Surface learning focuses on memorizing facts and details without understanding underlying concepts, often leading to short-term retention and poor application of knowledge. This approach can hinder deep comprehension and critical thinking, limiting your ability to connect ideas effectively. Explore the rest of the article to discover strategies for transforming surface learning into meaningful and lasting understanding.
Table of Comparison
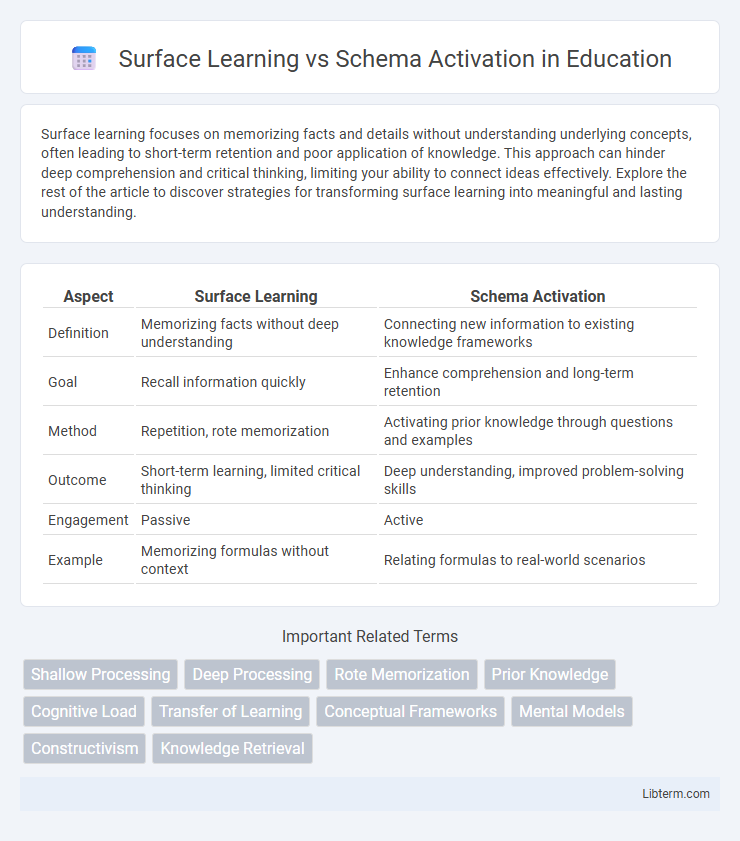
| Aspect | Surface Learning | Schema Activation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Memorizing facts without deep understanding | Connecting new information to existing knowledge frameworks |
| Goal | Recall information quickly | Enhance comprehension and long-term retention |
| Method | Repetition, rote memorization | Activating prior knowledge through questions and examples |
| Outcome | Short-term learning, limited critical thinking | Deep understanding, improved problem-solving skills |
| Engagement | Passive | Active |
| Example | Memorizing formulas without context | Relating formulas to real-world scenarios |
Understanding Surface Learning
Surface learning involves rote memorization and passive absorption of information without connecting new knowledge to existing cognitive frameworks. It often leads to superficial understanding and poor long-term retention, as learners focus on isolated facts rather than underlying concepts. Effective education strategies encourage moving beyond surface learning by integrating schema activation to enhance comprehension and critical thinking.
What is Schema Activation?
Schema activation is the cognitive process of recalling and utilizing pre-existing knowledge frameworks to enhance comprehension and learning efficiency. It involves linking new information to prior experiences or concepts stored in the brain, facilitating deeper understanding and better retention. This technique contrasts with surface learning by encouraging meaningful engagement rather than rote memorization.
Key Differences Between Surface Learning and Schema Activation
Surface learning involves memorizing facts and details without deep understanding, while schema activation engages prior knowledge frameworks to integrate new information meaningfully. Surface learning often leads to short-term retention, whereas schema activation promotes long-term comprehension and critical thinking. The key difference lies in depth of processing: surface learning targets rote memorization, schema activation facilitates cognitive connections within existing mental structures.
Importance of Deep Learning in Education
Deep learning in education fosters critical thinking and long-term retention by encouraging students to understand underlying concepts rather than merely memorizing facts, which is characteristic of surface learning. Schema activation enhances this process by linking new information to existing knowledge frameworks, improving comprehension and application. Emphasizing deep learning strategies transforms educational outcomes, leading to more meaningful engagement and better problem-solving skills.
Cognitive Processes Behind Schema Activation
Schema activation involves retrieving and integrating existing knowledge frameworks from long-term memory, facilitating deeper comprehension and meaningful learning. This cognitive process enables learners to connect new information with prior experiences, promoting effective encoding and organization of knowledge. In contrast, surface learning relies on rote memorization without engaging these schemas, leading to shallow understanding and reduced retention.
The Limitations of Surface Learning
Surface learning often results in rote memorization without deep understanding, limiting long-term retention and application of knowledge. It neglects the activation of prior schemas, which hinders the integration of new information into existing mental frameworks. This approach restricts critical thinking and problem-solving skills by emphasizing superficial recall over meaningful cognitive connections.
Benefits of Activating Prior Knowledge
Activating prior knowledge enhances comprehension and retention by connecting new information to existing cognitive frameworks, facilitating deeper learning. This process encourages schema activation, which helps learners organize and interpret material more efficiently compared to surface learning techniques. Research shows that students who engage in prior knowledge activation demonstrate improved problem-solving skills and long-term academic achievement.
Teaching Strategies for Schema Activation
Effective teaching strategies for schema activation include using preview questions, concept mapping, and connecting new content to students' prior knowledge. These methods stimulate existing cognitive frameworks, enabling deeper comprehension and retention compared to surface learning techniques. Integrating real-life examples and interactive discussions further strengthens schema construction and application.
Real-World Examples: Surface Learning vs Schema Activation
Surface learning emphasizes memorizing facts without deep understanding, as seen when students repetitively memorize historical dates without grasping the context. Schema activation involves connecting new information to existing knowledge frameworks, evident when medical students relate symptoms to prior cases, enhancing diagnostic skills. Real-world learning improves retention and problem-solving by fostering meaningful connections rather than rote memory.
Enhancing Student Outcomes Through Advanced Learning Techniques
Enhancing student outcomes involves shifting from surface learning, which emphasizes rote memorization, to schema activation that promotes deep understanding by connecting new information to existing knowledge frameworks. Advanced learning techniques such as concept mapping, retrieval practice, and elaborative interrogation facilitate schema activation, enhancing critical thinking and long-term retention. Research indicates that students engaging in schema-based learning demonstrate improved problem-solving skills and higher academic achievement across disciplines.
Surface Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com