Processing time directly impacts the efficiency and satisfaction of your service experience by determining how quickly tasks or requests are completed. Faster processing times can lead to improved productivity and customer retention, while delays may cause frustration and lost opportunities. Explore the rest of the article to understand how optimizing processing time benefits your operations and how you can implement effective strategies.
Table of Comparison
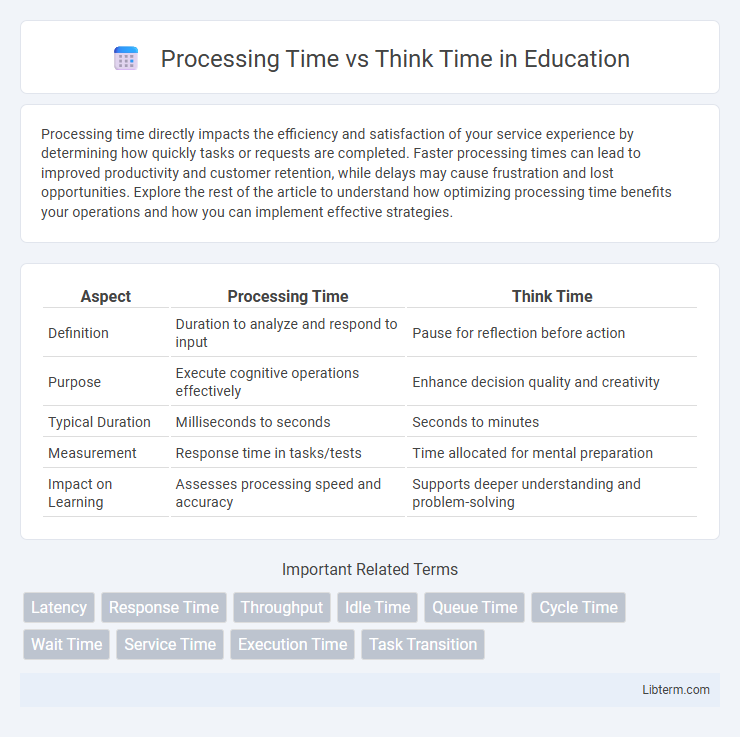
| Aspect | Processing Time | Think Time |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Duration to analyze and respond to input | Pause for reflection before action |
| Purpose | Execute cognitive operations effectively | Enhance decision quality and creativity |
| Typical Duration | Milliseconds to seconds | Seconds to minutes |
| Measurement | Response time in tasks/tests | Time allocated for mental preparation |
| Impact on Learning | Assesses processing speed and accuracy | Supports deeper understanding and problem-solving |
Introduction to Processing Time and Think Time
Processing time refers to the duration a system or resource takes to complete a specific task or transaction, reflecting the efficiency and speed of operations. Think time denotes the interval between the completion of one request and the initiation of the next, representing user contemplation or decision-making periods. Analyzing both processing time and think time is critical for accurate performance modeling and optimizing system throughput.
Defining Processing Time
Processing time refers to the duration a system or processor takes to complete a specific task or operation from start to finish, excluding any idle or waiting periods. It encompasses the actual computational work, such as executing instructions, data retrieval, and performing calculations, directly impacting overall system performance. Accurate measurement of processing time is critical for optimizing algorithms and improving response efficiency in computing environments.
Understanding Think Time
Think Time refers to the deliberate pause a user takes to process information, make decisions, or formulate responses during interactions with a system. It plays a critical role in accurately simulating real-world user behavior in performance testing by reflecting natural cognitive delays between actions. Distinguishing Think Time from Processing Time ensures more realistic load patterns and better assessment of a system's responsiveness under actual operating conditions.
Key Differences Between Processing Time and Think Time
Processing time refers to the duration a system or application spends executing a specific task or request, while think time denotes the interval a user takes to consider or respond before initiating the next action. Key differences include that processing time is system-driven and measurable through performance metrics, whereas think time is user-driven and varies based on individual decision-making. Understanding these distinctions aids in accurately modeling user behavior and system performance in load testing scenarios.
Importance of Processing Time in Workflows
Processing time directly impacts overall workflow efficiency by determining how quickly tasks are completed and resources are freed for subsequent activities. Reducing processing time enhances system throughput and minimizes bottlenecks in production lines or data pipelines, enabling faster delivery and improved customer satisfaction. Optimizing processing time through automation and streamlined protocols is critical for maintaining competitive advantages and operational scalability.
The Role of Think Time in Decision Making
Think time plays a crucial role in decision making by allowing individuals to process information and evaluate options before responding, which improves accuracy and reduces impulsive errors. Unlike processing time, which is the duration taken to execute a task or compute a response, think time involves cognitive deliberation that enhances problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Optimizing think time can lead to more informed and effective decisions in both human-computer interaction and real-world scenarios.
Impact on Productivity and Efficiency
Processing Time directly affects productivity by determining the speed at which tasks are completed, with shorter processing times leading to higher output rates. Think Time, or the pause between tasks for decision-making or cognitive processing, influences efficiency by allowing for error reduction and improved quality, although excessive Think Time can cause delays. Optimizing the balance between minimal Processing Time and adequate Think Time enhances overall workflow efficiency, reducing bottlenecks and maximizing productive capacity.
Measuring and Optimizing Processing Time
Processing time measures the actual duration a system takes to complete a specific task, excluding any delays or waiting periods like think time, which represents the pause between user actions. To optimize processing time, analyzing server logs and using profiling tools such as CPU and memory usage monitors can identify bottlenecks and inefficient code segments. Implementing strategies like query optimization, caching, and parallel processing significantly reduces processing time, improving overall system performance and user experience.
Strategies to Reduce Think Time
Reducing think time in user interactions can significantly enhance overall system efficiency by minimizing delays between processing cycles. Implementing predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms enables the anticipation of user decisions, thereby preloading necessary resources and shortening response intervals. Optimizing user interface design through intuitive workflows and real-time feedback mechanisms also streamlines cognitive load, effectively decreasing the time users spend deliberating before triggering system actions.
Balancing Processing and Think Time for Optimal Performance
Balancing processing time and think time is crucial for optimizing system performance, as processing time measures the duration a system spends handling tasks, while think time reflects user or system pause intervals between actions. Minimizing processing time without adequate think time can lead to resource bottlenecks, whereas excessive think time may cause underutilization of processing capabilities. Achieving optimal performance requires tuning these intervals to match workload characteristics and resource availability, ensuring efficient throughput and responsiveness.
Processing Time Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com