Traditional teaching methods emphasize structured classroom environments where teachers deliver content through lectures and direct instruction, focusing on memorization and repetition. This approach prioritizes discipline and a standardized curriculum designed to build foundational knowledge systematically. Explore the rest of the article to discover how traditional teaching compares to modern educational techniques and what it means for your learning journey.
Table of Comparison
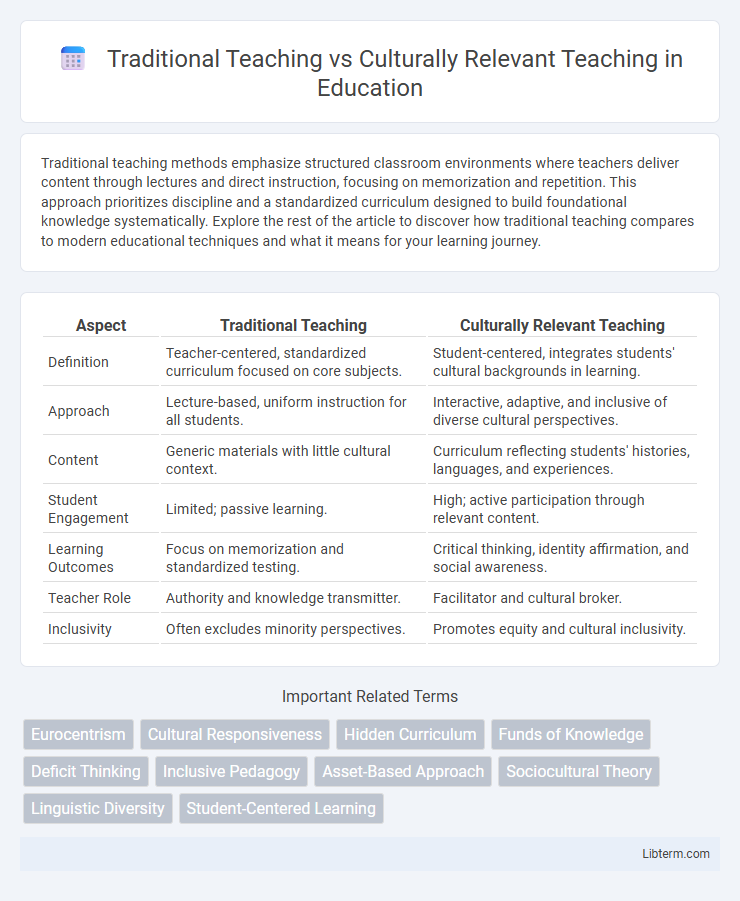
| Aspect | Traditional Teaching | Culturally Relevant Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-centered, standardized curriculum focused on core subjects. | Student-centered, integrates students' cultural backgrounds in learning. |
| Approach | Lecture-based, uniform instruction for all students. | Interactive, adaptive, and inclusive of diverse cultural perspectives. |
| Content | Generic materials with little cultural context. | Curriculum reflecting students' histories, languages, and experiences. |
| Student Engagement | Limited; passive learning. | High; active participation through relevant content. |
| Learning Outcomes | Focus on memorization and standardized testing. | Critical thinking, identity affirmation, and social awareness. |
| Teacher Role | Authority and knowledge transmitter. | Facilitator and cultural broker. |
| Inclusivity | Often excludes minority perspectives. | Promotes equity and cultural inclusivity. |
Introduction to Teaching Paradigms
Traditional teaching emphasizes standardized curricula and teacher-centered instruction, focusing on rote memorization and uniform assessment methods. Culturally relevant teaching integrates students' cultural backgrounds and experiences into the learning process, promoting critical thinking, engagement, and identity affirmation. These paradigms differ fundamentally in their approach to student learning, representation, and the role of culture within education.
Defining Traditional Teaching Methods
Traditional teaching methods emphasize direct instruction, rote memorization, and teacher-centered classrooms where educators deliver content and students passively receive information. This approach often relies on standardized curricula, uniform assessments, and a fixed hierarchy that prioritizes academic achievement through repetition and drill. Despite its structure, traditional teaching may overlook diverse cultural backgrounds and the unique lived experiences of students.
Principles of Culturally Relevant Teaching
Principles of Culturally Relevant Teaching emphasize the integration of students' cultural backgrounds into the learning experience to promote academic success, cultural competence, and critical consciousness. This approach contrasts with Traditional Teaching, which often follows a standardized curriculum that may not reflect diverse cultural perspectives. By validating students' identities and encouraging active engagement with social issues, Culturally Relevant Teaching fosters a more inclusive and effective educational environment.
Historical Context of Educational Approaches
Traditional teaching methods originated during the Industrial Revolution, emphasizing standardized curricula and uniform assessment to prepare students for factory-like work environments. In contrast, culturally relevant teaching emerged in the late 20th century as a response to educational inequities, aiming to incorporate students' cultural backgrounds and experiences to enhance engagement and academic success. This approach challenges the one-size-fits-all model by promoting inclusivity and addressing systemic biases rooted in historical education systems.
Curriculum Design: Standardization vs Personalization
Traditional teaching relies on standardized curriculum design, emphasizing uniform content and assessment to ensure consistent knowledge acquisition across diverse student populations. Culturally relevant teaching prioritizes personalized curriculum design, integrating students' cultural backgrounds, experiences, and languages to enhance engagement and academic success. This approach fosters critical thinking by connecting learning materials to real-life contexts, promoting inclusivity and deeper understanding.
Teacher-Student Relationships in Different Models
Traditional teaching models often emphasize a hierarchical teacher-student relationship, where the teacher is the primary knowledge authority and students follow structured instruction. Culturally relevant teaching fosters collaborative and reciprocal relationships, valuing students' cultural backgrounds as critical assets in the learning process. Research shows that culturally responsive teacher-student interactions enhance engagement, trust, and academic achievement among diverse student populations.
Impact on Student Engagement and Achievement
Traditional teaching often emphasizes standardized curricula and uniform assessment methods, which can limit student engagement by not addressing diverse cultural backgrounds. Culturally relevant teaching integrates students' cultural references in all aspects of learning, fostering greater motivation, participation, and academic achievement. Research shows that culturally relevant pedagogy improves student self-esteem and critical thinking, leading to higher retention rates and better overall performance.
Addressing Diversity and Inclusion in the Classroom
Traditional teaching methods often emphasize standardized curricula and uniform assessments that may not fully address the diverse cultural backgrounds of students. Culturally relevant teaching incorporates students' cultural references and experiences into the learning process, fostering inclusion and improving engagement across diverse classrooms. Research shows that culturally responsive pedagogy enhances academic achievement and social-emotional well-being by validating students' identities and promoting equity.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Traditional teaching often faces challenges such as limited student engagement and difficulty addressing diverse cultural backgrounds, leading to a one-size-fits-all approach that may hinder inclusive learning. Culturally relevant teaching, while promoting inclusivity and student identity affirmation, encounters limitations like inconsistent implementation, lack of teacher training, and resistance from institutions adhering to standardized curricula. Both approaches struggle to balance standardized educational goals with the need for personalized, culturally responsive pedagogy that effectively supports all learners.
Future Directions for Effective Teaching Practices
Future directions for effective teaching practices emphasize integrating culturally relevant teaching to address diverse student backgrounds alongside traditional methods. Utilizing culturally responsive pedagogy enhances student engagement, critical thinking, and academic achievement by connecting curriculum content with students' cultural contexts. Advances in teacher training now prioritize developing cultural competence and adaptive strategies to foster inclusive, equitable learning environments.
Traditional Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com