Project-Based Learning engages students through hands-on, real-world challenges that foster critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. This approach enhances retention and makes learning more meaningful by connecting academic concepts to practical applications. Discover how implementing Project-Based Learning can transform your educational experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
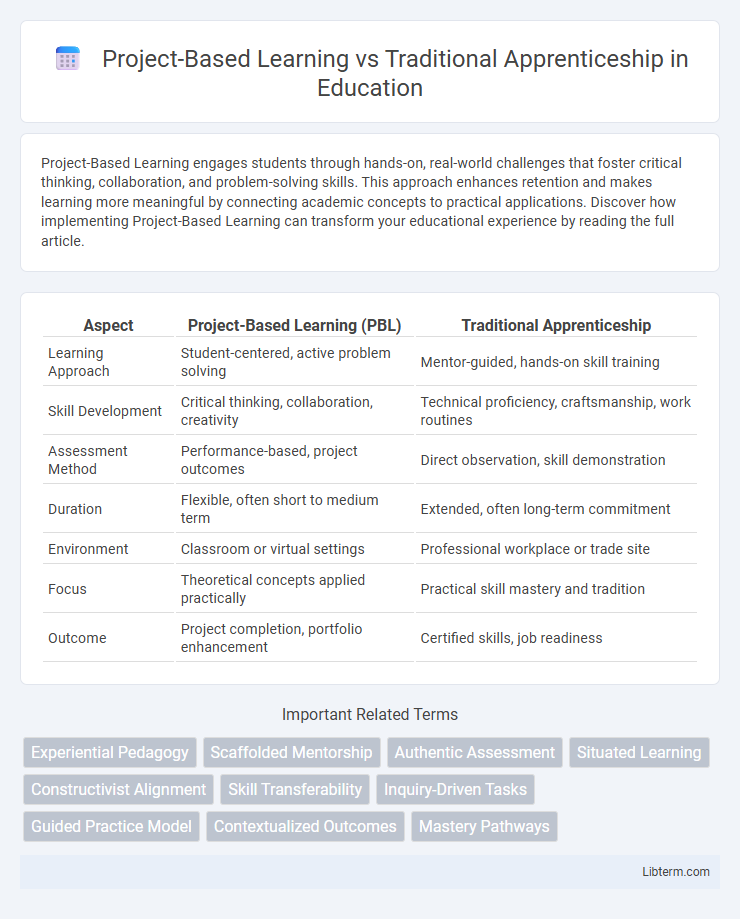
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Traditional Apprenticeship |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Approach | Student-centered, active problem solving | Mentor-guided, hands-on skill training |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, collaboration, creativity | Technical proficiency, craftsmanship, work routines |
| Assessment Method | Performance-based, project outcomes | Direct observation, skill demonstration |
| Duration | Flexible, often short to medium term | Extended, often long-term commitment |
| Environment | Classroom or virtual settings | Professional workplace or trade site |
| Focus | Theoretical concepts applied practically | Practical skill mastery and tradition |
| Outcome | Project completion, portfolio enhancement | Certified skills, job readiness |
Introduction to Experiential Learning Methods
Project-Based Learning emphasizes student-centered exploration through real-world tasks, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Traditional Apprenticeship relies on hands-on mentorship, where learners acquire skills directly from experienced practitioners in authentic work environments. Both experiential learning methods enhance practical knowledge but differ in structure, collaboration, and autonomy levels, shaping distinct pathways for skill development.
Defining Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional methodology where students actively engage in exploring real-world challenges and problems over an extended period, culminating in a tangible project or presentation. PBL emphasizes critical thinking, collaboration, and practical application of knowledge, fostering deeper understanding and skill development. Unlike Traditional Apprenticeship, which centers on hands-on training under a skilled mentor, PBL integrates interdisciplinary concepts and student-driven inquiry within a structured academic framework.
Understanding Traditional Apprenticeship
Traditional apprenticeship emphasizes hands-on learning through direct mentorship within a trade or craft, allowing apprentices to acquire practical skills by working alongside experienced professionals. This method fosters deep industry-specific knowledge and craftsmanship over time, often involving a gradual increase in responsibility. Unlike project-based learning, traditional apprenticeship relies heavily on real-world experience and repetition within a structured environment to develop expertise.
Core Objectives and Learning Outcomes
Project-Based Learning emphasizes critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving by engaging students in active projects that simulate professional environments. Traditional Apprenticeship focuses on skill mastery and hands-on experience under the direct supervision of a skilled mentor, ensuring practical knowledge transfer within a specific trade. Core learning outcomes for Project-Based Learning include creativity, communication, and adaptability, while Traditional Apprenticeship prioritizes technical proficiency, discipline, and immediate applicability of skills.
Instructional Design and Structure
Project-Based Learning (PBL) employs an instructional design centered on active, learner-driven exploration of real-world problems, promoting critical thinking and collaborative skills through structured project phases such as initiation, planning, execution, and reflection. In contrast, Traditional Apprenticeship relies on a master-apprentice hierarchical structure emphasizing observational learning, skill replication, and incremental responsibility within a defined trade or craft, often lacking formalized instructional frameworks. PBL's modular and flexible design allows for interdisciplinary integration and assessment strategies, whereas Apprenticeship's structure prioritizes hands-on experience and tacit knowledge transfer within a consistent, time-based progression.
Assessment Approaches: Projects vs Skills Demonstration
Project-based learning assessment emphasizes evaluating comprehensive project outcomes through rubrics measuring critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration, ensuring holistic skill development. Traditional apprenticeship assessment centers on direct skills demonstration, where mentors observe and verify proficiency in specific tasks and practical techniques within real work environments. Combining project evaluations with hands-on skills validation offers a balanced approach to measuring both theoretical understanding and practical expertise.
Roles of Educators and Mentors
Educators in Project-Based Learning facilitate student-centered inquiry, guiding learners to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills through real-world projects. In Traditional Apprenticeship, mentors provide hands-on training and direct skill transmission, emphasizing mastery through practical experience under close supervision. Both roles require adaptive communication techniques to effectively support learner progression within their respective instructional frameworks.
Industry Relevance and Career Pathways
Project-Based Learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world problem solving, directly aligning with current industry demands by integrating modern technologies and collaborative workflows. Traditional Apprenticeship offers deep, specialized skill development through guided mentorship within established trade practices, fostering strong networks in specific career pathways. Both approaches enhance industry relevance but differ in scope--Project-Based Learning promotes adaptability across multiple sectors, while Apprenticeships provide focused expertise for defined vocational tracks.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
Project-based learning fosters critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills by engaging students in active, collaborative projects, but may lack the structured guidance found in traditional apprenticeship models. Traditional apprenticeships provide hands-on experience under expert supervision, ensuring mastery of specific skills, yet they can be limited in exposing learners to diverse, interdisciplinary knowledge. Both methods support skill development effectively, though project-based learning emphasizes innovation and adaptability, while apprenticeships prioritize specialized expertise and direct mentorship.
Choosing the Right Approach for Learners
Project-Based Learning emphasizes hands-on problem-solving and interdisciplinary collaboration, fostering critical thinking and adaptability in diverse learning environments. Traditional Apprenticeship offers direct mentorship and skill mastery through real-world experience, ideal for learners seeking structured guidance in specific trades or professions. Selecting the right approach depends on learner goals, with PBL suited for developing innovation and independent learning, while apprenticeships prioritize practical expertise and industry-specific competencies.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com