Procedural knowledge refers to the understanding of how to perform tasks and processes, often gained through practice and experience. It encompasses skills such as riding a bike, playing an instrument, or coding, which are difficult to verbalize but essential for everyday activities. Discover how mastering procedural knowledge can enhance your abilities and productivity by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
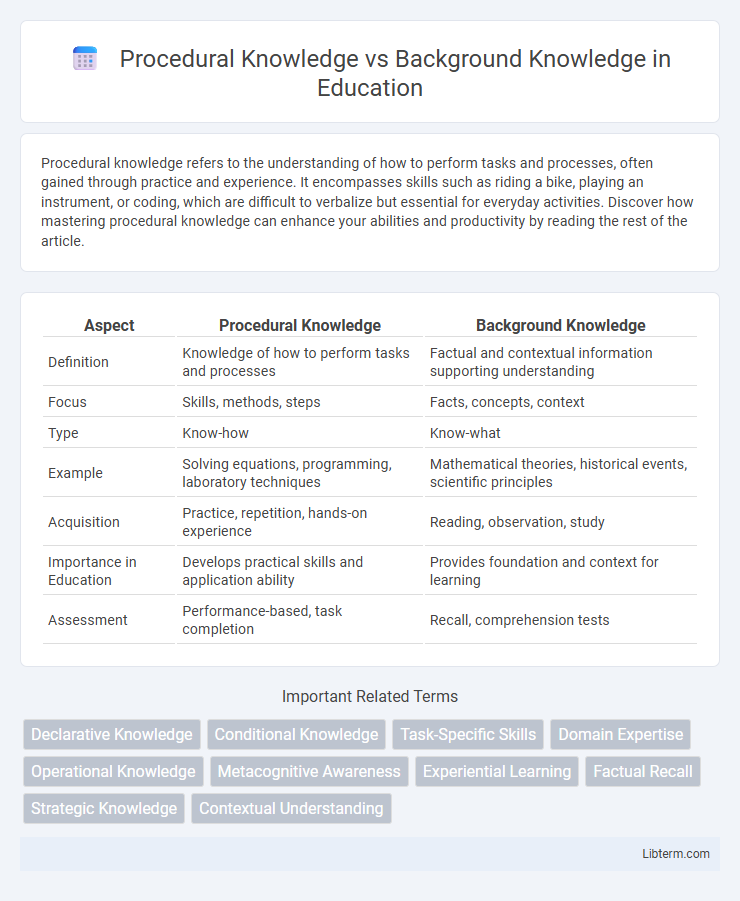
| Aspect | Procedural Knowledge | Background Knowledge |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Knowledge of how to perform tasks and processes | Factual and contextual information supporting understanding |
| Focus | Skills, methods, steps | Facts, concepts, context |
| Type | Know-how | Know-what |
| Example | Solving equations, programming, laboratory techniques | Mathematical theories, historical events, scientific principles |
| Acquisition | Practice, repetition, hands-on experience | Reading, observation, study |
| Importance in Education | Develops practical skills and application ability | Provides foundation and context for learning |
| Assessment | Performance-based, task completion | Recall, comprehension tests |
Understanding Procedural Knowledge
Understanding procedural knowledge involves recognizing it as the ability to perform tasks through skills and actions, distinct from background knowledge which refers to factual information and concepts. Procedural knowledge emphasizes "knowing how," such as executing techniques in cooking, software use, or machine operation, relying on practice and experience for mastery. This form of knowledge is often implicit, stored in memory as sequences of actions rather than explicit facts, making it critical for skill acquisition and problem-solving in dynamic environments.
Defining Background Knowledge
Background knowledge encompasses the information, facts, and concepts that individuals have accumulated through previous experiences and learning, serving as a cognitive foundation for understanding new information. Procedural knowledge, in contrast, refers to the skills and processes required to perform tasks, often described as "knowing how" versus "knowing what" which defines background knowledge. This distinction highlights background knowledge as essential for comprehension and context, while procedural knowledge is crucial for task execution and problem-solving.
Key Differences Between Procedural and Background Knowledge
Procedural knowledge involves understanding how to perform tasks or processes, emphasizing skills and step-by-step actions, whereas background knowledge consists of factual information and concepts accumulated from experience or learning. Procedural knowledge is often tacitative and action-oriented, guiding practical execution, while background knowledge provides the contextual framework necessary for comprehension and decision-making. These differences highlight procedural knowledge as "knowing how" and background knowledge as "knowing that," essential distinctions in cognitive psychology and educational theory.
The Role of Procedural Knowledge in Learning
Procedural knowledge, which involves understanding how to perform tasks and processes, plays a crucial role in learning by enabling the application of skills in real-world scenarios. It complements background knowledge by transforming theoretical understanding into actionable steps, improving problem-solving and decision-making capabilities. Mastery of procedural knowledge enhances cognitive efficiency and supports the development of expertise across various disciplines.
Importance of Background Knowledge in Comprehension
Background knowledge plays a critical role in comprehension by providing a mental framework that allows individuals to connect new information with what they already understand. It facilitates the interpretation of texts, enabling readers to infer meaning, recognize context, and grasp complex concepts more efficiently. Research shows that strong background knowledge significantly improves reading comprehension and learning outcomes across diverse subjects.
How Procedural Knowledge Enhances Skill Acquisition
Procedural knowledge, which involves the understanding of how to perform specific tasks or processes, enhances skill acquisition by enabling learners to apply rules and actions directly in practical scenarios. Unlike background knowledge that provides theoretical or factual information, procedural knowledge facilitates the development of expertise through repeated practice and real-time problem-solving. This hands-on approach builds automaticity and fluency, crucial for mastering complex skills in fields such as programming, surgery, or musical instrument performance.
Building Strong Background Knowledge for Success
Building strong background knowledge enhances comprehension and problem-solving by providing a rich framework of facts, concepts, and context that supports the application of procedural knowledge. Research shows students with extensive background knowledge perform better in critical thinking and transfer skills across disciplines, as they can efficiently connect new information to existing schemas. Emphasizing vocabulary development, domain-specific content, and real-world experiences cultivates a robust knowledge base essential for academic success and lifelong learning.
Interplay Between Procedural and Background Knowledge
Procedural knowledge, which involves knowing how to perform tasks, interacts dynamically with background knowledge, the foundational facts and concepts that inform understanding. Effective problem-solving relies on the seamless integration of procedural skills and relevant background knowledge to adapt strategies and apply principles accurately. This interplay enhances learning efficiency by allowing individuals to contextualize actions within a broader knowledge framework.
Teaching Strategies for Developing Both Knowledge Types
Effective teaching strategies for procedural knowledge emphasize hands-on activities, step-by-step instructions, and guided practice to help students master skills and processes. To develop background knowledge, educators utilize content-rich texts, discussions, and multimedia resources that build subject understanding and context. Combining both approaches through integrated lessons enhances students' ability to apply learned procedures within a strong conceptual framework.
Real-World Examples: Applying Procedural vs. Background Knowledge
Procedural knowledge involves knowing how to perform specific tasks, such as operating a software program or assembling machinery, while background knowledge encompasses understanding the context or concepts behind those tasks, like the principles of computer science or mechanical engineering. For instance, a chef uses procedural knowledge to follow a recipe step-by-step, whereas background knowledge helps them understand flavor pairings and cooking techniques to adapt recipes creatively. In fields like healthcare, procedural knowledge is critical for performing medical procedures accurately, whereas background knowledge enables practitioners to diagnose conditions and make informed decisions based on a patient's history and symptoms.
Procedural Knowledge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com