Explicit instruction provides clear, direct teaching of specific skills or concepts, ensuring learners understand exactly what is expected. This approach minimizes confusion and enhances retention by focusing on step-by-step guidance and immediate feedback. Discover how explicit instruction can transform your learning experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
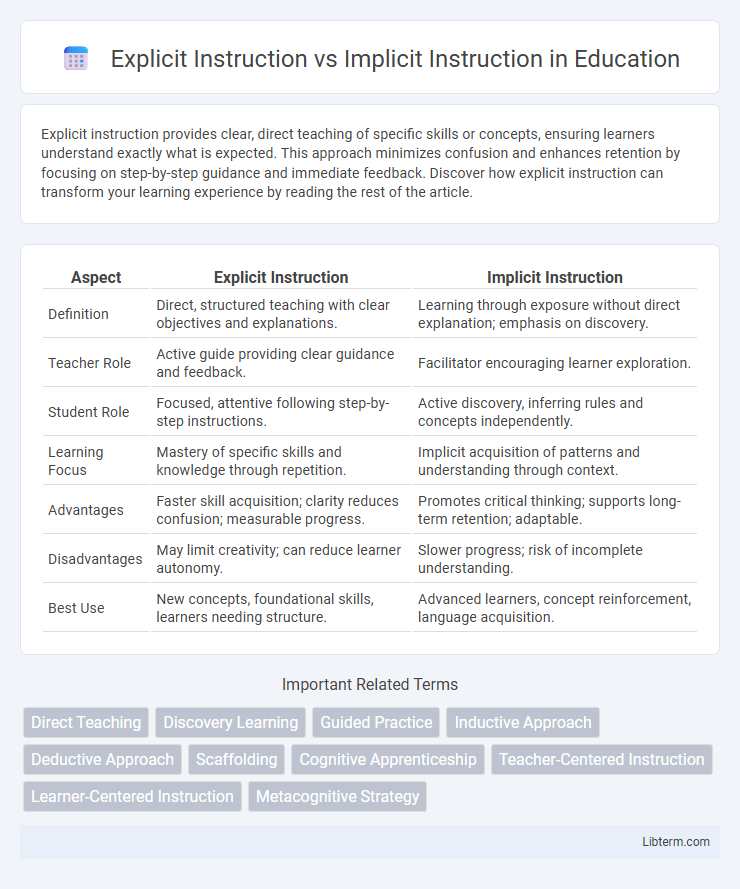
| Aspect | Explicit Instruction | Implicit Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct, structured teaching with clear objectives and explanations. | Learning through exposure without direct explanation; emphasis on discovery. |
| Teacher Role | Active guide providing clear guidance and feedback. | Facilitator encouraging learner exploration. |
| Student Role | Focused, attentive following step-by-step instructions. | Active discovery, inferring rules and concepts independently. |
| Learning Focus | Mastery of specific skills and knowledge through repetition. | Implicit acquisition of patterns and understanding through context. |
| Advantages | Faster skill acquisition; clarity reduces confusion; measurable progress. | Promotes critical thinking; supports long-term retention; adaptable. |
| Disadvantages | May limit creativity; can reduce learner autonomy. | Slower progress; risk of incomplete understanding. |
| Best Use | New concepts, foundational skills, learners needing structure. | Advanced learners, concept reinforcement, language acquisition. |
Understanding Explicit Instruction: Definition and Key Features
Explicit instruction is a teaching method characterized by clear, direct teaching of concepts and skills, where learning objectives are clearly stated and step-by-step guidance is provided. Key features include systematic explanation, modeling of tasks, guided practice, and immediate feedback to ensure student comprehension and mastery. This approach emphasizes structured, teacher-led delivery to make learning transparent and accessible.
What is Implicit Instruction? Core Characteristics Explained
Implicit instruction is a learning approach where students acquire knowledge and skills through indirect exposure and natural language use without direct explanation of rules or concepts. Core characteristics include reliance on contextual clues, pattern recognition, and learner intuition to internalize information subconsciously. This method emphasizes immersion and discovery-based learning, contrasting with explicit instruction's clear, structured, and systematic teaching techniques.
Historical Perspectives on Instructional Methods
Explicit instruction, rooted in behaviorist theories from the early 20th century, emphasizes clear, structured teaching with direct teacher guidance and modeling, reflecting the influence of educators like John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner. In contrast, implicit instruction, influenced by constructivist theorists such as Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky in the mid-20th century, supports learning through discovery, immersion, and social interaction without overt explanation. Historical shifts from explicit to implicit methods mirror evolving understandings of cognitive development and language acquisition within educational psychology.
Cognitive Theories Underlying Explicit vs. Implicit Instruction
Explicit instruction relies on cognitive load theory by reducing learner's working memory demands through clear, structured guidance, facilitating schema acquisition. Implicit instruction aligns with constructivist and discovery learning theories, promoting unconscious learning via exposure and pattern recognition in authentic contexts. Both approaches engage different memory systems: explicit instruction activates declarative memory, while implicit instruction strengthens procedural memory through repetition and practice.
Benefits of Explicit Instruction in the Classroom
Explicit instruction enhances student comprehension by providing clear, direct teaching of concepts, which reduces ambiguity and accelerates learning. This approach supports diverse learners by breaking down complex skills into manageable steps, ensuring mastery before progressing. Research indicates that explicit instruction significantly improves academic achievement, especially in literacy and math, by fostering structured practice and immediate feedback.
Advantages of Implicit Instruction for Student Learning
Implicit instruction fosters natural language acquisition by immersing students in contextualized, meaningful communication, enhancing their ability to infer rules without memorization. This method promotes deeper retention and transfer of knowledge by engaging learners in authentic experiences rather than isolated drills. Students benefit from reduced cognitive load, enabling more fluid and spontaneous use of language and concepts in real-world situations.
Challenges and Limitations of Explicit Instruction
Explicit instruction often faces challenges such as student dependency on teacher guidance, which can hinder the development of independent problem-solving skills. Its rigid structure may not accommodate diverse learning styles or promote deeper conceptual understanding, limiting flexibility in instruction. Furthermore, explicit instruction can be time-intensive, reducing opportunities for exploration and critical thinking in the classroom.
Potential Drawbacks of Implicit Instruction
Implicit instruction may hinder learning efficiency due to its reliance on learner inference, often leading to misconceptions and incomplete understanding. Without clear guidance, students might struggle to grasp complex concepts, resulting in slower skill acquisition and increased frustration. This approach can also create challenges in assessing comprehension, as learners' progress is less transparent compared to explicit instruction methods.
Comparing Effectiveness: When to Use Explicit or Implicit Instruction
Explicit instruction proves highly effective for teaching complex skills or new concepts where clear, structured guidance is essential for comprehension and mastery. Implicit instruction excels in contexts requiring intuitive learning, such as language acquisition or skill automation, where learners benefit from exposure and practice without overt explanation. Selecting between explicit and implicit instruction depends on the learner's prior knowledge, the task complexity, and the desired learning outcomes.
Practical Strategies for Blending Explicit and Implicit Approaches
Blending explicit and implicit instruction involves integrating direct teaching of concepts with natural, context-rich learning experiences to enhance student comprehension and retention. Practical strategies include using clear explanations and modeling of skills followed by immersive, meaningful practice that encourages discovery and application in authentic situations. Employing formative assessments to monitor progress enables targeted adjustments that balance clarity with exploratory learning, maximizing cognitive engagement and mastery.
Explicit Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com