcomes.
Impact on Student Engagement in Science Classrooms
Cooperative learning in science classrooms significantly increases student engagement by promoting active participation, peer discussions, and collaborative problem-solving, which fosters deeper understanding and interest in scientific concepts. Direct instruction, while efficient for delivering content, often results in passive learning, leading to lower levels of student interaction and engagement. Research shows cooperative learning strategies enhance motivation, improve critical thinking skills, and create a more dynamic learning environment compared to traditional direct instruction methods.
Developing Critical Thinking: Which Method Excels?
Cooperative learning science fosters critical thinking by encouraging collaboration, dialogue, and problem-solving among students, promoting deeper understanding through peer interaction. Direct instruction science, while efficient in delivering structured content, often emphasizes memorization and procedural tasks, which may limit opportunities for critical analysis. Research indicates cooperative learning environments generally excel in developing critical thinking skills by engaging students in active exploration and reflective discussion.
Academic Outcomes: Research-Based Comparisons
Research demonstrates that cooperative learning in science promotes higher retention, critical thinking, and conceptual understanding compared to direct instruction. Meta-analyses reveal that students engaged in cooperative science activities outperform peers in traditional direct instruction settings on standardized tests and problem-solving tasks. Cooperative learning increases academic outcomes by fostering peer interaction, collaborative inquiry, and active knowledge construction in science education.
Teacher Roles and Responsibilities in Each Method
In cooperative learning science, teachers act as facilitators who design collaborative tasks, monitor group dynamics, and support peer interaction to foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Direct instruction science requires teachers to take a central role in delivering structured content, providing clear explanations, and guiding student practice through explicit teaching. Both methods demand careful assessment, but cooperative learning emphasizes ongoing formative feedback, while direct instruction focuses more on summative evaluation.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Cooperative learning in science often faces challenges such as varied student participation, group conflict, and uneven skill development, which can hinder concept mastery and assessment accuracy. Direct instruction science methods may limit critical thinking and creativity due to their focus on teacher-led content delivery and passive student engagement. Both approaches require careful adaptation to diverse classroom dynamics and individual learning needs to optimize educational outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Science Education
Cooperative Learning Science promotes student engagement and critical thinking through collaborative problem-solving, enhancing deeper conceptual understanding in science education. Direct Instruction Science emphasizes explicit teaching, structured lessons, and step-by-step demonstrations, which can effectively build foundational knowledge quickly. Selecting the right approach depends on curriculum goals, student needs, and class dynamics, with a blended strategy often providing the most balanced and effective learning outcomes.
Cooperative Learning Science Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com