Expulsion is a formal disciplinary action used by institutions to remove a member, often due to serious violations of rules or policies. This severe consequence can impact academic records, future opportunities, and personal reputation. Discover how understanding the causes, processes, and implications of expulsion can help you navigate or prevent this situation effectively.
Table of Comparison
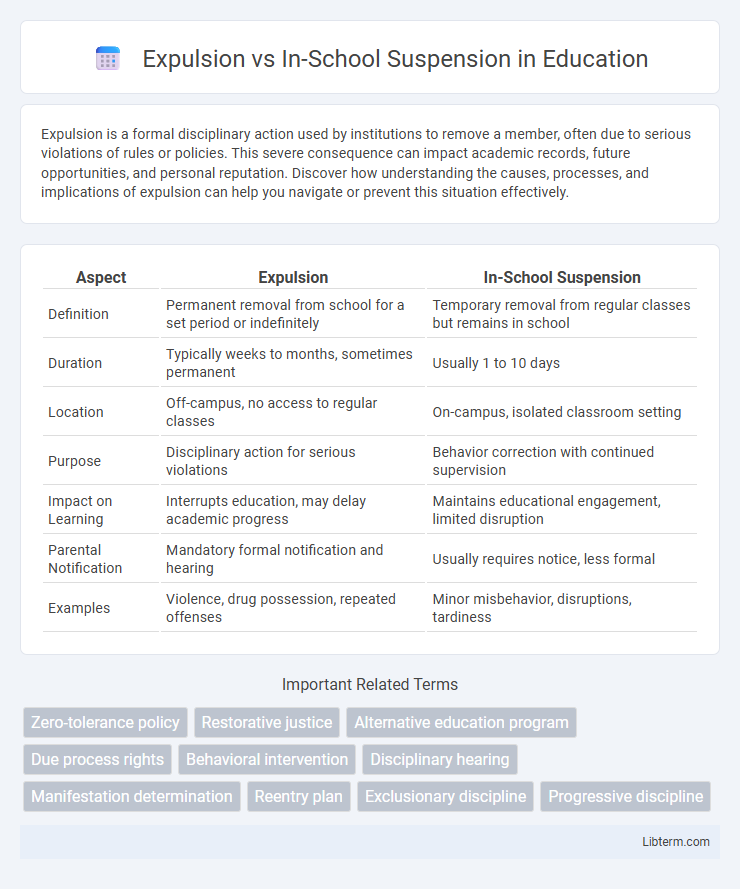
| Aspect | Expulsion | In-School Suspension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent removal from school for a set period or indefinitely | Temporary removal from regular classes but remains in school |
| Duration | Typically weeks to months, sometimes permanent | Usually 1 to 10 days |
| Location | Off-campus, no access to regular classes | On-campus, isolated classroom setting |
| Purpose | Disciplinary action for serious violations | Behavior correction with continued supervision |
| Impact on Learning | Interrupts education, may delay academic progress | Maintains educational engagement, limited disruption |
| Parental Notification | Mandatory formal notification and hearing | Usually requires notice, less formal |
| Examples | Violence, drug possession, repeated offenses | Minor misbehavior, disruptions, tardiness |
Understanding Expulsion and In-School Suspension
Expulsion is a school disciplinary action that removes a student from the school environment entirely due to severe behavioral violations, often lasting for an extended period. In-school suspension (ISS) involves removing a student from regular classes but keeping them within the school under supervision, allowing continued academic engagement in a controlled setting. Understanding the differences between expulsion and ISS highlights the varying levels of severity and impact on student education and behavior correction.
Definitions: Expulsion vs In-School Suspension
Expulsion is a formal removal of a student from a school or district, typically due to severe behavioral violations, resulting in the student being prohibited from attending classes on campus for a specified period or indefinitely. In-School Suspension (ISS) involves temporarily isolating a student within the school environment, where they complete assigned work under supervision, aimed at correcting behavior without removing them from educational settings. Both disciplinary actions serve distinct roles in school policy, balancing punitive measures with opportunities for academic continuity and behavior improvement.
Key Differences Between Expulsion and In-School Suspension
Expulsion involves the permanent removal of a student from school, typically for severe or repeated violations, and requires formal procedures that may include hearings and appeals. In-school suspension (ISS) confines the student to a designated area within the school, allowing continued academic work while restricting participation in regular classes and activities. Key differences include the duration, with expulsion often lasting an extended period or indefinitely, and the impact on educational access, since ISS maintains supervised learning opportunities whereas expulsion restricts school attendance entirely.
Reasons for Expulsion in Schools
Expulsion in schools is typically reserved for severe or repeated violations such as weapons possession, drug distribution, violent behavior, or chronic bullying that endangers students and staff. These serious infractions lead to permanent removal from the school environment, reflecting the institution's commitment to safety and discipline. In contrast, in-school suspension serves as a temporary corrective measure for less egregious offenses, allowing students to remain on campus under supervision while addressing behavioral issues.
Common Causes for In-School Suspension
Common causes for in-school suspension include repeated classroom disruptions, violation of school policies such as dress code or tardiness, and minor physical altercations. Students placed in in-school suspension often exhibit behavioral issues that interfere with the learning environment but do not warrant expulsion, such as insubordination or possession of prohibited items. This disciplinary method aims to address misconduct while keeping students within the educational setting for continued supervision and instruction.
Short-Term and Long-Term Impacts on Students
Expulsion often results in significant long-term educational setbacks, including increased dropout rates and limited access to higher education and employment opportunities compared to in-school suspension. In-school suspension allows students to remain in the academic environment, promoting continuity in learning and social development while still addressing behavioral issues. Short-term, in-school suspension helps maintain school safety without removing students entirely, whereas expulsion can lead to social isolation and increased risk of involvement with the juvenile justice system.
Legal and Policy Implications
Expulsion removes a student from school for a prolonged period, often requiring a formal hearing and adherence to due process rights mandated by federal laws like the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA). In-school suspension (ISS) allows continued access to education within the school setting while restricting participation in regular activities, aligning with policies that promote student rehabilitation and minimize educational disruption. Legal implications of expulsion include potential denial of Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE) under IDEA, whereas ISS is generally considered a less severe disciplinary measure with fewer legal restrictions but must still comply with state and district regulations.
Role of School Administration in Disciplinary Actions
School administration plays a critical role in determining appropriate disciplinary actions, balancing the need for maintaining a safe learning environment with fair treatment of students. Expulsions are typically reserved for severe infractions or repeated offenses, requiring thorough investigation and formal hearings conducted by school officials. In contrast, in-school suspension allows administrators to enforce discipline while keeping students engaged academically under supervised conditions, emphasizing corrective measures over exclusion.
Alternatives to Expulsion and In-School Suspension
Alternatives to expulsion and in-school suspension include restorative justice programs, which emphasize repairing harm through mediated dialogue and community service, and positive behavioral interventions and supports (PBIS) that promote proactive strategies for defining, teaching, and supporting appropriate student behaviors. Implementing counseling and mentorship programs can address underlying issues contributing to behavioral problems, reducing recidivism and improving student outcomes. These alternatives foster a supportive school environment by maintaining student engagement and minimizing academic disruption compared to traditional punitive measures.
Best Practices for Effective Student Discipline
Implementing clear communication and consistent enforcement of school rules enhances the effectiveness of expulsion and in-school suspension as disciplinary measures. Prioritizing restorative practices within in-school suspension promotes accountability while maintaining student engagement and minimizing learning loss. Data-driven decision-making and individualized intervention plans ensure disciplinary actions address the root causes of behavior, supporting long-term student success and school safety.
Expulsion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com