Licensure ensures that professionals meet established standards of competence and ethics required in their field, protecting public safety and enhancing credibility. Obtaining your license involves fulfilling specific educational, examination, and experience criteria set by regulatory authorities. Explore the rest of the article to understand the detailed licensure process and its importance across various professions.
Table of Comparison
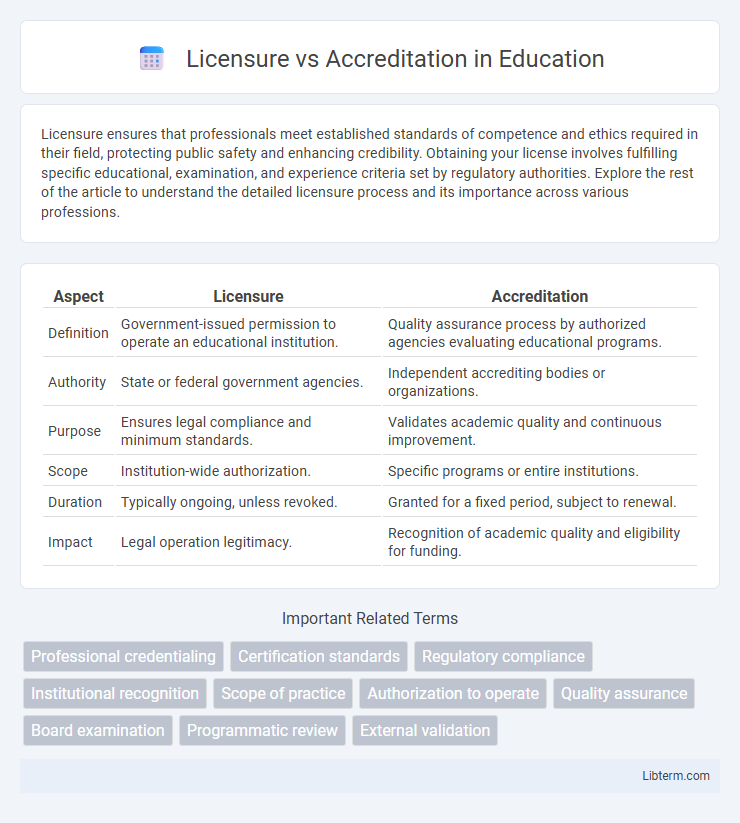
| Aspect | Licensure | Accreditation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government-issued permission to operate an educational institution. | Quality assurance process by authorized agencies evaluating educational programs. |
| Authority | State or federal government agencies. | Independent accrediting bodies or organizations. |
| Purpose | Ensures legal compliance and minimum standards. | Validates academic quality and continuous improvement. |
| Scope | Institution-wide authorization. | Specific programs or entire institutions. |
| Duration | Typically ongoing, unless revoked. | Granted for a fixed period, subject to renewal. |
| Impact | Legal operation legitimacy. | Recognition of academic quality and eligibility for funding. |
Introduction to Licensure and Accreditation
Licensure is a mandatory process whereby a government agency grants legal permission to operate a facility or practice a profession, ensuring compliance with specific regulatory standards and protecting public safety. Accreditation is a voluntary process conducted by independent organizations that assess and recognize an institution or program for meeting predetermined quality standards and academic excellence. Both licensure and accreditation serve crucial roles in maintaining credibility and trust in healthcare, education, and professional fields.
Defining Licensure
Licensure refers to the legal authorization granted by a governmental agency that allows professionals to practice within a specific field, ensuring compliance with established standards and regulations. It serves as a mandatory credential that protects public safety by verifying qualifications and competence. Unlike accreditation, which evaluates institutions or programs, licensure focuses on the individual's right to operate professionally within regulated industries such as healthcare, engineering, and law.
What Is Accreditation?
Accreditation is a voluntary process in which an independent accrediting body evaluates an educational institution or program to ensure it meets established standards of quality and effectiveness. It serves as a marker of credibility, signifying that the institution adheres to rigorous criteria related to curriculum, faculty qualifications, and student services. Unlike licensure, which is a mandatory government approval to operate legally, accreditation focuses on continuous improvement and academic excellence.
Key Differences Between Licensure and Accreditation
Licensure is a mandatory legal requirement granted by government agencies authorizing individuals or institutions to operate and provide specific services, ensuring compliance with minimum standards of safety and competence. Accreditation is a voluntary process conducted by independent accrediting bodies that evaluates institutions or programs against established quality standards to promote excellence and continuous improvement. The key differences lie in licensure being legally required to operate, focusing on basic regulatory compliance, while accreditation emphasizes quality enhancement and public assurance beyond minimum legal standards.
The Purpose and Scope of Licensure
Licensure serves to protect public health and safety by ensuring individuals and organizations meet specific government-mandated standards to legally provide professional services. It involves a rigorous process of evaluation, including examinations and compliance checks, to verify competency within defined scopes of practice. Licensure restricts unauthorized practice by granting formal permission to qualified practitioners, establishing accountability and trust in regulated professions.
The Role of Accreditation in Quality Assurance
Accreditation plays a crucial role in quality assurance by evaluating educational institutions and programs against established standards to ensure consistent academic excellence and institutional effectiveness. Unlike licensure, which grants legal permission to operate, accreditation serves as a voluntary, rigorous peer-review process that enhances credibility and continuous improvement. This external validation fosters trust among students, employers, and stakeholders by verifying that institutions meet or exceed industry benchmarks and educational best practices.
Licensure Processes and Requirements
Licensure processes require healthcare professionals or educational institutions to meet specific state-mandated criteria, including completion of accredited programs, passing standardized examinations, and undergoing background checks. These requirements ensure compliance with legal standards and protection of public safety by verifying the applicant's qualifications and competency. Licensure must be renewed periodically, often necessitating continuing education to maintain eligibility and stay updated with industry regulations.
Accreditation Standards and Evaluation
Accreditation standards are a set of rigorous criteria developed by independent accrediting bodies to assess the quality and effectiveness of educational institutions or programs. Evaluation processes involve comprehensive reviews, including self-assessment, peer reviews, and site visits, to ensure compliance with these standards. Unlike licensure, which grants legal permission to operate within a jurisdiction, accreditation focuses on continuous quality improvement and institutional accountability through recognized benchmarks.
Impact on Professionals and Institutions
Licensure ensures professionals meet state-mandated standards, directly impacting career eligibility, job mobility, and public trust, while accreditation signifies an institution's adherence to quality education and operational excellence, influencing reputation and student enrollment. Professionals rely on licensure for legal authorization to practice, whereas institutions seek accreditation to validate programs and qualify for federal funding. The distinction shapes professional credibility and institutional legitimacy, affecting long-term career development and organizational growth.
Choosing Between Licensure and Accreditation
Choosing between licensure and accreditation depends on legal requirements and industry standards; licensure is mandatory government authorization to operate certain professions or organizations, while accreditation is a voluntary process demonstrating adherence to quality standards set by an independent body. Licensure ensures compliance with regulatory laws, often impacting eligibility for practice or operation, whereas accreditation enhances credibility, consumer trust, and competitive advantage without legal compulsion. Assessing your organization's goals, regulatory environment, and market expectations helps determine whether obtaining licensure, accreditation, or both best supports operational legitimacy and professional reputation.
Licensure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com