Inquiry-Based Learning sparks curiosity by encouraging students to ask questions and explore topics deeply, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This student-centered approach transforms learners into active participants who construct knowledge through investigation and reflection. Discover how adopting this method can enhance Your educational experience throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
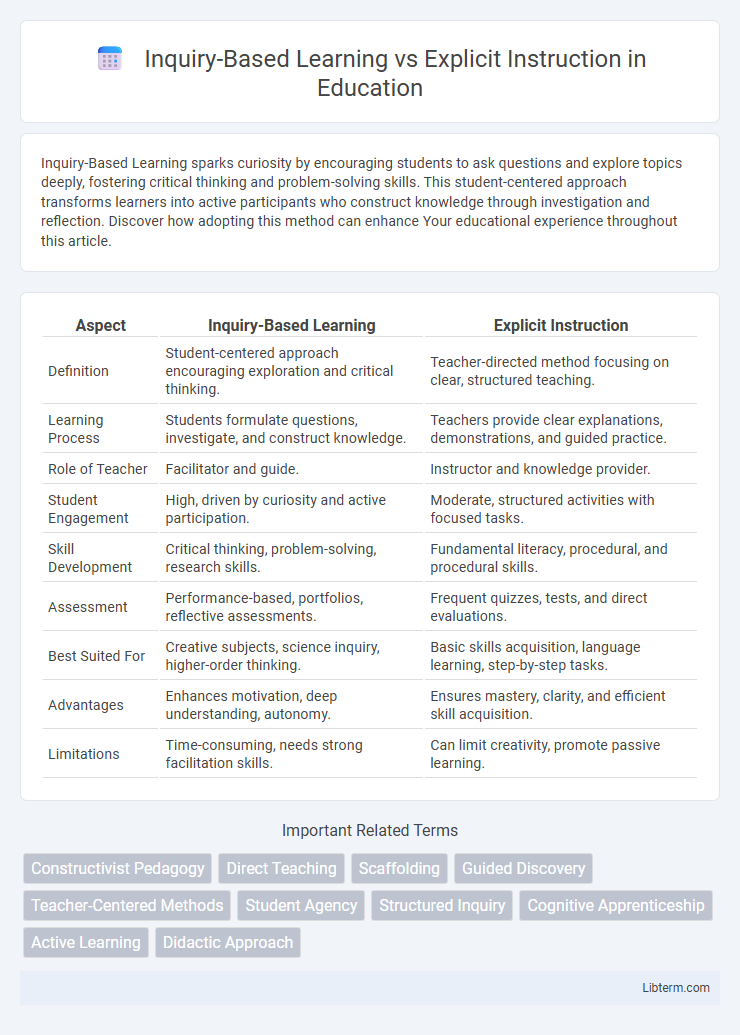
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Explicit Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach encouraging exploration and critical thinking. | Teacher-directed method focusing on clear, structured teaching. |
| Learning Process | Students formulate questions, investigate, and construct knowledge. | Teachers provide clear explanations, demonstrations, and guided practice. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide. | Instructor and knowledge provider. |
| Student Engagement | High, driven by curiosity and active participation. | Moderate, structured activities with focused tasks. |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, problem-solving, research skills. | Fundamental literacy, procedural, and procedural skills. |
| Assessment | Performance-based, portfolios, reflective assessments. | Frequent quizzes, tests, and direct evaluations. |
| Best Suited For | Creative subjects, science inquiry, higher-order thinking. | Basic skills acquisition, language learning, step-by-step tasks. |
| Advantages | Enhances motivation, deep understanding, autonomy. | Ensures mastery, clarity, and efficient skill acquisition. |
| Limitations | Time-consuming, needs strong facilitation skills. | Can limit creativity, promote passive learning. |
Understanding Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-centered exploration where learners actively investigate questions, problems, or scenarios to construct knowledge. This approach fosters critical thinking, creativity, and deeper understanding by encouraging curiosity and hands-on experience. Research shows Inquiry-Based Learning enhances retention and engagement compared to passive learning methods, making it effective in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education.
Defining Explicit Instruction
Explicit instruction is a structured teaching approach characterized by clear, direct teaching of concepts and skills through systematic, step-by-step demonstrations. It emphasizes clarity in learning objectives, guided practice, immediate feedback, and mastery of foundational knowledge before advancing. This method contrasts with inquiry-based learning by prioritizing teacher-led explanation over student-driven exploration, ensuring precise understanding and skill acquisition.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on student-driven exploration, encouraging learners to ask questions, investigate solutions, and develop critical thinking skills through active engagement. This approach emphasizes curiosity, hands-on experiences, and the construction of knowledge rather than passive reception of facts. Core principles include fostering autonomy, promoting deep understanding through inquiry cycles, and supporting reflective thinking to enhance problem-solving abilities.
Key Components of Explicit Instruction
Explicit instruction centers on clear, structured teaching where concepts are broken down into manageable steps, ensuring students achieve mastery through guided practice and immediate feedback. Key components include clear learning objectives, teacher modeling, systematic scaffolding, and frequent assessment to monitor progress. This approach contrasts with inquiry-based learning by prioritizing direct explanation over student-led discovery, supporting foundational skill development and minimizing misconceptions.
Comparing Teaching Approaches: Inquiry vs Explicit
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes student-driven exploration and critical thinking, fostering deeper understanding through questioning and discovery. Explicit instruction relies on clear, direct teaching with structured guidance and modeling to build foundational skills efficiently. Both approaches support learning, but inquiry encourages autonomy and creativity while explicit instruction ensures clarity and mastery of core concepts.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to explore and investigate topics independently. This approach enhances student engagement and motivation through active participation, fostering deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. It also cultivates creativity and curiosity, preparing learners for real-world applications and lifelong learning.
Advantages of Explicit Instruction
Explicit instruction enhances learning efficiency through clear, structured teaching methods that reduce cognitive load and minimize misconceptions. This approach provides direct guidance and immediate feedback, supporting mastery of complex skills and foundational knowledge. Research consistently shows that explicit instruction results in higher retention rates and improved academic performance, especially for students requiring additional support.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Methods
Inquiry-based learning faces challenges such as lower structure causing confusion for students lacking prior knowledge, leading to inefficient content acquisition. Explicit instruction may limit critical thinking development due to its teacher-centered approach, causing passive learning and reduced creativity. Both methods require balancing guidance and autonomy to address diverse learner needs and optimize educational outcomes.
Situational Effectiveness: When to Use Each Approach
Inquiry-based learning excels in fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills in environments where exploration and student-driven discovery are desirable, such as science labs or project-based classrooms. Explicit instruction proves most effective in teaching foundational skills and complex procedures requiring clear, structured guidance, often necessary in early literacy or math interventions. Educators should match the approach to learners' needs and content complexity, leveraging inquiry for engagement and explicit instruction for skill mastery and error correction.
Blending Inquiry-Based Learning and Explicit Instruction
Blending Inquiry-Based Learning and Explicit Instruction enhances student engagement while providing clear guidance on complex concepts. This hybrid approach fosters critical thinking through exploration, complemented by structured teaching that reinforces targeted skills and knowledge retention. Research demonstrates that combining these methods improves academic performance and supports diverse learning styles across STEM education.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com