Vocational education equips individuals with practical skills and specialized knowledge tailored to specific trades or careers, enhancing employability and job readiness. It focuses on hands-on training and real-world application, bridging the gap between theoretical learning and industry demands. Discover how vocational education can transform your career prospects by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
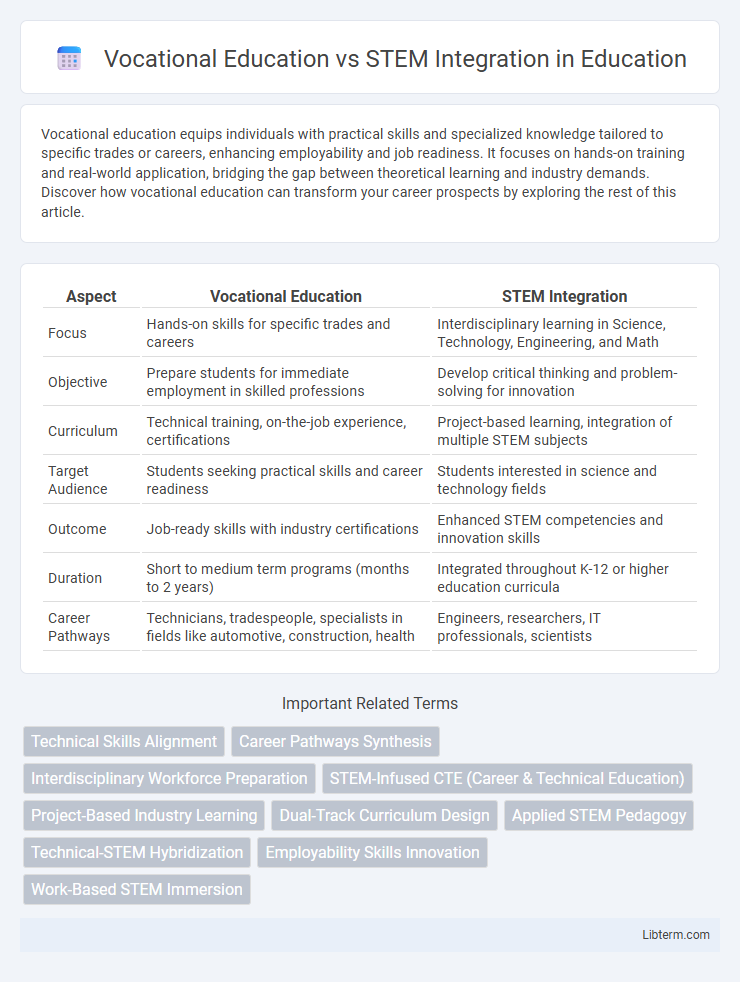
| Aspect | Vocational Education | STEM Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Hands-on skills for specific trades and careers | Interdisciplinary learning in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math |
| Objective | Prepare students for immediate employment in skilled professions | Develop critical thinking and problem-solving for innovation |
| Curriculum | Technical training, on-the-job experience, certifications | Project-based learning, integration of multiple STEM subjects |
| Target Audience | Students seeking practical skills and career readiness | Students interested in science and technology fields |
| Outcome | Job-ready skills with industry certifications | Enhanced STEM competencies and innovation skills |
| Duration | Short to medium term programs (months to 2 years) | Integrated throughout K-12 or higher education curricula |
| Career Pathways | Technicians, tradespeople, specialists in fields like automotive, construction, health | Engineers, researchers, IT professionals, scientists |
Introduction to Vocational Education and STEM Integration
Vocational education equips learners with specialized skills focused on specific trades and practical professions, enhancing workforce readiness and technical competence. STEM integration combines science, technology, engineering, and mathematics concepts to foster critical thinking, innovation, and problem-solving abilities across disciplines. This fusion of vocational training and STEM principles cultivates versatile, skilled professionals capable of adapting to evolving industry demands.
Defining Vocational Education: Scope and Objectives
Vocational education encompasses specialized training aimed at equipping students with practical skills and knowledge for specific trades or occupations, focusing on direct workforce readiness and hands-on experience. Its scope includes career-focused programs in fields such as manufacturing, healthcare, and information technology, designed to meet industry demands and improve employability. The primary objective of vocational education is to bridge the gap between theoretical learning and real-world application, fostering technical competence and job-specific expertise.
Understanding STEM Integration in Modern Curriculums
STEM integration in modern curriculums combines science, technology, engineering, and mathematics to create interdisciplinary learning experiences that reflect real-world applications. Vocational education emphasizes hands-on skills and practical training, while STEM integration fosters problem-solving, critical thinking, and innovation by blending theoretical knowledge with practical projects. This approach enhances student engagement and prepares learners for diverse career paths in technology-driven industries.
Comparing Educational Pathways: Vocational vs. STEM
Vocational education emphasizes hands-on skill development tailored to specific trades, offering direct entry into the workforce through practical training and certifications. STEM integration focuses on cultivating critical thinking and problem-solving abilities in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, preparing students for innovation-driven careers and higher education opportunities. Both pathways address workforce needs but differ in their approach: vocational programs prioritize applied expertise, while STEM education fosters analytical and interdisciplinary skills.
Skill Development: Hands-On vs. Analytical Approaches
Vocational education emphasizes hands-on skill development through practical training in trades such as carpentry, plumbing, and automotive repair, fostering immediate job readiness. STEM integration focuses on analytical problem-solving skills alongside technical knowledge in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, promoting innovation and critical thinking. Combining hands-on vocational training with STEM analytical approaches enhances comprehensive skill sets, preparing students for diverse and evolving career demands.
Industry Demands: Workforce Needs and Future Careers
Vocational education aligns closely with immediate industry demands by providing specialized skills tailored to workforce needs in trades like manufacturing, construction, and healthcare. STEM integration emphasizes critical thinking and innovation, preparing students for future careers in technology-driven fields such as software development, engineering, and data science. Both approaches address evolving labor market trends, with vocational programs targeting practical expertise and STEM fostering adaptability for emerging industries.
Advantages and Challenges of Vocational Education
Vocational education offers practical skills and hands-on training tailored to specific trades, enhancing employability and meeting labor market demands efficiently. It faces challenges such as limited adaptability to rapidly evolving technologies and sometimes lower societal recognition compared to STEM programs. Integrating vocational education with STEM fields can bridge skill gaps but requires curriculum alignment and investment in instructor expertise.
Benefits and Limitations of STEM Integration
STEM integration in vocational education enhances critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and prepares students for high-demand technology-driven careers by combining science, technology, engineering, and mathematics principles with practical trade skills. Benefits include increased innovation potential, adaptability in emerging industries, and higher employment rates in competitive job markets. Limitations involve the potential cost of technology implementation, the need for specialized teacher training, and the risk of overshadowing traditional hands-on skills essential to vocational trades.
Bridging the Gap: Hybrid Models and Collaborative Strategies
Hybrid models combining vocational education and STEM integration enhance skill acquisition by merging hands-on training with advanced technological knowledge. Collaborative strategies between industry partners, educators, and policymakers foster curricula that address real-world demands, ensuring students gain both practical expertise and critical STEM competencies. These integrated approaches reduce the skills gap, increase employability, and support economic growth by preparing a workforce adept in innovation and applied sciences.
Conclusion: Shaping the Workforce for Tomorrow
Vocational education and STEM integration collectively shape a future-ready workforce by blending practical skills with critical thinking and innovation. Emphasizing hands-on training in technical fields alongside STEM's problem-solving methodologies ensures adaptability in evolving industries. This synergy fosters a diverse talent pool equipped to meet the dynamic demands of tomorrow's job market.
Vocational Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com