Dual enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits while completing their secondary education, accelerating their academic progress and saving on future tuition costs. This program enhances college readiness by exposing students to rigorous coursework and developing critical thinking skills. Explore the benefits and opportunities dual enrollment offers to maximize Your educational journey in the following article.
Table of Comparison
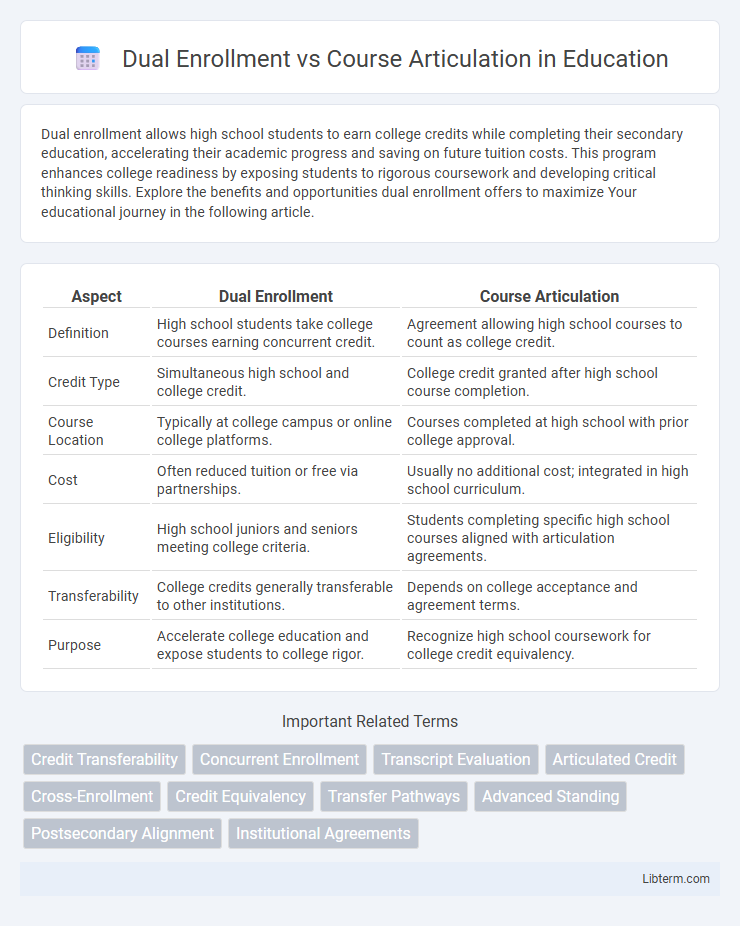
| Aspect | Dual Enrollment | Course Articulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High school students take college courses earning concurrent credit. | Agreement allowing high school courses to count as college credit. |
| Credit Type | Simultaneous high school and college credit. | College credit granted after high school course completion. |
| Course Location | Typically at college campus or online college platforms. | Courses completed at high school with prior college approval. |
| Cost | Often reduced tuition or free via partnerships. | Usually no additional cost; integrated in high school curriculum. |
| Eligibility | High school juniors and seniors meeting college criteria. | Students completing specific high school courses aligned with articulation agreements. |
| Transferability | College credits generally transferable to other institutions. | Depends on college acceptance and agreement terms. |
| Purpose | Accelerate college education and expose students to college rigor. | Recognize high school coursework for college credit equivalency. |
Introduction to Dual Enrollment and Course Articulation
Dual Enrollment allows high school students to enroll in college courses and earn both high school and college credits simultaneously, accelerating their academic progress. Course Articulation involves formal agreements between educational institutions that ensure completed coursework is recognized and transferable for credit towards a college degree. Understanding these options helps students make informed decisions about earning college credit early and aligning their academic pathways.
Defining Dual Enrollment Programs
Dual Enrollment programs allow high school students to enroll in college courses for credit, offering an accelerated path to earning a college degree while still in high school. These programs provide students with exposure to college-level curriculum and instruction, enhancing academic rigor and preparedness for postsecondary education. Unlike course articulation, which transfers credits after completion, dual enrollment integrates college credits directly into the high school experience.
What is Course Articulation?
Course articulation is a formal agreement between high schools and postsecondary institutions that ensures specific courses completed in high school are recognized for college credit. This process clearly defines the equivalency of courses, enabling students to bypass introductory college classes and reduce time to degree completion. Unlike dual enrollment, which involves concurrent enrollment in high school and college courses, course articulation focuses on credit transfer after course completion.
Key Differences Between Dual Enrollment and Course Articulation
Dual Enrollment allows high school students to take college courses for credit while still in high school, earning simultaneous credit for both institutions. Course Articulation involves the formal agreement between high schools and colleges to recognize specific courses as equivalent, ensuring seamless credit transfer after high school completion. The key difference lies in Dual Enrollment offering concurrent enrollment in college-level classes, whereas Course Articulation guarantees credit acceptance for completed coursework.
Benefits of Dual Enrollment for High School Students
Dual Enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits while completing their high school education, accelerating their academic progress and reducing future college costs. This program provides exposure to college-level coursework, enhancing critical thinking skills and improving college readiness. Participation in Dual Enrollment often leads to higher college enrollment rates and increased student motivation.
Advantages of Course Articulation Agreements
Course articulation agreements streamline the transition between high school and college by clearly mapping out which courses transfer for credit, reducing redundancy and saving students time and money. These agreements ensure academic consistency and maintain program integrity by specifying equivalent courses, fostering a smoother and more predictable pathway to degree completion. Institutions benefit from strengthened partnerships, enhancing curriculum alignment and improving student retention and success rates.
Credit Transferability: Dual Enrollment vs Course Articulation
Dual enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits simultaneously with their high school courses, ensuring direct credit transfer to the partnering college or university. Course articulation agreements outline predefined credit transfer pathways between institutions, facilitating course equivalency recognition and smoother credit acceptance during college admission. While dual enrollment guarantees credit that often applies directly to degree requirements, course articulation provides structured validation for credits earned independently, emphasizing institutional compatibility.
Academic and Career Outcomes
Dual enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits, accelerating degree completion and enhancing college readiness, which boosts academic achievement and career prospects. Course articulation agreements facilitate smooth credit transfers between institutions, minimizing redundant coursework and reducing time-to-degree, thereby improving retention and employment opportunities. Both strategies support efficient educational pathways that promote higher graduation rates and better alignment with workforce demands.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Dual Enrollment and Articulation
Factors to consider when choosing between dual enrollment and course articulation include credit transferability, cost, and academic rigor. Dual enrollment offers direct college credit while still in high school, often with reduced tuition, but may vary in acceptance across institutions. Course articulation agreements guarantee credit transfer for specific courses completed at partner schools, providing clarity and consistency in degree progression.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Path for College Readiness
Dual enrollment offers high school students direct college credit through concurrent enrollment in college courses, accelerating degree progress and reducing overall tuition costs. Course articulation agreements establish guaranteed credit transfer between specific high school and college courses, ensuring seamless academic recognition but without the accelerated timeline of dual enrollment. Selecting between dual enrollment and course articulation depends on a student's readiness for college-level work and their goals for credit accumulation, with dual enrollment best for immediate college experience and articulation agreements ideal for credit certainty without concurrent college attendance.
Dual Enrollment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com