A well-crafted report presents clear, concise information critical for decision-making and analysis. It organizes data logically, highlights key findings, and supports conclusions with evidence, ensuring effective communication. Explore the full article to master the skills needed to create impactful reports tailored to your needs.
Table of Comparison
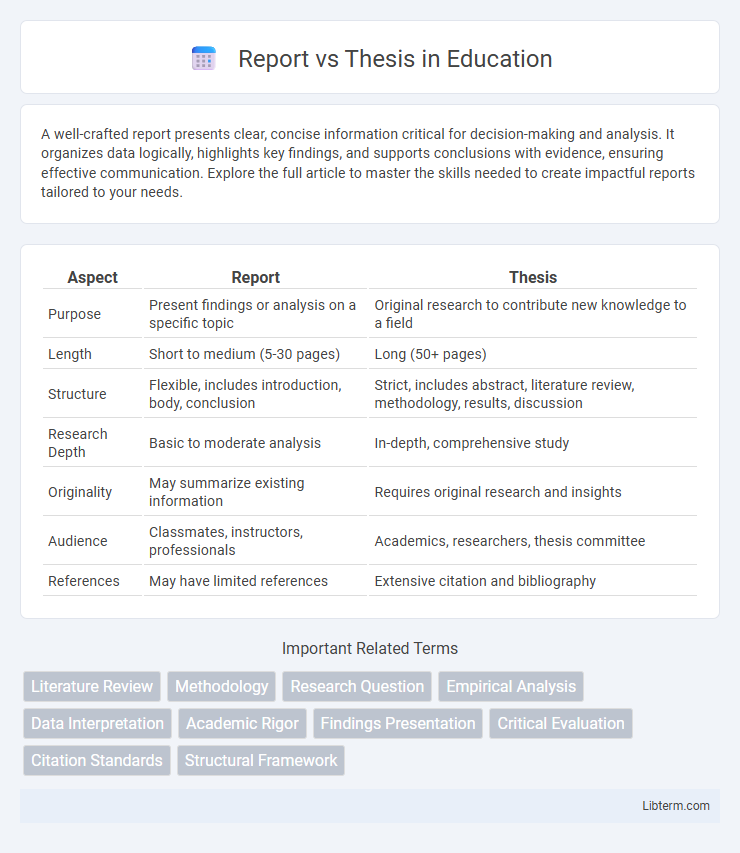
| Aspect | Report | Thesis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Present findings or analysis on a specific topic | Original research to contribute new knowledge to a field |
| Length | Short to medium (5-30 pages) | Long (50+ pages) |
| Structure | Flexible, includes introduction, body, conclusion | Strict, includes abstract, literature review, methodology, results, discussion |
| Research Depth | Basic to moderate analysis | In-depth, comprehensive study |
| Originality | May summarize existing information | Requires original research and insights |
| Audience | Classmates, instructors, professionals | Academics, researchers, thesis committee |
| References | May have limited references | Extensive citation and bibliography |
Understanding Reports and Theses: A Definition
Reports are concise documents focused on presenting data, analysis, and findings related to specific projects or research, often structured with clear headings and sections such as introduction, methodology, results, and conclusions. Theses are comprehensive academic works demonstrating original research, critical analysis, and theoretical understanding, typically required for obtaining advanced degrees and including extensive literature reviews, methodology, data interpretation, and discussions. Both serve distinct academic purposes, with reports emphasizing succinct information delivery and theses highlighting in-depth scholarly contribution.
Purpose and Objectives: Report vs Thesis
Reports aim to present factual information and analysis succinctly to address specific questions or problems, often for practical decision-making. Theses pursue original research to contribute new knowledge or theories, supported by detailed evidence and critical evaluation. The objective of a report is clarity and utility, while a thesis focuses on advancing academic understanding.
Structural Differences Between Reports and Theses
Reports typically have a structured format including a title page, abstract, table of contents, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references, with emphasis on clarity and concise presentation of specific findings. Theses follow a more comprehensive structure, often incorporating detailed literature review, extensive methodology, in-depth analysis, multiple chapters, and appendices to support a broader argument or original research contribution. Reports prioritize straightforward presentation of data and outcomes, whereas theses are organized to demonstrate scholarly research depth and critical evaluation.
Scope and Depth of Research
A report typically has a narrower scope, focusing on specific findings or results of a project or study, with concise analysis and limited depth in research. A thesis demands broader scope, encompassing comprehensive literature review, in-depth analysis, and critical evaluation to contribute original knowledge or insights to the academic field. The depth of research in a thesis is significantly greater, requiring extensive data collection, methodological rigor, and theoretical framework application compared to the more straightforward approach of a report.
Methodology: Approaches in Reports and Theses
Reports typically emphasize practical, step-by-step methodologies focused on concrete problem-solving, often using experimental or observational data. Theses require a comprehensive, rigorous approach to methodology, involving detailed theoretical frameworks and extensive research design to justify data collection and analysis methods. Methodological transparency and reproducibility remain critical in both, but theses demand deeper scholarly engagement with research approaches and underlying principles.
Academic Standards and Evaluation Criteria
Reports emphasize concise presentation of research findings with strict adherence to predefined academic format and clear, objective data analysis targeting specific evaluation rubrics. Theses demonstrate comprehensive scholarly research involving critical literature review, hypothesis formulation, and original contribution, evaluated primarily on methodological rigor, theoretical framework, and depth of argumentation. Academic standards for reports prioritize clarity and precision, while theses require extensive synthesis, coherence, and academic originality to meet higher education evaluation criteria.
Writing Style and Language Usage
Reports employ a concise and straightforward writing style with clear headings and bullet points to present factual information objectively. Thesis writing demands a formal and academic tone with complex sentences and specialized vocabulary to demonstrate critical analysis and original research. Language usage in reports favors clarity and brevity, while thesis language emphasizes depth, coherence, and scholarly rigor.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
A report typically presents data analysis in a structured format with clear headings, emphasizing factual findings and concise interpretation to support specific objectives or questions. In contrast, a thesis involves a deeper, more comprehensive interpretation of data, integrating theoretical frameworks and critical analysis to contribute original knowledge to the field. The thesis demands rigorous justification of methods and data, aiming for scholarly discourse, whereas reports prioritize clarity and direct application of results.
Audience and Target Readers
Reports are typically written for a specific audience such as business stakeholders, project managers, or technical experts who require factual data and concise analysis to support decision-making. Theses target academic audiences including professors, researchers, and scholars, emphasizing detailed research findings, theoretical context, and methodological rigor. Reports prioritize clarity and brevity to facilitate quick understanding, while theses focus on comprehensive discussion and contribution to academic knowledge.
Conclusion: Choosing Between a Report and a Thesis
The conclusion of a report typically summarizes key findings and offers practical recommendations based on data analysis, emphasizing clear, concise results tailored for specific audiences. In contrast, a thesis conclusion synthesizes broader research insights, highlighting contributions to academic knowledge and suggesting avenues for future study. Selecting between a report and a thesis depends on the purpose: reports suit applied projects with targeted objectives, while theses are ideal for in-depth scholarly investigation.
Report Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com