Integration seamlessly combines different systems and processes to improve efficiency and data flow within your organization. By enabling better communication between software and devices, integration reduces errors and saves time. Explore the rest of the article to discover how integration can transform your operations.
Table of Comparison
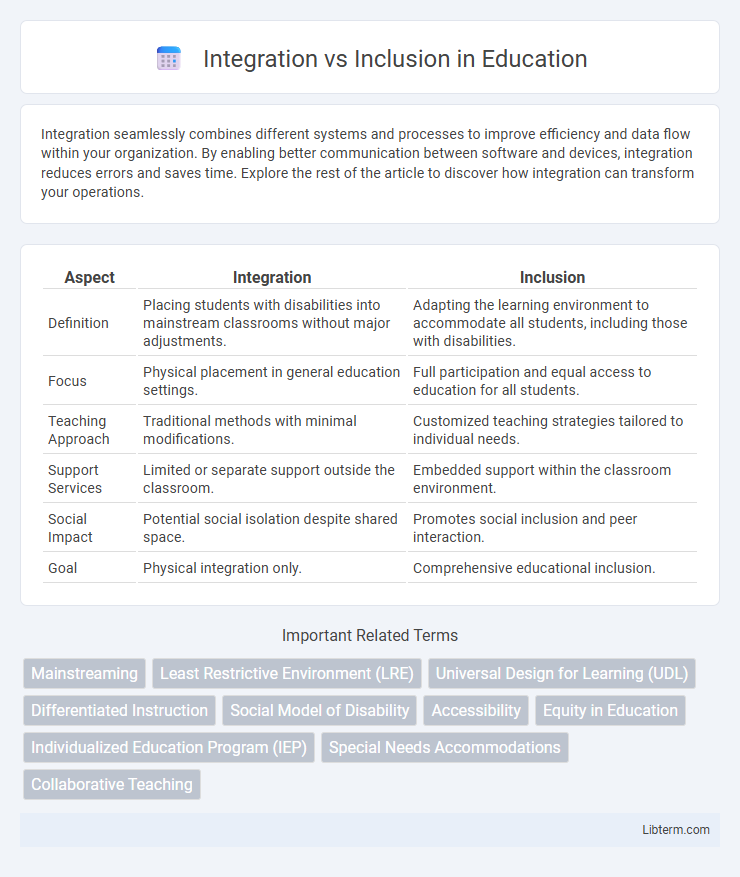
| Aspect | Integration | Inclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Placing students with disabilities into mainstream classrooms without major adjustments. | Adapting the learning environment to accommodate all students, including those with disabilities. |
| Focus | Physical placement in general education settings. | Full participation and equal access to education for all students. |
| Teaching Approach | Traditional methods with minimal modifications. | Customized teaching strategies tailored to individual needs. |
| Support Services | Limited or separate support outside the classroom. | Embedded support within the classroom environment. |
| Social Impact | Potential social isolation despite shared space. | Promotes social inclusion and peer interaction. |
| Goal | Physical integration only. | Comprehensive educational inclusion. |
Defining Integration and Inclusion
Integration refers to placing individuals from diverse backgrounds into existing systems or environments without fundamentally altering the structure or culture of those systems. Inclusion goes beyond mere placement by actively transforming organizational practices and attitudes to ensure full participation, equity, and belonging for all members. Defining integration emphasizes physical or social proximity, while inclusion centers on meaningful involvement and empowerment within the community or institution.
Historical Context of Integration and Inclusion
The historical context of integration often traces back to civil rights movements in the mid-20th century, emphasizing the physical placement of marginalized groups, particularly racial minorities, into mainstream institutions. Inclusion evolved later as a broader concept, promoting not only physical presence but also active participation, acceptance, and equal access to opportunities for individuals with diverse abilities and backgrounds. This shift reflects a deeper understanding of social equity and the need for systemic changes beyond mere integration.
Key Differences Between Integration and Inclusion
Integration focuses on placing students with disabilities into existing mainstream classrooms, often requiring them to adapt to the established environment, whereas inclusion involves restructuring the educational setting to accommodate diverse learning needs equitably. Inclusion emphasizes collaborative teaching strategies, individualized support, and full participation, promoting belonging and academic success for all students. Key differences lie in the approach to adaptation: integration centers on physical placement, while inclusion prioritizes systemic change and equity in education.
Benefits of Inclusion Over Integration
Inclusion fosters a sense of belonging by actively involving individuals with diverse abilities in all aspects of learning, improving social skills and self-esteem. It promotes equitable access to resources and personalized support, leading to better academic outcomes compared to mere physical placement in integrated settings. Inclusive environments encourage collaboration and understanding, reducing stigma and enhancing the overall community dynamic.
Challenges in Implementing Inclusive Practices
Challenges in implementing inclusive practices often stem from limited resources, inadequate teacher training, and resistance to change within educational institutions. Schools may struggle with adapting curricula and providing necessary support services for students with diverse learning needs, impacting the effectiveness of inclusion. Overcoming these barriers requires comprehensive policy frameworks, continuous professional development, and fostering a culture of acceptance and collaboration.
Case Studies: Schools and Workplaces
Case studies in schools reveal that inclusive education promotes better academic and social outcomes by adapting environments to meet diverse needs, contrasting with integration approaches that place students in regular classrooms without sufficient support. In workplaces, inclusion strategies demonstrate higher employee satisfaction and retention rates by fostering equitable participation and addressing systemic barriers, whereas integration often limits minority employees to assimilation without structural change. Data from multiple sectors emphasize that inclusion, unlike mere integration, requires proactive policy and cultural shifts to achieve meaningful equity.
Role of Policy in Fostering Inclusion
Policies play a crucial role in fostering inclusion by establishing legal frameworks and guidelines that ensure equal access to education, employment, and social services for all individuals, including those with disabilities. Inclusive policies promote systemic changes that go beyond mere physical integration, emphasizing the adaptation of environments, curricula, and attitudes to accommodate diverse needs. Effective policy implementation involves collaboration among government agencies, educators, and community stakeholders to create supportive, equitable opportunities that enable full participation and belonging.
Measuring Success: Metrics and Outcomes
Measuring success in integration involves assessing the extent to which individuals physically participate in mainstream settings, often using metrics like attendance rates and academic performance. Inclusion success metrics prioritize qualitative outcomes such as social engagement, sense of belonging, and individualized support effectiveness, evaluated through surveys and behavioral observations. Data-driven approaches combine quantitative academic results with qualitative social indicators to provide a comprehensive understanding of both integration and inclusion outcomes.
Voices from the Community: Experiences and Perspectives
Voices from the community highlight that integration often results in physical placement without full participation, whereas inclusion fosters genuine belonging and respect for diverse abilities. Parents and educators commonly report that inclusion promotes meaningful social interactions and academic growth by adapting environments to meet all learners' needs. Community members emphasize that inclusive practices challenge stigma and empower individuals with disabilities through shared experiences and mutual support.
Future Directions for True Inclusion
Future directions for true inclusion emphasize transforming educational and social environments to accommodate diverse needs from the outset rather than retrofitting existing systems, fostering a culture where all individuals feel valued and supported. Emphasizing personalized learning, universal design for learning (UDL), and community collaboration can enhance accessibility and engagement for people with disabilities. Technology-driven tools, policy reforms, and ongoing professional development play critical roles in moving beyond integration--where individuals are merely placed in mainstream settings--to authentic inclusion marked by full participation and equity.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com