Culturally sustaining pedagogy empowers educators to honor and incorporate students' diverse cultural backgrounds into the learning process, fostering a more inclusive and equitable classroom environment. It promotes academic success by validating students' identities and encouraging critical thinking about social justice issues. Explore the rest of this article to discover how you can implement these transformative teaching strategies in your educational practice.
Table of Comparison
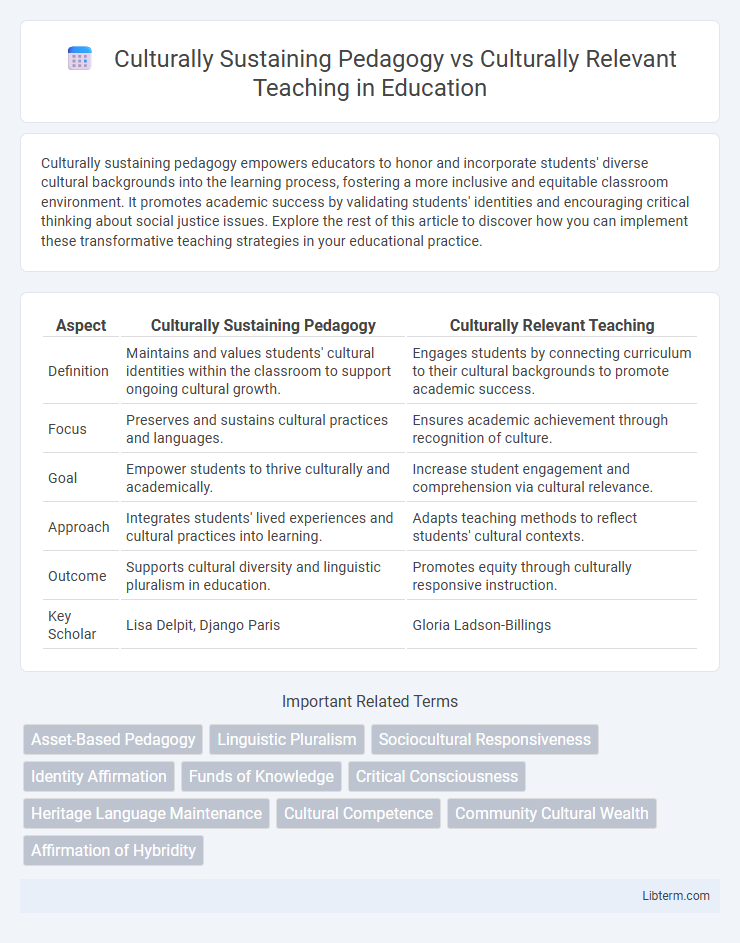
| Aspect | Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy | Culturally Relevant Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintains and values students' cultural identities within the classroom to support ongoing cultural growth. | Engages students by connecting curriculum to their cultural backgrounds to promote academic success. |
| Focus | Preserves and sustains cultural practices and languages. | Ensures academic achievement through recognition of culture. |
| Goal | Empower students to thrive culturally and academically. | Increase student engagement and comprehension via cultural relevance. |
| Approach | Integrates students' lived experiences and cultural practices into learning. | Adapts teaching methods to reflect students' cultural contexts. |
| Outcome | Supports cultural diversity and linguistic pluralism in education. | Promotes equity through culturally responsive instruction. |
| Key Scholar | Lisa Delpit, Django Paris | Gloria Ladson-Billings |
Introduction to Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy and Culturally Relevant Teaching
Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy centers on maintaining and fostering students' cultural identities within the educational process, aiming to sustain diverse cultural practices while promoting academic achievement. Culturally Relevant Teaching emphasizes connecting academic content to students' cultural backgrounds to improve engagement and learning outcomes. Both frameworks prioritize inclusivity but differ in their approach--Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy seeks to preserve cultural integrity over time, whereas Culturally Relevant Teaching focuses on validating and leveraging cultural experiences for immediate educational relevance.
Historical Foundations and Evolution of Both Approaches
Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy builds on the foundation of Culturally Relevant Teaching by emphasizing the continuous support and validation of students' cultural identities, evolving from Gloria Ladson-Billings' 1990s framework which sought to empower marginalized students through meaningful curriculum. Culturally Relevant Teaching emerged as a response to traditional education's failure to address cultural diversity, focusing on academic success, cultural competence, and critical consciousness, influenced by scholars like Geneva Gay and Lisa Delpit. The evolution of both approaches reflects a shift from merely incorporating culture to actively sustaining and evolving students' cultural experiences within education systems.
Core Principles of Culturally Relevant Teaching
Culturally Relevant Teaching centers on student identity validation, academic success, and critical consciousness to empower learners by connecting curriculum to their cultural backgrounds. It emphasizes high expectations and meaningful engagement through culturally responsive materials and instructional strategies. This approach fosters academic achievement while promoting social justice and equity within diverse classrooms.
Defining Features of Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy
Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy emphasizes validating and perpetuating students' cultural identities while promoting critical engagement with dominant norms. It prioritizes dynamic cultural fluidity, supporting students in maintaining their linguistic, cultural, and community practices within the educational context. This approach contrasts with Culturally Relevant Teaching by actively sustaining cultural pluralism and fostering empowerment beyond academic achievement.
Key Similarities Between the Two Frameworks
Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy and Culturally Relevant Teaching both prioritize affirming students' cultural identities to enhance academic success and engagement. Each framework emphasizes the incorporation of students' cultural references in teaching methodologies and curriculum design, promoting inclusivity and respect for diversity. Both approaches aim to empower marginalized communities by validating their cultural backgrounds within the educational environment.
Fundamental Differences and Theoretical Distinctions
Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy (CSP) emphasizes the ongoing support and nurturing of students' cultural identities, aiming to empower learners by integrating their dynamic cultural practices into the curriculum. In contrast, Culturally Relevant Teaching (CRT) focuses on validating students' cultural backgrounds to improve academic success and sociopolitical consciousness by connecting content to their existing cultural knowledge. Theoretically, CSP extends CRT by advocating for the preservation and evolution of culture within education, shifting from mere relevance to sustainability and transformation of cultural identities in learning environments.
Impact on Student Engagement and Achievement
Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy (CSP) enhances student engagement and achievement by affirming and integrating students' cultural identities into the curriculum, fostering a sense of belonging and validation that motivates deeper learning. Culturally Relevant Teaching (CRT) also boosts engagement by connecting academic content to students' cultural backgrounds, promoting academic success through relevance and meaningful context. While both approaches improve outcomes, CSP emphasizes maintaining and evolving cultural practices, which can lead to sustained student participation and long-term academic growth.
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy emphasizes ongoing support for students' cultural identities, requiring educators to continuously adapt curricula to reflect diverse cultural practices, which can challenge standardized assessment frameworks. Culturally Relevant Teaching focuses on student engagement through cultural references but may face obstacles in institutional resistance and insufficient teacher training to authentically integrate cultural knowledge. Both approaches demand significant professional development and systemic support to overcome barriers related to curriculum rigidity, resource availability, and educator preparedness for effective implementation.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Case studies highlight Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy (CSP) as an approach that not only validates but actively preserves students' cultural identities in classroom practices, promoting long-term cultural competence. Real-world applications of Culturally Relevant Teaching (CRT) demonstrate its effectiveness in improving academic outcomes by connecting curriculum content to students' cultural backgrounds and lived experiences. Research evidence suggests CRT and CSP both transform educational environments, with CSP extending CRT's foundational principles by emphasizing ongoing cultural maintenance and critical consciousness development.
Future Directions in Culturally Responsive Education
Future directions in culturally responsive education emphasize integrating culturally sustaining pedagogy with culturally relevant teaching to create inclusive learning environments that honor students' diverse identities. This approach promotes dynamic, asset-based curricula that evolve with cultural shifts, fostering critical consciousness and empowering marginalized communities. Advances in technology and community partnerships also support personalized, culturally meaningful instruction that bridges home and school experiences effectively.
Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com