School accreditation ensures educational institutions meet established standards of quality and effectiveness, enhancing your child's learning experience and future opportunities. Accreditation involves rigorous evaluation by authorized agencies to verify curriculum relevance, faculty qualifications, and facility adequacy. Explore the rest of this article to understand how accreditation impacts school choice and student success.
Table of Comparison
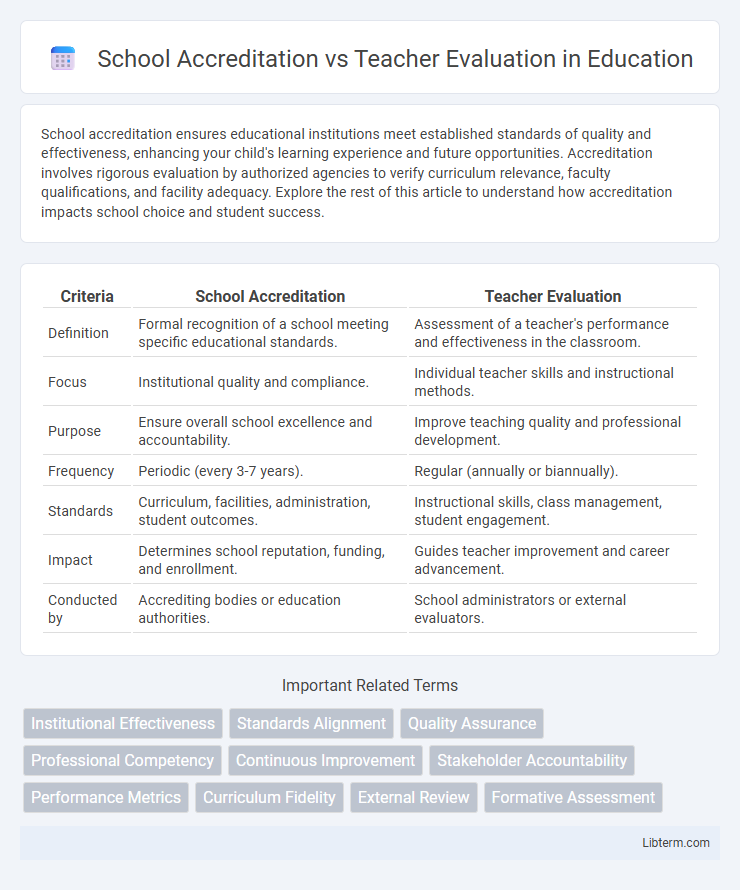
| Criteria | School Accreditation | Teacher Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal recognition of a school meeting specific educational standards. | Assessment of a teacher's performance and effectiveness in the classroom. |
| Focus | Institutional quality and compliance. | Individual teacher skills and instructional methods. |
| Purpose | Ensure overall school excellence and accountability. | Improve teaching quality and professional development. |
| Frequency | Periodic (every 3-7 years). | Regular (annually or biannually). |
| Standards | Curriculum, facilities, administration, student outcomes. | Instructional skills, class management, student engagement. |
| Impact | Determines school reputation, funding, and enrollment. | Guides teacher improvement and career advancement. |
| Conducted by | Accrediting bodies or education authorities. | School administrators or external evaluators. |
Understanding School Accreditation
School accreditation is a comprehensive process that evaluates an educational institution's overall quality based on established standards, including curriculum, governance, facilities, and student services. Unlike teacher evaluation, which assesses individual educator performance, accreditation examines the school's capacity to deliver effective education and foster continuous improvement. Accreditation by recognized agencies such as AdvancED or the Middle States Association ensures accountability, validates institutional credibility, and enhances opportunities for student advancement.
Defining Teacher Evaluation
Teacher evaluation is a systematic process designed to assess educators' performance, effectiveness, and professional growth, often involving classroom observations, student feedback, and standardized test scores. It aims to improve teaching quality by identifying strengths and areas for development, directly impacting student learning outcomes. Unlike school accreditation, which evaluates overall institutional standards and resources, teacher evaluation specifically targets individual educator competencies and instructional practices.
Core Objectives: Accreditation vs. Evaluation
School accreditation focuses on assessing institutional quality against established standards to ensure comprehensive educational effectiveness, while teacher evaluation targets individual performance to enhance instructional skills and student outcomes. Core objectives of accreditation include verifying curriculum quality, resource adequacy, and compliance with regulatory requirements, whereas evaluation prioritizes pedagogical competence, classroom management, and professional development. Both processes aim to improve education but operate at different systemic levels with distinct criteria and impact.
Accreditation Standards and Processes
School accreditation involves comprehensive evaluation based on established standards such as curriculum quality, facility adequacy, student outcomes, and administrative effectiveness, ensuring institutions meet benchmarks set by accrediting bodies like AdvancED or regional agencies. Teacher evaluation focuses specifically on individual educator performance, using criteria like instructional skills, classroom management, and student engagement, often incorporating observations, student assessments, and professional development. Accreditation standards and processes provide a broad framework for institutional quality, whereas teacher evaluations target the continuous improvement of teaching effectiveness within that framework.
Teacher Evaluation Criteria and Methods
Teacher evaluation criteria primarily focus on instructional quality, classroom management, student engagement, and professional development. Methods include direct observations, student performance data analysis, self-assessments, and peer reviews to ensure comprehensive performance measurement. These evaluations aim to improve teaching effectiveness and enhance student learning outcomes through continuous feedback and targeted training.
Impact on Educational Quality
School accreditation establishes a comprehensive framework ensuring institutions meet predefined standards for curriculum, facilities, and governance, directly influencing educational quality by promoting continuous improvement and accountability. Teacher evaluation targets individual instructional effectiveness, providing targeted feedback and professional development opportunities that enhance classroom performance and student outcomes. Together, these processes create a systemic approach to elevating education standards by addressing both institutional integrity and teaching excellence.
Stakeholder Roles in Accreditation and Evaluation
Stakeholders in school accreditation primarily include accreditation agencies, school administrators, and governing bodies responsible for setting and maintaining educational standards, while teacher evaluation involves teachers, school leaders, and sometimes students and parents to assess instructional effectiveness. Accreditation processes emphasize institutional quality assurance, requiring collaboration among boards, faculty, and external reviewers to validate curriculum, facilities, and governance, whereas teacher evaluation focuses on individual performance metrics, professional development, and classroom outcomes. Engaging diverse stakeholders ensures transparency and accountability in both systems, promoting continuous improvement in educational institutions and teaching practices.
Challenges in Implementation
Challenges in implementing school accreditation often include inconsistent criteria across regions, resource limitations, and insufficient training for evaluators, leading to variability in school performance assessment. Teacher evaluation faces obstacles such as subjective measurement, lack of standardized tools, and resistance from educators concerned about fairness and professional development. Both processes require robust data systems and stakeholder engagement to ensure accurate, effective evaluations that drive educational improvement.
Comparative Benefits and Drawbacks
School accreditation offers a comprehensive assessment of an institution's overall quality, ensuring standardized educational environments that promote student outcomes, while teacher evaluation targets individual performance, fostering personalized professional development and instructional improvement. Accreditation provides external validation and accountability across multiple criteria but can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, whereas teacher evaluation delivers direct feedback to educators but may induce stress and variability in evaluation fairness. Balancing both processes enables schools to maintain institutional standards and support teacher growth, optimizing educational effectiveness.
Aligning Accreditation and Evaluation for School Improvement
Aligning school accreditation and teacher evaluation systems enhances overall school improvement by creating a cohesive framework that supports continuous growth and accountability. Accreditation standards often focus on institutional quality and student outcomes, while teacher evaluations target instructional effectiveness; integrating these processes ensures that teaching practices directly contribute to meeting accreditation goals. Synchronizing these elements promotes data-driven decision-making, fosters professional development, and ultimately leads to higher educational performance and student achievement.
School Accreditation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com