An integrated curriculum combines multiple subject areas into a cohesive learning experience that reflects real-world applications, enhancing student engagement and understanding. This approach fosters critical thinking, collaboration, and deeper retention by connecting concepts across disciplines. Explore the article to discover how an integrated curriculum can transform Your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
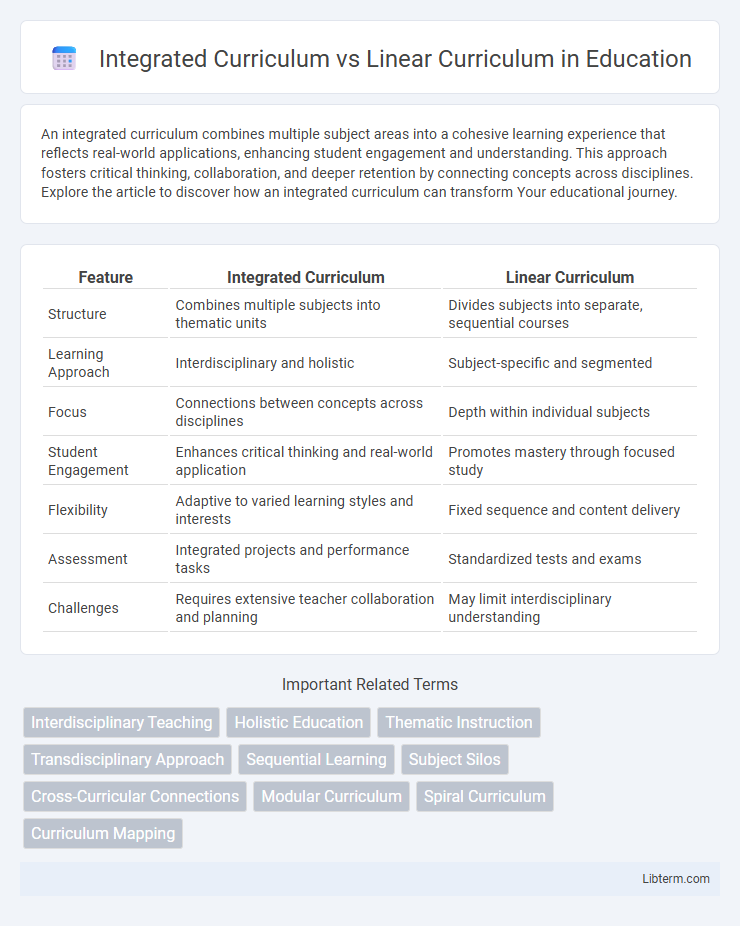
| Feature | Integrated Curriculum | Linear Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Combines multiple subjects into thematic units | Divides subjects into separate, sequential courses |
| Learning Approach | Interdisciplinary and holistic | Subject-specific and segmented |
| Focus | Connections between concepts across disciplines | Depth within individual subjects |
| Student Engagement | Enhances critical thinking and real-world application | Promotes mastery through focused study |
| Flexibility | Adaptive to varied learning styles and interests | Fixed sequence and content delivery |
| Assessment | Integrated projects and performance tasks | Standardized tests and exams |
| Challenges | Requires extensive teacher collaboration and planning | May limit interdisciplinary understanding |
Understanding Integrated and Linear Curricula
Integrated curriculum merges multiple subject areas into cohesive learning experiences, promoting deeper understanding and real-world application by connecting concepts across disciplines. Linear curriculum organizes content in a sequential, subject-specific manner, emphasizing mastery of individual topics before progressing to the next. Understanding these approaches helps educators design instruction that either fosters interdisciplinary thinking or builds foundational knowledge step-by-step.
Key Differences Between Integrated and Linear Approaches
Integrated curriculum emphasizes interconnected learning across subjects, promoting holistic understanding and real-world application, while linear curriculum follows a sequential and subject-specific structure focusing on depth within individual disciplines. Integrated approaches enhance critical thinking and collaboration by blending multiple disciplines into thematic units, whereas linear curricula prioritize systematic skill acquisition and knowledge progression in isolated subjects. Assessment in integrated curricula often involves project-based and interdisciplinary evaluation, contrasting with the linear model's reliance on traditional testing specific to each subject area.
Advantages of Integrated Curriculum
Integrated curriculum fosters holistic learning by connecting concepts across subjects, enhancing meaningful understanding and retention. It develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills through real-world applications, promoting student engagement and motivation. Collaboration among teachers ensures cohesive instruction, addressing diverse learning styles and encouraging interdisciplinary insights.
Benefits of Linear Curriculum Structure
Linear curriculum structure offers clear, sequential learning paths that enhance student comprehension by building foundational knowledge step-by-step. It supports systematic skill development and makes it easier for educators to assess progress through well-defined milestones. This approach reduces cognitive overload by breaking complex subjects into manageable units, facilitating focused mastery.
Challenges in Implementing Integrated Curriculum
Implementing an integrated curriculum faces challenges such as aligning diverse subject content cohesively while ensuring adherence to standardized testing requirements. Teachers often require extensive professional development to effectively design and deliver interdisciplinary lessons that maintain academic rigor. Schools may struggle with scheduling complexities and resource allocation needed to support collaborative teaching models inherent in integrated curricula.
Potential Drawbacks of Linear Curriculum
Linear curriculum often limits the connection between subject areas, restricting students' ability to see interdisciplinary relationships and apply knowledge in real-world contexts. This segmented approach can lead to gaps in critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as it encourages rote memorization rather than deep understanding. Moreover, the rigid structure reduces flexibility for adapting to diverse learning styles and interests, potentially hindering student engagement and motivation.
Impact on Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes
Integrated curriculum fosters deeper student engagement by connecting multiple subjects through thematic units, promoting critical thinking and real-world application of knowledge. Linear curriculum structures content in a sequential, subject-specific manner, which may simplify assessment but often limits interdisciplinary understanding and student motivation. Research indicates that integrated approaches enhance learning outcomes by increasing retention, relevance, and student autonomy compared to the compartmentalized nature of linear curricula.
Teacher Roles in Integrated vs Linear Curriculum
In an integrated curriculum, teacher roles shift towards facilitators and collaborators, guiding interdisciplinary learning and encouraging critical thinking across multiple subjects. In contrast, teachers in a linear curriculum primarily act as content deliverers, focusing on sequential subject knowledge and standardized assessments. The integrated approach demands adaptive teaching strategies that connect concepts, whereas the linear model emphasizes structured lesson planning and focused expertise in a single discipline.
Real-World Examples of Integrated and Linear Curricula
Integrated curricula in schools like High Tech High in San Diego merge subjects such as science, math, and art through project-based learning, promoting critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills. Linear curricula, exemplified by traditional programs in many public schools, teach subjects sequentially, focusing on mastery of individual disciplines like algebra or biology before moving to the next topic. The integrated approach encourages interdisciplinary connections reflecting workplace collaboration, whereas the linear model emphasizes step-by-step skill acquisition and standardized assessment readiness.
Choosing the Right Curriculum for Your Educational Goals
Selecting the right curriculum depends on your educational goals and teaching context; an integrated curriculum combines multiple subjects to promote holistic understanding and real-world application, enhancing critical thinking skills. In contrast, a linear curriculum follows a sequential, subject-specific approach that builds foundational knowledge systematically and supports mastery in distinct disciplines. Consider student needs, learning outcomes, and flexibility requirements when choosing between integrated and linear models to align curriculum design with desired academic and developmental objectives.
Integrated Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com