Pluridisciplinary approaches integrate multiple academic disciplines to address complex problems, enhancing the depth and breadth of analysis. This method encourages collaboration among experts with diverse perspectives, leading to innovative solutions that single-discipline studies might miss. Discover how pluridisciplinary strategies can transform your research or projects by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
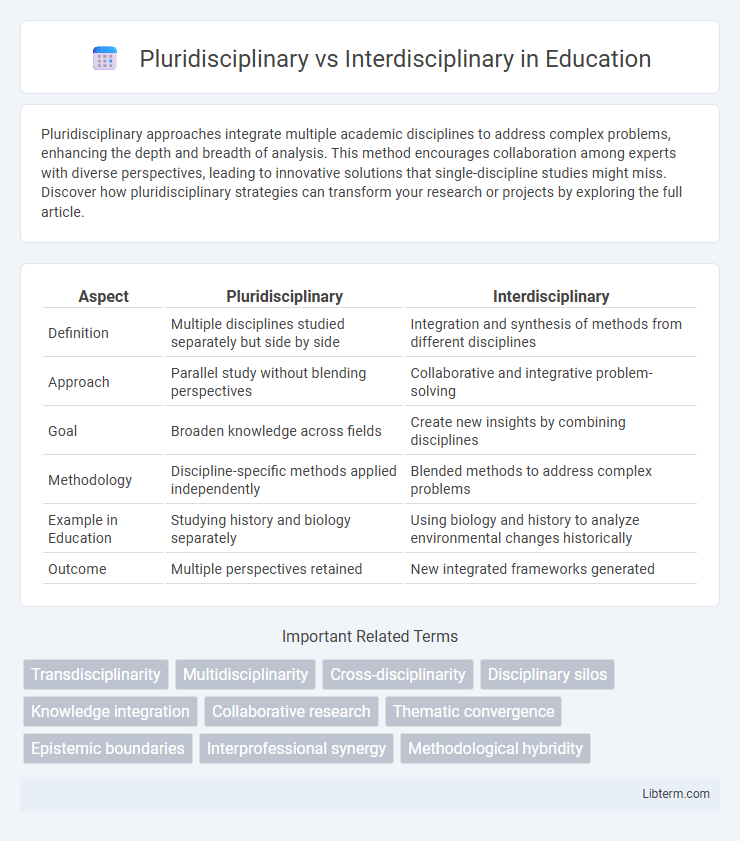
| Aspect | Pluridisciplinary | Interdisciplinary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple disciplines studied separately but side by side | Integration and synthesis of methods from different disciplines |
| Approach | Parallel study without blending perspectives | Collaborative and integrative problem-solving |
| Goal | Broaden knowledge across fields | Create new insights by combining disciplines |
| Methodology | Discipline-specific methods applied independently | Blended methods to address complex problems |
| Example in Education | Studying history and biology separately | Using biology and history to analyze environmental changes historically |
| Outcome | Multiple perspectives retained | New integrated frameworks generated |
Defining Pluridisciplinary and Interdisciplinary Approaches
Pluridisciplinary approaches involve researchers from multiple disciplines working side by side, each contributing their expertise without integrating methods or concepts. Interdisciplinary approaches emphasize collaboration across disciplines to create synthesized frameworks and novel solutions by combining theories and methodologies. Defining these approaches clarifies the extent of integration and cooperation in addressing complex research questions.
Historical Evolution of Academic Collaboration
The historical evolution of academic collaboration highlights a shift from pluridisciplinary approaches, where multiple disciplines work side by side independently, to interdisciplinary methods that integrate insights and methods across fields, fostering deeper innovation and problem solving. Early 20th-century academia primarily favored pluridisciplinarity, emphasizing parallel expertise without blending methodologies, whereas post-World War II developments underscored the value of interdisciplinary synthesis to address complex societal challenges. This transition reflects the growing recognition that holistic understanding and collaborative frameworks drive advancements in research, education, and knowledge production.
Core Principles of Pluridisciplinarity
Pluridisciplinarity involves multiple disciplines working side by side, maintaining their distinct methodologies and perspectives without necessarily integrating them. The core principles emphasize the coexistence of diverse disciplinary approaches, allowing each to contribute independently toward a shared objective. This approach contrasts with interdisciplinarity, which seeks to synthesize knowledge and methods across disciplines to create unified frameworks or solutions.
Key Characteristics of Interdisciplinarity
Interdisciplinarity integrates methods, concepts, and theories from multiple disciplines to create cohesive solutions addressing complex problems. It emphasizes collaboration, knowledge synthesis, and the emergence of new frameworks beyond traditional boundaries. Key characteristics include cross-disciplinary communication, shared goals, and the blending of epistemologies to generate innovative insights.
Differences in Methodology and Integration
Pluridisciplinary research involves parallel contributions from multiple disciplines, each maintaining its own methodologies and perspectives without significant integration of concepts. Interdisciplinary research actively combines and synthesizes methods, theories, and data from different fields to create a unified framework addressing complex problems. The key methodological difference lies in pluridisciplinarity preserving distinct disciplinary boundaries, while interdisciplinarity merges approaches to generate new insights beyond individual disciplines.
Advantages and Challenges of Pluridisciplinary Work
Pluridisciplinary work integrates knowledge from multiple disciplines while maintaining their separate methodologies, fostering comprehensive perspectives and innovation by leveraging diverse expertise. Advantages include enhanced creativity through diverse viewpoints and the ability to address complex problems from various angles. Challenges involve potential communication barriers between disciplines, difficulty in synthesizing findings, and the risk of fragmented outcomes without cohesive integration.
Benefits and Limitations of Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Interdisciplinary collaboration enhances problem-solving by integrating diverse expertise, fostering innovation, and creating comprehensive solutions that single disciplines may overlook. It promotes holistic understanding and adaptability but often faces challenges such as communication barriers, conflicting methodologies, and difficulty in harmonizing different disciplinary vocabularies. Effective interdisciplinary collaboration requires structured frameworks and mutual respect to overcome limitations and maximize benefits in research and practical applications.
Real-World Applications Across Fields
Pluridisciplinary approaches involve multiple disciplines working side-by-side without integrating methods or perspectives, useful for broad projects like urban planning where distinct expertise coexists. Interdisciplinary methods combine insights and techniques from various fields to create cohesive solutions, evident in healthcare innovations that blend biology, engineering, and data science for personalized medicine. Real-world applications benefit from pluridisciplinary efforts in maintaining distinct expertise, while interdisciplinary projects drive novel outcomes through integration and synthesis across fields.
Selecting the Right Approach for Research Goals
Choosing between pluridisciplinary and interdisciplinary approaches depends on research goals and the desired depth of integration. Pluridisciplinary research involves parallel contributions from multiple disciplines without merging perspectives, suitable for studies requiring broad, diverse insights. Interdisciplinary research integrates methods and theories from different fields to create new frameworks, ideal for complex problems demanding synthesis and innovation.
Future Trends in Knowledge Integration
Future trends in knowledge integration emphasize a shift from pluridisciplinary approaches, where multiple disciplines operate side by side, toward interdisciplinary methods that blend concepts, theories, and tools to create cohesive frameworks. Interdisciplinary research fosters innovation by addressing complex problems through collaborative synthesis, enhancing the adaptability of scientific inquiry in rapidly evolving fields like artificial intelligence and sustainability. Advances in digital collaboration platforms and data analytics accelerate this integration, enabling seamless knowledge exchange and driving the emergence of novel hybrid disciplines.
Pluridisciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com