Curriculum articulation ensures seamless alignment between educational programs, facilitating smooth student transitions and consistent learning outcomes. Effective articulation supports your academic progression by clearly mapping course equivalencies and prerequisites across institutions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how curriculum articulation can enhance your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
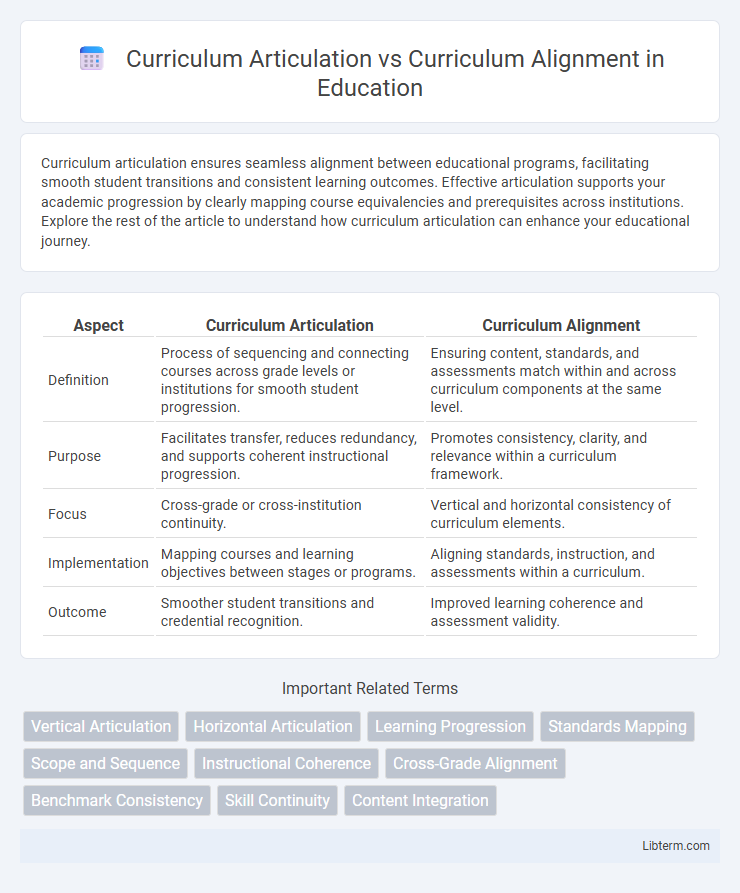
| Aspect | Curriculum Articulation | Curriculum Alignment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of sequencing and connecting courses across grade levels or institutions for smooth student progression. | Ensuring content, standards, and assessments match within and across curriculum components at the same level. |
| Purpose | Facilitates transfer, reduces redundancy, and supports coherent instructional progression. | Promotes consistency, clarity, and relevance within a curriculum framework. |
| Focus | Cross-grade or cross-institution continuity. | Vertical and horizontal consistency of curriculum elements. |
| Implementation | Mapping courses and learning objectives between stages or programs. | Aligning standards, instruction, and assessments within a curriculum. |
| Outcome | Smoother student transitions and credential recognition. | Improved learning coherence and assessment validity. |
Introduction to Curriculum Articulation and Alignment
Curriculum articulation defines the systematic coordination of educational content across grade levels to ensure smooth student progression without gaps or redundancies. Curriculum alignment refers to the process of matching instructional objectives, teaching methods, and assessments with standards to maintain consistency and relevance. Both concepts serve to optimize curriculum coherence but operate distinctly: articulation emphasizes sequence and continuity, while alignment ensures content congruence and compliance with expected learning outcomes.
Defining Curriculum Articulation
Curriculum articulation refers to the deliberate process of organizing and sequencing educational content across different grade levels or courses to ensure a coherent and logical progression of student learning. It involves mapping out learning objectives, skills, and competencies to avoid gaps or unnecessary overlaps in instruction. Effective curriculum articulation supports smooth transitions between educational stages, promoting cumulative knowledge and skill development.
Understanding Curriculum Alignment
Curriculum alignment ensures that learning objectives, instructional methods, and assessments are consistently connected across all grade levels to promote coherent student progress toward educational standards. Understanding curriculum alignment involves examining the vertical and horizontal integration of content to prevent gaps or redundancies in knowledge delivery. Effective alignment supports seamless transitions between courses and grades, optimizing student learning outcomes by maintaining clear, targeted expectations throughout the education system.
Key Differences Between Articulation and Alignment
Curriculum articulation focuses on sequencing and ensuring smooth student progression between educational levels or institutions, emphasizing clear communication and transferability of credits. Curriculum alignment concentrates on synchronizing learning objectives, instructional methods, and assessments within and across grade levels to maintain consistency and coherence in educational standards. Key differences include articulation's role in external transitions versus alignment's focus on internal curriculum coherence and standardized learning outcomes.
Purpose and Goals of Curriculum Articulation
Curriculum articulation ensures seamless progression of learning outcomes across different educational levels by clearly defining course content, skills, and competencies to avoid gaps and redundancies. Its primary purpose is to create cohesive academic pathways that facilitate student transfer and credit recognition between institutions. Curriculum alignment, in contrast, focuses on matching instructional strategies and assessments with learning objectives within a single program or course to improve educational effectiveness.
Objectives and Benefits of Curriculum Alignment
Curriculum alignment ensures that learning objectives, instructional materials, and assessments are cohesively designed to promote consistent student outcomes across grade levels and subjects, enhancing educational effectiveness. The primary benefits of curriculum alignment include improved student achievement through clear learning goals, streamlined teacher collaboration, and reduced content gaps or redundancies. Unlike curriculum articulation, which sequences content across grades to maintain continuity, curriculum alignment emphasizes coherence and consistency within and across courses to optimize teaching and learning processes.
Challenges in Implementing Articulation and Alignment
Challenges in implementing curriculum articulation include inconsistent communication between institutions, varying academic standards, and the complexity of credit transfer processes, which can impede seamless student transitions. Curriculum alignment faces difficulties such as ensuring coherence across diverse disciplines, adjusting curricula to meet evolving industry standards, and overcoming resistance from faculty to modify established content. Both processes require continuous collaboration, clear guidelines, and flexible frameworks to address discrepancies and maintain educational quality.
Best Practices for Effective Curriculum Integration
Curriculum articulation ensures a smooth transition between educational stages by mapping and sequencing content to avoid gaps and redundancies, while curriculum alignment focuses on harmonizing learning objectives, assessments, and instructional strategies within a specific grade or course. Best practices for effective curriculum integration involve collaborative planning among educators, use of standardized frameworks like Common Core or NGSS, and continuous data-driven evaluation to ensure coherence and relevance across academic programs. Implementing cross-disciplinary projects and vertical teaming promotes deeper understanding and skill transfer, reinforcing both articulation and alignment for student success.
Impact on Student Learning and Outcomes
Curriculum articulation ensures a seamless transition between grade levels or courses, preventing gaps and redundancies that negatively affect student learning progression and mastery of skills. Curriculum alignment systematically matches instructional objectives, teaching methods, and assessments to state standards, directly enhancing the relevance and rigor of student outcomes. Effective implementation of both processes improves coherence, equity, and consistency in education, which collectively supports higher student achievement and readiness for subsequent academic challenges.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting between curriculum articulation and curriculum alignment depends on the specific educational goals and context. Curriculum articulation ensures a seamless progression of content across grade levels, preventing gaps and redundancies, while curriculum alignment focuses on the consistency of instructional methods and assessments with established standards. Educators should evaluate their institution's needs to implement the approach that best enhances student learning outcomes and curricular coherence.
Curriculum Articulation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com