Summative data provides a clear overview of overall performance by summarizing key metrics and outcomes. It enables you to quickly assess the effectiveness of a process or intervention without delving into detailed breakdowns. Explore the rest of the article to understand how summative data can enhance your decision-making.
Table of Comparison
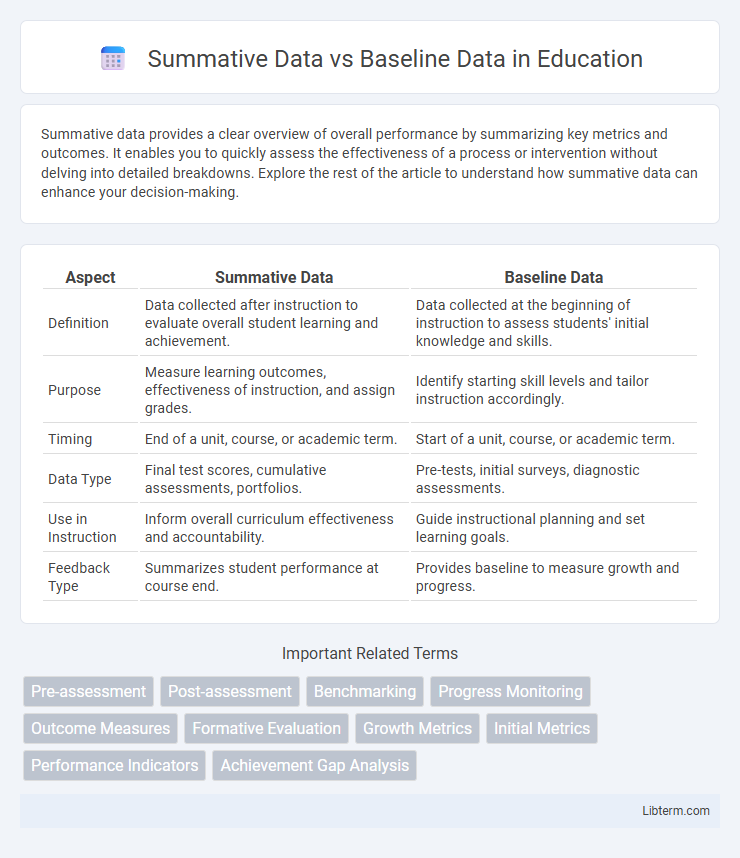
| Aspect | Summative Data | Baseline Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data collected after instruction to evaluate overall student learning and achievement. | Data collected at the beginning of instruction to assess students' initial knowledge and skills. |
| Purpose | Measure learning outcomes, effectiveness of instruction, and assign grades. | Identify starting skill levels and tailor instruction accordingly. |
| Timing | End of a unit, course, or academic term. | Start of a unit, course, or academic term. |
| Data Type | Final test scores, cumulative assessments, portfolios. | Pre-tests, initial surveys, diagnostic assessments. |
| Use in Instruction | Inform overall curriculum effectiveness and accountability. | Guide instructional planning and set learning goals. |
| Feedback Type | Summarizes student performance at course end. | Provides baseline to measure growth and progress. |
Introduction to Summative and Baseline Data
Summative data measures the overall effectiveness of a program or intervention by evaluating outcomes after completion, providing a comprehensive view of success or failure. Baseline data establishes initial conditions or starting points before any intervention, enabling meaningful comparisons and tracking of progress. Together, these data types create a framework for assessing growth and impact in educational, clinical, or business settings.
Defining Summative Data
Summative data refers to information collected at the end of an instructional period or intervention to evaluate overall student learning and program effectiveness. It provides measurable outcomes demonstrating the extent to which educational goals and standards have been achieved. Unlike baseline data, which captures initial performance levels, summative data offers a comprehensive assessment of final results for decision-making and accountability.
Defining Baseline Data
Baseline data represents the initial set of measurements collected before any intervention or treatment begins, serving as a reference point to evaluate future changes. It establishes the starting conditions of a program or study, allowing comparison to post-intervention outcomes for assessing effectiveness. Accurate collection of baseline data is essential for meaningful analysis in both educational and clinical settings.
Key Differences Between Summative and Baseline Data
Summative data measures overall performance or outcomes at the end of a process, providing a conclusive assessment of effectiveness, while baseline data captures initial conditions or performance levels before any intervention begins, serving as a reference point for comparison. Summative data is often quantitative and used for evaluation and accountability, whereas baseline data is critical for setting goals and tracking progress over time. Key differences include timing--summative data is collected post-intervention, and baseline data is collected pre-intervention--and purpose, with summative data assessing results and baseline data establishing a starting benchmark.
Importance of Baseline Data in Research
Baseline data establishes the initial conditions or characteristics of a study population before interventions or changes occur, enabling accurate measurement of progress and outcomes. It provides a critical reference point for comparing summative data collected after the intervention, ensuring the validity and reliability of research conclusions. Effective use of baseline data enhances the ability to detect true effects and minimizes bias in clinical trials, social sciences, and educational research.
Role of Summative Data in Evaluation
Summative data plays a critical role in evaluation by providing comprehensive insights into the overall effectiveness of a program or intervention after its completion, measuring outcomes against predetermined goals. Unlike baseline data, which establishes the initial conditions before the intervention, summative data facilitates assessment of the program's impact, guiding decision-making to determine success or areas for improvement. This type of data includes final test scores, overall performance metrics, and user feedback collected at the end of a project cycle.
When to Use Summative Data vs Baseline Data
Summative data is used after a process or intervention to evaluate overall effectiveness and measure outcomes against predefined goals. Baseline data is collected at the beginning to establish a reference point for future comparison and to identify initial conditions. Use baseline data to set benchmarks and summative data to assess progress or the impact of changes over time.
Common Applications in Education and Healthcare
Summative data in education is used to evaluate overall student learning at the end of an instructional period, while baseline data establishes initial performance levels to measure progress. In healthcare, summative data assesses treatment outcomes and effectiveness after interventions, whereas baseline data captures patients' health status before treatment to guide decision-making. Both data types are essential for monitoring progress, shaping personalized plans, and evaluating program efficacy in educational and clinical settings.
Challenges in Collecting and Analyzing Data
Collecting summative data often encounters challenges such as timing constraints and participant attrition, which can affect the accuracy of final assessments. Baseline data collection faces difficulties in establishing consistent starting points due to variations in initial conditions and participant engagement. Analyzing both summative and baseline data requires robust statistical methods to manage missing data and ensure valid comparisons over time.
Best Practices for Effective Data Comparison
Summative data, collected at the end of a program, offers a comprehensive evaluation of overall outcomes, while baseline data provides initial metrics for comparison. Best practices for effective data comparison include ensuring consistent measurement criteria, aligning data collection timelines, and employing statistical methods to identify significant changes. Utilizing clear benchmarks and visual analytics enhances the accuracy and interpretability of comparisons between baseline and summative data.
Summative Data Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com